Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Account Management M.com 3
Uploaded by
Sakshi Borkar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesOriginal Title
ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT M.COM 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesAccount Management M.com 3
Uploaded by
Sakshi BorkarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
UNIT 1
the objectives of management accounting
1. Providing financial information to assist with decision-
making: Management accounting provides financial information to
managers to help them make informed decisions about the organization.
This includes information about the costs and benefits of different
options, as well as forecasting future financial performance.
2. Planning and budgeting: Management accounting helps managers
to develop plans and budgets for the organization, by providing
information about the costs and resources required to achieve specific
goals. This helps managers to allocate resources effectively and to
ensure that the organization is operating efficiently.
3. Performance evaluation: Management accounting provides
information about the organization's financial performance, which can
be used to evaluate the effectiveness of different departments and teams.
This helps managers to identify areas where improvements can be made
and to allocate resources accordingly.
4. Control and monitoring: Management accounting provides
information to help managers to monitor the organization's financial
performance and to identify any deviations from the plan or budget. This
helps managers to take corrective action if necessary, to ensure that the
organization stays on track and meets its financial objectives.
5. Strategic planning: Management accounting helps managers to
identify the most profitable opportunities and to allocate resources
accordingly. This helps the organization to achieve its long-term goals
and to stay competitive in the market.
Regenerate response
the importance of management accounting
Management accounting is an essential tool for any business. It
provides valuable information that helps managers make
informed decisions and effectively manage the financial resources
of the organization. Here are some key reasons why management
accounting is important:
1. Planning and decision-making: Management accounting
provides the data needed to develop and implement strategic
plans, set budgets, and make informed business decisions.
2. Performance evaluation: Management accounting helps
managers track and evaluate the financial performance of the
organization. This enables them to identify areas of strength and
weakness and make necessary adjustments.
3. Resource allocation: Management accounting helps managers
allocate resources effectively and make informed decisions about
where to allocate resources.
4. Internal control: Management accounting helps to establish
and maintain internal control systems that help prevent fraud and
errors.
5. Communication: Management accounting helps to
communicate financial information to different stakeholders such
as shareholders, investors, and management.
Overall, management accounting is a crucial component of
effective business management, as it helps to ensure that
financial resources are used efficiently and effectively to
achieve the organization's goals.
Some of the key benefits of management
accounting include:
1. Financial planning and forecasting: Management accounting
helps managers to develop financial plans and forecasts based on
historical data and industry trends. This enables them to identify
potential challenges and opportunities and to make informed
decisions about the allocation of resources.
2. Performance measurement: Management accounting helps
managers to track and measure the financial performance of the
organization, including key performance indicators (KPIs) such as
revenue, profitability, and return on investment. This enables
managers to identify areas of the business that are
underperforming and to take corrective action.
3. Resource allocation: Management accounting provides
information on the cost of resources, including labor, materials,
and overhead, which helps managers to make informed decisions
about how to allocate resources to maximize efficiency and
profitability.
4. Decision making: Management accounting provides managers
with the financial information they need to make informed
decisions about the future direction of the organization. This
includes decisions about investments, expansion, and pricing
strategies.
Overall, management accounting is an essential tool for managers
to ensure that the organization is operating effectively and
efficiently and to achieve its long-term financial goals.
Regenerate response
Discuss the role and responsibilities of
Accountant in Management Accounting.
In management accounting, the role of the accountant is to provide financial
information and analysis to help managers make informed business decisions.
This includes preparing financial reports, analyzing financial data, and making
recommendations for improving the financial performance of the
organization. Some specific responsibilities of an accountant in management
accounting may include:
1. Preparing financial reports: This involves collecting and analyzing
financial data, and then presenting it in the form of financial statements,
such as income statements and balance sheets.
2. Analyzing financial data: The accountant will use financial data to identify
trends and patterns, and to make recommendations for improving the
financial performance of the organization.
3. Budgeting and forecasting: The accountant will work with management to
develop budgets and forecast future financial performance.
4. Cost analysis: The accountant will analyze the costs associated with
different business activities, and recommend ways to reduce costs and
increase efficiency.
5. Performance measurement: The accountant will use financial data to
measure the performance of the organization, and to identify areas for
improvement.
6. Providing financial advice: The accountant will provide financial advice to
management on a range of topics, including investment decisions,
financing options, and risk management.
Overall, the role of the accountant in management accounting is to provide
financial information and analysis that helps managers make informed
decisions, and to support the financial performance of the organization.
Regenerate response
UNIT 2
the objectives of analysis and interpretation of financial
statements
The main objectives of analyzing and interpreting financial statements are:
1. To understand the financial position and performance of a
business: Financial statements provide information about a
business's assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses, which
allows analysts to understand the financial position and
performance of the business.
