Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy PDF
Uploaded by
Joydee Liza MarcoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy PDF
Uploaded by
Joydee Liza MarcoCopyright:
Available Formats
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
REFERENCE: Hist- Tissue
Marieb,Elaine Nicpon. Essentials of Human Homo- Same
Anatomy and Physiology. San Francisco, Hydro- Water
CA: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings.12th ed. Hygro- Moisture
Pearson,2017. Hyper- Excess
Hypo- Below
VanPutte, Regan, Russo, et.al., Seeley’s Ileo- Ileum
Anatomy and Physiology. McGrawHill. 12th In- Within, in, inot
ed., 2020 Inter- Between
Lapar- Abdomen
Word Roots, Prefixes and Suffixes Laryngo- Larynx
Leuko- White
PREFIXES Myelo- Marrow, spinal cord
MEANING Neo- New
a-, an- Absence, lack Nitro- Nitrogen
ab- away from Non- Not
acro extreme, extremities Ob- Before, against
ad- toward, to Pan- All
adeno- gland Para- Beside
ambi- round, on both Path- Disease
sides
Ped- Child, foot
amyl- starch
Peri- Around
ante- before, preceding
Pharyngo- Pharynx
ant-, anti- opposed to,
Pod- Food
preventing,
Poly- Multiple
inhibiting
Procto- Rectum
bili- bile
Pseudo- False
brachi- arm
Psycho- Mind
brady- slow
Pyel- Pelvis of the kidney
Pyo- Pus
cholecysto- gallbladder
Quadri- Four
co, con- together
Radio- Radiation
Re- Back
demi- half
Ren- Kidney
derm- skin
Retro- Backward
dis- from
Sacro- Flesh
dors- back
Salpingo- Fallopian tube
dys- difficult, faulty,
Sclero- hard
painful
Sub- Beneath
eryth- red
Syn- Together
exo- outside, outer
Tachy- Rapid
layer
Trache- Trachea
extra- outside, beyond
Tri- Three
Ferr- Iron
Ultra- Beyond
Fibro- fiber
Uni- One
fore- before, in front of
Uretero- Ureter
glyco- sugar
Uro- Urine, urinary organs
hemi- half
hemo- Blood
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
Suffixes
-able Able to
-algia Pain
-Cele Tumor
-centesis Surgical puncture
-cide Kill,destroy
-ectasia Dilating, stretching
-ectomy Cutting out
-esis Action
-form Shape
-genesis,genetic Formation
-ism Conditon
-Itis Inflammation
-Ize To treat
-Lith Stone, calculus
-Lithiasis Presence of stones
-megaly Enlargement
-oid Like, resemble
-orrhaphy Surgical repair
-osis Disease, condition
-ostomy To form an opening
/ outlet
-otomy To incise
-Pathy Disease
-pexy Fixation
-phage Ingesting
-phobia Fear
-plasty Plastic surgery
-plegia Paralysis
-rhexis Rupture
-rrhagia Abnormal/excessive
discharge
-rrhea Flow/discharge
-scopy To examine visually
-Stomy Establishment of an
artificial opening
-Tomy Incision into
-uria Urine
-zyme Enzyme, ferment
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
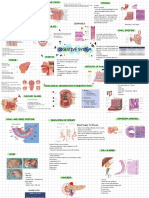
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION FOR THE HUMAN BODY
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
MAJOR ORGANS OF THE BODY.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
PART 1: o Involves looking the exterior of the
body to visualize structures deeper
Human Anatomy:
inside the body.
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology:
Physiology:
Anatomy: o Study of how the body its parts work
/ function.
Greek words:
o “Apart” (Ana) Example:
o “Cut” (tomy)
o Neuroophysiology
o The study of the structure and shape
o Cardiavascular physiology
of the body and its parts and their
o Cell physiology
relationships to one another.
o Systemic physiology
Anatomy can be studied at different levels:
Developmental anatomy:
Levels of Structural Organization
o Studies the structural changes that o The human body exhibits many
occur between conception and levels of structural complexity.
adulthood.
o Subspecialties:
Atoms:
o Embryology o Tiny building blocks of matter
o Cytology o Water, sugar, proteins.
o Histology
Cells:
Gross Anatomy:
o Smallest units of living things.
o Studies of structures that can be o Some have common structures and
examined without the aid of functions.
microscope. o Individual cells vary widely in size,
shape and their particular roles in
o System:
body.
