Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ab - Rac PDF
Uploaded by
Varun BharadwajOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ab - Rac PDF
Uploaded by
Varun BharadwajCopyright:
Available Formats
JYOTHY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Answer Bank : K. V . M Sharma RAC
Q1. Define refrigeration and refrigerator and how refrigeration differs from cooling.
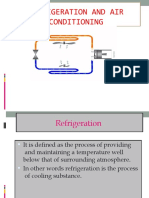
Ans:- refrigeration is the process of cooling or reducing the temperature of a substance below that of the
surrounding atmosphere and maintaining within the boundary of a given space by continuously abstracting
the heat.
Refrigerator is the machine that produces the refrigeration
Cooling is a method of NATURAL refrigeration.
Cooling is a spontaneous natural process without any external aid.
Refrigeration is an artificial cooling that is cooling with an external aid (help). Heat is extracted from
the cooler body with the help of external work.
Q2. List and explain the use of refrigeration.
Ans:- various application can be broadly grouped as
a. Food processing, preservation and distribution
Storage of raw fruits, vegetables.
Storage of meat and poultry.
Processing and distribution of frozen foods.
Production and cooling of fruit juice and wine beer etc….
b. Chemical and process industry
Petroleum refineries and petrochemical plants.
Paper and pulp industries.
Separation and liquefying gases and vapours in chemical industry.
For chilling the oil to remove wax in oil refineries.
c. Dairy products
Storage of dairy products like milk, butter
Preparing, storage, transport of ice creams.
d. Industries air conditioning
Printing and textiles.
Pharmaceuticals and mechanical industries
Power plants
Steel plants
Cold treatment of metals.
e. Transport facilities
Car air condition and bus air condition.
Railways, ships and aircrafts.
f. Household and public amenities
House/rooms air conditions.
Office air conditions.
Hospitals, theaters, malls.
g. Medical and laboratory applications
Operation Theater.
Pathological and advanced testing
Medical workings
Blood storage and transportation
Organs storage and transportation
Processing, preservation and storage of medicines
h. Water and ice
Desalination of water, ice making
i. Cryogenic applications.
Q3. What is refrigeration? Name some important refrigeration where they are used?
Ans:- refrigeration is a working fluid or a medium which continuously extracts heat from the refrigerated
space and rejects it to the surroundings.
Sl Name Chemical Used in Commercial application
no formula
1 Ammonia NH3 Ice manufacturing plants ,cold storage Vapors absorption
Packaging plants Large commercial plants
2 Carbon Co2 Marine refrigeration, theaters, air Large capacity
dioxide conditioning, dry ice making.
3 Methyl CH3Cl Domestic and industrial refrigeration Small capacity equipment
chloride (not much in use) obsolete
4 Freon 12 CCl2F2 / R12 Domestic refrigeration , Small capacity.
water cooler ,Automobile
5 Freon 22 CHClF2 / R22 Air conditioning plants food freezing Low and medium
cold storage temperature, large capacity.
6 Sulphur SO2 Earlier domestic application (no longer Domestic (Earlier)
dioxide in use) Now Obsolete
Q4 What are the different Ideal properties of refrigerants
Thermodynamic properties
Boiling point – low
Freezing point –low
Latent heat of evaporation - Very high
Physical properties
Specific volume – low
Specific heat – low
Viscosity – low
Safety working properties
Toxity-non toxic – Eg Ammonia is highly toxic
Flammability-non flammable
Corrosiveness-non corrosive
chemical stability - non reactive
Leakages if any should be easily locatable.
Other properties
C O P – high
Action with lubricating oil - non reactive
Available at an affordable cost /low cost
Odorless
[Q5] Compare VCR and VAR
Principle Chemical Mechanical
Concept Endothermic& Exothermic Alter saturation temp by altering pressure
Mode of refrigerant circulation Pump Compressor
[Q6] Explain the following terminologies
1. REFRIGERATION EFFECT ,2. TON OF REFRIGERATION ,3. C O P,4. Relative coefficient of
erformance ,5. REFRIGERANT
1. REFRIGERATION EFFECT
In a refrigeration system, the rate at which the heat is absorbed in a cycle from the interior space to
be cooled is called refrigerating effect.
Capacity of refrigeration system is expressed in tons of refrigeration (unit of refrigeration)
2. TON OF REFRIGERATION
A ton of refrigeration is defined as the quantity of heat absorbed in order to form one ton of ice in 24 hours
when the initial temperature of the water is 0°c.
1 ton of refrigeration= 210 KJ/min = 3.5 KW
Note: one American ton (2000 pounds) is taken as the standard in refrigeration practice.
3. C O P
The performance of a refrigeration system is expressed by a factor known as the co-efficient of
performance
It is the ratio of heat absorbed in a system to the work supplied
Q=Heat absorbed or removed (KW)
W=Work supplied (KW)
COP=Q/W
4. Relative coefficient of Performance
The ratio of actual COP to the theoretical COP is known as Relative COP.
