2.
6
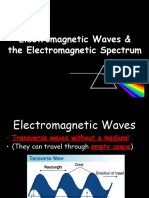
Electromagnetic waves
Water and sound waves travel through and uses of the waves in the electromagnetic
substances. They cause the particles in the spectrum.
substances to vibrate. The vibrating particles carry Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength.
the energy in the wave. They are produced by some radioactive atoms.
Electromagnetic waves can travel where there Gamma rays are very penetrating and can go
are no substances and no particles. They are made through lead and concrete. They are dangerous
of oscillating (= vibrating regularly) electric and because they can damage the cells of our body.
magnetic fields. The fields are at right angles to X-rays were discovered accidentally, and the
each other and to the direction of the wave. name X means unknown because people did not
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. understand them. We cannot see X-rays directly
Electromagnetic waves are formed by changes but they affect photographic film. X-rays are
inside atoms. When atoms gain energy they absorbed much more by bone than soft tissue, so
absorb it and then re-emit it as electromagnetic bones stand out as a shadow when you have an
energy. Sometimes the energy carried by electro- X-ray taken.
magnetic waves seems like it is in packets, and Ultraviolet means ‘beyond violet’. This is the
the packets of energy are called photons. part of the spectrum beyond the violet part of the
All electromagnetic waves are similar to each light spectrum. We cannot see UV light, but
other. They are all made of oscillating fields. They insects can. UV light is sometimes called black
all travel at the same speed, 35 108 metres per light, and is used in detecting forgeries and
second. They differ in their wavelength and checking signatures. Ultraviolet light causes skin
frequency. As the wavelength gets longer the cancers and sunburn. Luckily most UV light from
frequency gets lower. And as the wavelength gets the sun is absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer.
shorter the frequency gets higher. Remember that Light is sometimes called visible light because
wavelength is the length of one wave. Frequency it is the only part of the spectrum that we can see.
is the number of waves per second. It is measured Our eyes contain special cells that detect only this
in hertz, Hz. The frequencies of electromagnetic type of electromagnetic radiation. Light also
waves are very high. affects the dyes in photographic film, and
Electromagnetic waves with a very short provides all the energy needed to maintain life on
wavelength and a very high frequency are called Earth. Light is discussed further in activities 2.9 to
gamma rays. If electromagnetic waves have long 2.11.
wavelengths and low frequencies then they are Infrared light is the part of the spectrum
radio and television waves. The range of all the beside red light. We feel infrared radiation as
different electromagnetic waves is called a heat. It is sometimes called heat radiation.
spectrum. The diagram below shows the names Infrared radiation with the shortest wavelengths
frequency 10 6 Hz frequency 1014 Hz very high frequency, about 1020 Hz
long wavelength short wavelength
1 km 1.0 cm 0.01 mm 0.5 m 0.1 m 1.0 nm 0.01 nm
radio television microwaves infrared radiation visible light ultraviolet X-rays gamma rays
1.00
radio communication
UHF, VHF, television, AM and FM radio, radar special machines
detecting gamma rays
The electromagnetic spectrum
50
� WAVES AND RADIATION 51
infrared red orange yellow green blue indigo violet ➞UV
The visible light spectrum
passes through some gases and glass, but the Microwave oven
radiation with longer wavelengths does not.
Greenhouses work by trapping the infrared way radio, FM radio and
radiation with long wavelengths, which warms amateur radio.
up the air inside. This is what is happening with Note that there are no
the greenhouse effect around the Earth. sharp distinctions or bound-
Microwaves are used in telecommunications, aries where one type of
for example, with satellite telephone towers. radiation stops and the
Radars in aircraft and ships use microwaves. In next begins. They overlap.
microwave ovens, the microwaves make the The name given depends
water molecules in the food vibrate, which heats on the energy, the source
and cooks the food. Microwave ovens are white and the use of the radi-
inside because this helps reflect microwaves ation. Some microwaves
around the oven. are used in radio, TV and
Television and radio waves have the longest mobile phone communi-
wavelengths of all of the electromagnetic cation, and are classified A telecommunications tower
spectrum. Radio waves have been grouped into as radio waves. Similar waves
bands, and each band has a special set of uses. are also used in radar and ovens, and these
Some examples are television signals, two radiations are grouped as microwaves.
COPY AND COMPLETE
CHECKPOINT:
Electromagnetic waves can ______ where there are no __________ and no _________. They are made of oscillating
________ and ________ fields. The ______ are at _____ angles to ____ other and to the _________ of the wave.
Electromagnetic waves are __________ waves. They all travel at the ____ speed, _______ metres per second.
Gamma rays are very ___________ and can go through ____ and ________. We cannot see ______ directly but they
affect ____________ film. Ultraviolet means ‘______ ______’. Light is sometimes called _______ light because it is
the ____ part of the ________ that we can ___. We feel ________ radiation as ____. Microwaves are used in
__________________. Television and _____ waves have the longest ___________ of all of the _______________
spectrum.
QUESTIONS 7 Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is used
in the following?
1 Where does the name electromagnetic wave a absorbed by the ozone layer
come from? b passes through thick solids
2 How do we know electromagnetic waves are c is beamed to satellites
transverse waves? d is used in photosynthesis
e provides images of inside the body
3 What is meant by wavelength and frequency? f is felt as heat
4 What is the speed of all electromagnetic waves? g detects forgeries
5 What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How are all 8 Explain this sentence: ‘Light provides all the energy
the waves in the spectrum different? needed to maintain life on Earth.’
6 Name eight parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. 9 What is the connection between the wavelength and
frequency of electromagnetic waves?