2. To assess the risks and opportunities facing a business: By
analyzing financial statements, analysts can identify areas of
weakness or strength in a business, which can help them assess
the risks and opportunities facing the business.
3. To make informed business decisions: Financial analysis and
interpretation can help managers, investors, and other
stakeholders make informed decisions about the business. For
example, investors can use financial analysis to decide whether to
invest in a company, and managers can use it to make strategic
decisions about the direction of the business.
4. To compare the performance of a business to its competitors:
Financial analysis and interpretation can be used to compare the
financial performance of a business to its competitors or industry
benchmarks, which can help identify areas where the business
may be outperforming or underperforming.
5. To communicate financial information to stakeholders:
Financial statements are often used to communicate financial information
to stakeholders such as shareholders, creditors, and regulatory agencies.
Financial analysis and interpretation can help stakeholders better
understand the financial information presented in the financial
statements.
State the different stages of preparation of Financial
Statement
There are several stages involved in the preparation of financial statements:
1. Gathering and organizing financial data: This involves
collecting all the necessary financial information and data from
various sources such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and
other financial records.
2. Analyzing and classifying financial data: After gathering the
financial data, it must be analyzed and classified into appropriate
categories such as revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
3. Adjusting entries: Some transactions may not be recorded in the
accounting records on a timely basis, or they may not be recorded
properly. Adjusting entries are made to correct these errors and
ensure that the financial statements are accurate.
4. Preparing the financial statements: The financial statements are
then prepared based on the analyzed and adjusted financial data.
The main financial statements include the balance sheet, income
statement, and statement of cash flows.
5. Reviewing and finalizing the financial statements: After
preparing the financial statements, they should be reviewed for
completeness and accuracy. Any errors or discrepancies should be
corrected before the financial statements are finalized.
6. Disclosing notes: Financial statements often include notes that
provide additional information and context. These notes may
include information on accounting policies, significant
transactions, and other matters that may be relevant to
understanding the financial statements.
Regenerate response
UNIT 3
what are the function and limitation of management
information system
A management information system (MIS) is a computerized system that
provides managers with the tools they need to make informed decisions
about their organization. The main function of an MIS is to provide timely,
accurate, and relevant information to support the decision-making process.
Some specific functions of an MIS include:
1. Data collection and storage: An MIS gathers and
stores data from a variety of sources within the
organization, such as transactions, operations, and
market trends.
2. Data processing and analysis: The MIS processes and
analyzes the collected data, using algorithms and
statistical techniques to identify patterns, trends, and
relationships.
3. Reporting and presentation: The MIS generates reports
and presents the results of the data analysis in a clear and
concise manner, allowing managers to easily understand
the information and use it to make informed decisions.
4. Decision support: The MIS provides decision-making
tools and techniques, such as decision trees, to help
managers choose the best course of action.
5. Communication and collaboration: The MIS allows
managers to share information and collaborate with others
within the organization, helping to facilitate better
communication and teamwork.
Limitations of an MIS include:
1. Dependence on accurate data: The accuracy and
completeness of the information provided by an MIS
depends on the quality of the data that is input into
the system. If the data is incorrect or incomplete, the
output of the system may also be flawed.
2. Limited flexibility: An MIS is designed to provide
specific types of information and support certain
types of decision-making. It may not be flexible
enough to adapt to changing needs or new types of
information.
3. Cost: Implementing and maintaining an MIS can be
expensive, especially for small businesses.
4. Complexity: An MIS can be complex to use,
requiring specialized training and technical expertise
to operate effectively.
5. Security risks: An MIS stores and processes sensitive
data, which can be vulnerable to security breaches or
unauthorized access.
Regenerate response
Explain the relation of Management
Information System with Management
Accounting.
Management Information Systems (MIS) and management
accounting are closely related, as both deal with the use of
information to support decision-making within an organization.
MIS is a field of study that focuses on the design, development,
and use of information systems to support the activities of
management. These systems are used to collect, store, and
analyze data, and to generate information that can be used to
support decision-making. This can include anything from financial
data to customer information to supply chain data.
Management accounting, on the other hand, is the process of
using financial and non-financial data to inform the decision-
making of managers within an organization. This can include the
preparation of financial statements, the analysis of costs and
revenues, and the development of budgeting and forecasting
models.
Both MIS and management accounting rely on the use of
information to support decision-making, but they differ in the
types of information they use and the specific decisions they
support. MIS focuses on the use of information systems to
support the activities of management, while management
accounting focuses on the use of financial and non-financial data
to inform the decision-making of managers.
Regenerate response
UNIT 4
what do you mean by fund flow
statement
A fund flow statement is a financial statement that shows the
inflow and outflow of cash in a company. It is used to analyze the
company's financial performance and understand the changes in
its financial position over a period of time.