Relative COP= Actual COP/ Theoritical COP
5. REFRIGERANT
In a refrigerator, a medium which continuously extracts the heat from the space within the
refrigerator which is to be kept cool at temperatures less than the atmosphere and finally rejects that heat
to the atmosphere itself is called a refrigerant.
[Q7] What is the principle of refrigeration?
It is based on 2nd law of thermodynamics. As per Clausius Statement, heat cannot flow from a body at
lower temperature to a body at higher temperature unless assisted by some external means.
In refrigeration, heat is continuously removed from the system at a lower temperature and same heat is
rejected to the surroundings at a higher temperature. This is done by using an external source like a
compressor (or) a pump.
[Q8] Explain the working of VAR with a neat sketch
The vapour absorption refrigerator is a heat operated system.
It differs from the vapour compression system only in the manner by which the circulation of the
refrigerant is achieved.
In the vapour absorption system, the compressor is replaced by an absorber, a generator and a pump.
The refrigerant used in this system must be highly soluble in the solution known as 'absorbent'.
The system uses ammonia as the refrigerant and water as absorbent.
The liquid refrigerant (ammonia) in the evaporator absorbs the heat from the medium that is to be cooled
and it undergoes a change of phase form liquid to vapour. The low pressure vapour is then passed to the
absorber.
In the absorber, the low pressure ammonia vapour is dissolved in the weak ammonia solution producing
strong ammonia solution at low pressure. The strong ammonia solution is then pumped to a generator
through the heat exchanger at high pressure. While passing through the heat exchanger, the strong
ammonia solution is warmed up by the hot weak ammonia solution flowing from the generator to the
absorber.
The warm strong ammonia solution is heated by an external source in the generator. Due to heating, the
vapour gets separated from the solution. The vapour which is at high pressure and high temperature is
condensed to low temperature in a condenser by cold water circulation.
The high pressure liquid ammonia then passes through the expansion valve where it is expanded to low
pressure and temperature. The low pressure-low temperature ammonia liquid again enters the evaporator
where it absorbs the heat from the medium (cools the medium) and the cycle repeats.
[Q9] Explain the working of VCR with a neat sketch
The vapour compression refrigerator operates on MECHANICAL principle.
Heat extraction is is achieved though evapotaion and condensation in evaporator and condenser and the
compressor and expansion valve helps in modifieng the evaporation and condensation tempeatures.
Refrigerant is cyclically circulate between Evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion
valve.
1. EVAPORATOR
It is the heart of the refrigerator.
The function of the evaporator is to reduce the temperature of the refrigerator cabinet.
The low temperature two phase mixture of refrigerant passing through the evaporator coils absorbs
heat from the cabinet and changes into vapour phase.
Here the liquid refrigerant is evaporated by the absorption of heat from refrigerator cabinet.
2. COMPRESSOR (OR) PUMP
To compress low temperature and low pressure working fluid into high temperature and high-
pressure and circulate the same to undergo the refrigeration cycle.
They are power absorbing mechanical devices and need input power. An electrical motor supplies
power to these drives.
Compressor Circulate the refrigerant to undergo the refrigeration cycle and Increase the pressure
and therefore the temperature of the refrigerant.
3. CONDENSER
The high pressure, high temperature refrigerant from the compressor enters condenser
Where the refrigerant rejects its heat to the surrounding atmosphere.
The latent heat of the refrigerant is given to the surrounding atmosphere, which results in change
of phase of the refrigerant.
The latent heat comprises of:
o Heat absorbed in the refrigerator &
o Heat developed due to compression
Heat from the refrigerant is rejected to atmosphere. Hence refrigerant gets cooled i.e. refrigerant
gives off its latent heat and condenses into liquid.
4. EXPANSION DEVICE / VALVE
The high pressure and temperature liquid refrigerant expands in the expansion valve to low
pressure & low temperature two-phase mixture.
The temperature of the refrigerant drops in the expansion valve due to partial evaporation
Expansion Device reduce the pressure and temperature of the liquid before it passes to the
evaporator.