o A group of structures that
Example:
have one or more common o One-celled organism(amoebas)
functions (Cardiovascular, o Multicellular organism(dogs,human)
nervous, respiratory and
etc.). Tissues:
o Systemic anatomy o Tissues consist of groups of similar
o Body is studied system by system cells that have a common function.
o Regional Anatomy:
o Studied the body area by
area Examples:
Epithelium tissue:
o Covering, lining, and glandular
Surface anatomy: tissue.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
o Its functions include protection, Epithelia and connective tissues
absorption, and secretion. regenerate well.
o Epithelia are named according: o Mature cardiac muscle and nervous
o To number of layers (simple, tissue are repaired by fibrosis.
stratified)
o Cell shape (squamous, Organ
cuboidal, columnar). o Is a structure composed of two or
Connective tissue more tissue types that performs a
o The supportive, protective, and specific function for the body.
binding tissue.
o It is characterized by the presence of Organ system:
a nonliving, extracellular matrix o Group of organs that work together
(ground substance plus fibers) to accomplish a common purpose.
produced and secreted by the cells.
it varies in amount and consistency. Organism level:
o Fat, ligaments and tendons, bones, o Are made up of many organ
and cartilage are all connective systems.
tissues or connective tissue
structures. Organ system overview:
Muscle tissue: Integumentary system:
o Specialized to contract, or shorten,
which causes movement.
There are three types:
o Skeletal
o (Attached to the skeleton)
o Cardiac
o (In the heart wall)
o Smooth
o (in the walls of hollow
organs).
Nervous tissue:
o Composed of irritable cells called
neurons, which are highly specialized
to receive and transmit nerve
impulses, and supporting cells called
neuroglia.
o Neurons are important in control of
body processes.
o Located in nervous system
structures—brain, spinal cord, and
nerves. o External covering of the body or the
skin including hair and fingernails.
Tissue repair (wound healing): o Waterproofs the body and cushions
o May involve regeneration, fibrosis, or and protects the deeper tissues from
both. injury.
In regeneration, the injured tissue is o Via direct sunlight:
replaced by the same type of cells. o produced of vit. D
o In fibrosis, the wound is repaired with
scar tissue.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
o Excretes salts in perspiration and
helps regulate body temperature.
Skeletal System: Muscular System:
o Function:
Consists: o Contract/shorten
o Bone o When this happens, movement
o Cartilages o occurs.
o Joints o The mobility of the body as a whole
o It supports the body and provides a reflects the activity of skeletal
framework that the skeletal muscles muscles, the large, fleshy muscles
use to cause movement. attached to bones.
o Protective function o When these contracts, you are able
o Sites (the blood cells formed) to stand erect, walk, jump, grasp,
o Storage (minerals) throw a ball, or smile.
The skeletal muscles form the
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
muscular system. These muscles are o Decreases in oxygen or
distinct from the muscles of the heart stretching of tissue.
and of other hollow organs, which o The central nervous system then
move fluids assesses this information and
o (such as blood or urine) or other responds by activating the
substances (such as food). appropriate body effectors.
Nervous System:
Endocrine System
o The nervous system is the body’s fast-
acting control system.
It consists of:
o Brain
o Spinal cord
o Nerves o Endocrine glands produce:
o Sensory receptors hormones and release them into the
o The body must be able to respond to blood to travel to relatively distant
stimuli coming from outside the body target organs.
such as:
o Light The endocrine glands:
o Sound o Pituitary
o Changes in temperature o Thyroid
o Inside the body: o Parathyroids
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
o Adrenals o The heart propels blood out of its
o Thymus chambers into blood vessels to be
o Pancreas transported to all body tissues.
o Pineal
o Ovaries (in the female) Lymphatic System:
o Testes (in the male)
Cardiovascular System
o The role of the lymphatic system
complements that of the
cardiovascular system.
Its organs include:
o Lymphatic vessels
o Lymph nodes
o other lymphoid organs (spleen &
tonsils)
o When fluid is leaked into tissues from
the blood, lymphatic vessels return it
to the bloodstream so that there is
enough blood to continuously
circulate through the body. The
lymph nodes and other lymphoid
organs help to cleanse the blood
and house white blood cells involved
in immunity.
o The primary organs:
o Heart
o Blood vessels.
o White blood cells:
o Protect the body from such
foreign invaders.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
Respiratory System: Digestive System:
o To keep the body supplied with
oxygen and to remove carbon
dioxide.