The fund flow statement consists of two main sections:
1. Inflows: These are the sources of cash that increase the
company's cash balance. Examples include cash received from the
sale of goods or services, borrowings, and investments.
2. Outflows: These are the uses of cash that decrease the company's
cash balance. Examples include payments made to suppliers,
employees, and other expenses.
The fund flow statement can help a company understand where
its cash is coming from and where it is going, which can be useful
in making financial decisions and planning for the future. It can
also be used by investors and creditors to evaluate the company's
financial health and risk.
importance of fund flow statement
A fund flow statement is a financial statement that shows the inflow and
outflow of a company's cash and cash equivalents. It is important for a
number of reasons:
1. It helps in understanding the company's financial position:
The fund flow statement shows the company's ability to generate
cash and manage its cash flow. This helps in understanding the
company's financial position and its ability to meet its financial
obligations.
2. It helps in identifying financial problems: If a company is
experiencing negative fund flow, it could indicate financial
problems. The fund flow statement can help in identifying such
problems and finding ways to address them.
3. It helps in forecasting future cash needs: The fund flow
statement can be used to forecast future cash needs of the
company. This helps in ensuring that the company has sufficient
funds to meet its financial obligations.
4. It helps in analyzing the company's liquidity: The fund flow
statement helps in analyzing the company's liquidity, which is its
ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. This is
important for investors and creditors who want to know if the
company has sufficient funds to meet its obligations.
5. It helps in decision making: The fund flow statement provides
valuable information to management, which can be used in
decision making. For example, if the company is experiencing
negative fund flow, management may need to consider measures
such as cost-cutting or seeking additional financing.
Regenerate response
What are the limitations of cash flow
statement
A cash flow statement is a financial report that provides information about the
inflows and outflows of cash for a business. While a cash flow statement can
be a useful tool for understanding the financial health of a business, it has
several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the
information it provides:
1. Timing differences: The cash flow statement reflects the actual
cash received and paid out during a specific period, but the
timing of these transactions may not match the timing of when
the related revenues or expenses were recognized on the income
statement. This can lead to discrepancies between the two
statements.
2. Non-cash transactions: The cash flow statement does not
include non-cash transactions, such as the issuance or retirement
of debt or the issuance of stock. These transactions can have a
significant impact on a company's financial position, but they are
not reflected on the cash flow statement.
3. Subjectivity: The preparation of a cash flow statement involves
making certain assumptions and estimates, such as the expected
useful life of fixed assets or the expected timing of future cash
flows. These assumptions and estimates can introduce subjectivity
into the statement.
4. Limited information: The cash flow statement provides
information about cash inflows and outflows, but it does not
provide information about a company's liquidity, solvency, or
financial leverage. To get a more complete picture of a company's
financial health, it is necessary to consider other financial
statements, such as the balance sheet and the income statement.
You might also like
- Name Kausar HanifDocument43 pagesName Kausar HanifIqra HanifNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument38 pagesManagement AccountingHari Haran100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word Document-1Document73 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Document-1Toshar JindalNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Definition and FunctionsDocument16 pagesManagement Accounting Definition and FunctionsRahul kumar100% (1)
- Scope of Management AccountingDocument3 pagesScope of Management AccountingMuhammad Akmal HossainNo ratings yet
- Finance For Managers TPDocument9 pagesFinance For Managers TPNoela KibondeNo ratings yet
- RA 8293 Intellectual Property LawDocument25 pagesRA 8293 Intellectual Property Lawjohn paolo josonNo ratings yet
- Intro to Management Accounting FunctionsDocument12 pagesIntro to Management Accounting FunctionskipovoNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Tools & TechniquesDocument17 pagesManagement Accounting Tools & TechniquesAniket KarpeNo ratings yet
- Bca Unit Iii Mgt. AcoountingDocument13 pagesBca Unit Iii Mgt. AcoountingGautham SajuNo ratings yet
- Draft APDocument6 pagesDraft APhchi7171No ratings yet
- Management Accounting NotesDocument72 pagesManagement Accounting NotesALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Management Accounting - Notes.Document47 pagesManagement Accounting - Notes.mar231775No ratings yet