[Q10] Explain the working of room air conditioning with a neat sketch
You might also like
- IC ENGINES /R&AC CourseDocument55 pagesIC ENGINES /R&AC CourseSrivikas MathesvaranNo ratings yet
- Vapour Compression RefrigerationDocument30 pagesVapour Compression RefrigerationLohith Narasimha swamyNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument26 pagesRefrigerationTeeyansh singh SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning SystemsDocument21 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning SystemstheNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument67 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningJoe Kamal Raj100% (1)
- Rac PPT1.Document22 pagesRac PPT1.andu gashuNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument41 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioningrejeesh_rajendranNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument102 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument11 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningRavikumar TNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument52 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- R&ac Unit-1Document27 pagesR&ac Unit-1Dinesh ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Sax PPT 25.3 Rac - MescDocument82 pagesSax PPT 25.3 Rac - Mescllh dilsahnNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Refrigeration SystemsDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Refrigeration SystemsNELMIDA AIRISH JOY N.No ratings yet
- Mee 181 - L7Document9 pagesMee 181 - L7Tawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument52 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningYashawantha Gowda100% (1)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering UNIT V Presentation PDFDocument70 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering UNIT V Presentation PDFA.R. Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- R&ACDocument66 pagesR&AC19-309 Khaleel ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument19 pagesRefrigerationDDCMNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document29 pagesModule 4YUG VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Unit-3Document31 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit-3ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration: Coefficient of PerformanceDocument2 pagesRefrigeration: Coefficient of PerformanceaadhanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedDocument113 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedHosnii QamarNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document32 pagesCH 1beila.amu.22No ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning GuideDocument22 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning GuideDhairya GohilNo ratings yet
- EME Notes RefrigerationDocument7 pagesEME Notes RefrigerationedhanaaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Refrigeration ExplainedDocument24 pagesAbsorption Refrigeration ExplainedanshdivyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Process Design PDFDocument10 pagesRefrigeration Process Design PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- Warm Space: Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VDocument11 pagesWarm Space: Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Cycles ExplainedDocument8 pagesRefrigeration Cycles ExplainedAwais Asghar KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 RefrigerationDocument37 pagesModule 2 Refrigerationsindhujaj6No ratings yet
- ME 201 Fundamentals: Refrigerants, COP, PsychrometricsDocument26 pagesME 201 Fundamentals: Refrigerants, COP, PsychrometricssaimunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanicsposhan lalNo ratings yet
- How Refrigeration WorksDocument29 pagesHow Refrigeration Worksaaisha pariNo ratings yet
- What Is RefrigerationDocument10 pagesWhat Is RefrigerationxyonieNo ratings yet
- 3-Unit - V - Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument57 pages3-Unit - V - Refrigeration & Air Conditioningrameshsairaagav100% (1)
- Unit IvDocument39 pagesUnit IvKalyan KalapalaNo ratings yet
- UNIT V - Reverse Carnot Cycle - COP - Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle and Systems (OnlyDocument18 pagesUNIT V - Reverse Carnot Cycle - COP - Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle and Systems (OnlyLogesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning by Waqas Ali Tunio (21-10-10)Document15 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning by Waqas Ali Tunio (21-10-10)waqasalitunioNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics - Refrigeration CycleDocument59 pagesApplied Thermodynamics - Refrigeration CycleSHREYASINo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 2 - Refrigeration - 1Document111 pagesCHAPTER - 2 - Refrigeration - 1Samuel WozabNo ratings yet
- R and AC Presentation - 1Document39 pagesR and AC Presentation - 1teddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment Lab:: Thermodynamics 2Document11 pagesLab Assignment Lab:: Thermodynamics 2Syed Sajjad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning - 220308 - 155054Document13 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning - 220308 - 155054Dhruvi PadmaniNo ratings yet
- RAC Introduction ClassDocument32 pagesRAC Introduction ClassRuturaj UmaranikarNo ratings yet
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle and ComponentsDocument26 pagesVapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle and ComponentsMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- COMPRESSION, REFRIGERATION CYCLE DocumentDocument26 pagesCOMPRESSION, REFRIGERATION CYCLE DocumentMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Air Conditioning: Manu Sivadas Assistant Professor Marian Engineering CollegeDocument35 pagesBasic Concepts in Air Conditioning: Manu Sivadas Assistant Professor Marian Engineering Collegeaparna baburajNo ratings yet
- Uice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesUice001-Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringBoovendra VarmanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Refrigeration SeminarDocument8 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration SeminarKEYUR100% (7)
- EShop Lab Report 04 (Introduction To Home Appliances II) - ACSDocument7 pagesEShop Lab Report 04 (Introduction To Home Appliances II) - ACSShawkat Khanz TuhinNo ratings yet
- EBE 2505 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2022 Part OneDocument30 pagesEBE 2505 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2022 Part OneNeomi IdonijeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Refrigeration and Air ConditioningCharan Reddy Abbadi100% (2)
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning IntroDocument30 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning IntroJANANI MNo ratings yet
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle and ComponentsDocument26 pagesVapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle and ComponentsMarcelo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Basic Concepts in RefrigerationDocument27 pagesLecture 1. Basic Concepts in Refrigerationaddisudagne33% (3)
- RefrigerationDocument21 pagesRefrigerationAdeel iqbalNo ratings yet
- MCE 407 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning CourseDocument100 pagesMCE 407 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Coursem_alodat6144No ratings yet
- Refrigeration & AC: Principles, Cycles, ComponentsDocument16 pagesRefrigeration & AC: Principles, Cycles, ComponentsÄkshày Khâñgrë AKNo ratings yet