- Research Paper 9.13Document4 pagesResearch Paper 9.13Gerard Albert PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Ntre, Scope Accntng MNGMNTDocument4 pagesNtre, Scope Accntng MNGMNTPankaj2cNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting FunctionsDocument34 pagesManagerial Accounting FunctionsIvy Bucks WanjikuNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument5 pagesFinancial AccountingB SIBA PRASAD REDDYNo ratings yet
- Projects Ma 1Document16 pagesProjects Ma 1nikkiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements Are The End Products of Financial AcountingDocument20 pagesFinancial Statements Are The End Products of Financial AcountingAnkita Tolasaria100% (1)
- Management Accounting Ratio Analysis/TITLEDocument13 pagesManagement Accounting Ratio Analysis/TITLEPravin TejasNo ratings yet
- Managemnt Accountant Theroy (Year QuestionDocument3 pagesManagemnt Accountant Theroy (Year QuestionJack SonNo ratings yet
- Copy Cost Accting-1Document205 pagesCopy Cost Accting-1Kassawmar DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Bcom 203Document134 pagesBcom 203Dharmesh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial AccountingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Managerial AccountingMark Ronnier VedañaNo ratings yet
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University: For More Information Visit: HTTP://WWW - Msuniv.ac - inDocument204 pagesManonmaniam Sundaranar University: For More Information Visit: HTTP://WWW - Msuniv.ac - inDhirendra Singh patwalNo ratings yet
- Management Acc NotesDocument8 pagesManagement Acc NotesShubham KattaNo ratings yet
- Intro to Managerial AcctDocument9 pagesIntro to Managerial AcctMark Ronnier VedañaNo ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument5 pagesManagerial Accountingjaninemaeserpa14No ratings yet
- Actg35 1Document2 pagesActg35 1api-3744266No ratings yet
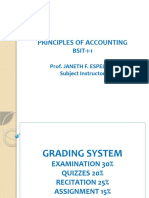
- Principles of Accounting: BSIT-1-1Document8 pagesPrinciples of Accounting: BSIT-1-1edilcon GorospeNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Cost AccountingDocument36 pagesStudy Material - Cost AccountingdahigaonkarNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Definitions of Management AccountingDocument9 pagesMeaning and Definitions of Management AccountingHafizullah Ansari100% (1)
- Management Accounting: S.K. Gupta Guest LecturerDocument37 pagesManagement Accounting: S.K. Gupta Guest LecturersantNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument54 pagesManagement AccountingjibharatNo ratings yet
- Accounts BDocument13 pagesAccounts Bzabi ullah MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Management Accouting: What Is Management Accounting? Discuss Nature and Scope of Management AccountingDocument9 pagesManagement Accouting: What Is Management Accounting? Discuss Nature and Scope of Management AccountingIT'S MD CREATIONNo ratings yet
- Gage University College Financial and Managerial Accounting Group Assignment AnalysisDocument10 pagesGage University College Financial and Managerial Accounting Group Assignment AnalysisHailuNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting FrameworkDocument45 pagesFinancial Accounting Frameworkajit_satapathy1988No ratings yet
- 2 Zapya StatiscDocument10 pages2 Zapya StatiscLOND SONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Nandini SinhaNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING Assignment 1Document8 pagesACCOUNTING Assignment 1Betelhem WendwosenNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: DefinitionDocument5 pagesManagement Accounting: DefinitionSangram PandaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting-Short Answers - Quick Revision NotesDocument23 pagesManagement Accounting-Short Answers - Quick Revision Notesfathimathabasum67% (9)
- Financial Statement Analysis - Chp01 - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - Chp01 - Summary NotesBrainNo ratings yet
- Accounting Unit. 1Document19 pagesAccounting Unit. 1downlodemaster1No ratings yet
- What Is Management AccountingDocument11 pagesWhat Is Management AccountingSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- MGT AC Notes - Unit I, II - CGDocument17 pagesMGT AC Notes - Unit I, II - CGVISHAGAN MNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument11 pagesAccounting Noteszabi ullah MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument135 pagesManagement Accountingdibakardas10017100% (1)
- DM102 WK1 13Document68 pagesDM102 WK1 13Licht ZoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document72 pagesUnit 1Sumit SoniNo ratings yet
- Role of Managerial Accounting and Its Direction Toward A Specific FieldDocument4 pagesRole of Managerial Accounting and Its Direction Toward A Specific FieldBududut BurnikNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Techniques and Cost TypesDocument24 pagesManagerial Accounting Techniques and Cost TypesRavi guptaNo ratings yet
- MAEDocument9 pagesMAEArjen PaderogNo ratings yet
- Intro To MA Aug 2013Document14 pagesIntro To MA Aug 2013Nakul AnandNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument18 pagesManagement AccountingmayankNo ratings yet
- Acctg 3329 - Chapter 1 Framework For Business Analysis & ValuationDocument5 pagesAcctg 3329 - Chapter 1 Framework For Business Analysis & ValuationShaina PuertollanoNo ratings yet
- Management AccountngDocument12 pagesManagement AccountngAnil LouraNo ratings yet
- Finance for Nonfinancial Managers: A Guide to Finance and Accounting Principles for Nonfinancial ManagersFrom EverandFinance for Nonfinancial Managers: A Guide to Finance and Accounting Principles for Nonfinancial ManagersNo ratings yet