The respiratory system consists:
o Nasal passages
o Pharynx
o Larynx
o Trachea o The digestive system is basically a
o Bronchi tube running through the body from
o Lungs mouth to anus.
The organs of digestive system:
o Oral cavity (mouth)
o Esophagus
o Stomach
o Small
o Large intestines
o Rectum
W/: accessory organs:
o Liver
o Salivary glands
o Pancreas
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
Urinary System
Reproductive System
o The role of the reproductive system is
to produce offspring.
Male reproductive system:
o The male testes (sperm).
o Scrotum
Functions: o Penis
o Eliminates waste products: o Accessory glands
o Urea o Duct system (carries sperm to the
o Uric acid outside of the body).
o Maintaining the body’s water and o The female reproductive system:
electrolyte balance. o Ovaries/ova (eggs)
o Regulating the acid-base balance o The female duct system:
of the blood. o Uterine tubes
o Helping to regulate normal blood o Uterus (The site for the development
pressure. of the fetus (immature infant).
o Which results when the body cells o Vagina
break down:
o Proteins and Nucleic acids Necessary Life Functions
o Often called the excretory system
Composed of the: Maintaining boundaries
o Kidneys Movement:
o Ureters o Muscular system
o Bladder - e.g: walking, swimming,
o Urethra Responsiveness/Irritability:
o accidentally touch a hot pan
(involuntarily pull your hand
away from the painful
stimulus).
o Excess carbon dioxide
(breathing rate speeds up)
o Due to: nerve cells are highly
irritable and can
communicate rapidly with
each other via electrical
impulses, the nervous system
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
bears the major responsibility Brachial Arm
for responsiveness. Buccal Cheek are
o Digestion Carpal Wrist
o Metabolism: Cervical Neck region
o Breaking down complex Coxal Hip
substances into simpler Crucal Anterior leg; the shin
building blocks. Deltoid Curved of shoulder
o Excretion: formed by large deltoid
o Process of removing wastes muscles
from the body. Digital Fingers, toes
Reproduction Femoral Thigh(anterior/posterior)
Growth
Fibular Lateral part of leg
Survival Needs: Frontal Forehead
o Nutrients: Inguinal Area where thigh meets
o e.g: Carbohydrates, Minerals, body trunk; groin
vitamins. Mental Chin
o Oxygen Nasal Nose area
o Normal body temperature Oral Mouth
Orbital Eye area
Patellar Anterior knee
Anatomical Position: Pectoral Relating to, or occurring
o To accurately describe body parts in/on, the chest
and position, we must have an initial Pelvic Area overlying the pelvis
reference point and use directional anteriorly
terms. Pubic Genital region
Sternal Breastbone area
Directional Terms:
Tarsal Ankle region
o Allows medical personnel and
Thoracic Area between the neck
anatomists to explain exactly where
and abdomen; supported
one body structure is in relation to
by the ribs, sternum and
another.
costal cartilages
Umbilical Navel
Give the relationship between the following
body parts using the correct anatomical
terms.
The wrist is _____________ to the hand.
Posterior Body Landmarks
The breastbone is _____________ to the spine.
The brain is _____________ to the spinal cord. Calcaneal Heel of foot
The thumb is _____________ to the fingers. Cephalic Head
Femoral Thigh
Gluteal Buttock
Regional terms: Lumbar Area of back b/w
Anterior Body landmarks: ribs and hips, the
Abdominal Anterior body loin
trunk inferior to ribs Occipital Posterior surface of
Acromial Point of shoulder head / base of skull
Antebrachial Forearm Olecranal Posterior surface of
elbow.
Antecubital Anterior surface of elbow Popliteal Posterior knee area.
Axillary Armpit
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
Sacral Area between hips
of base of spine. Frontal Section (Coronal section):
Scapular Shoulder blade
region
Sural Posterior surface of
leg; the calf
Vertebral Area of spinal
column
Plantar Sole of the
foot(inferior body
surface)
Body Planes and Sections:
Section (Cut)
Sagittal Section
o Cut along a lengthwise plane that
divides the body/organ into anterior
& posterior parts.
Transverse section (cross section):
o Cut along the
lengthwise/longitudinal, plane of the
body, dividing the body into the right
and left parts.
o If equal in size: The cut is
coming down the median
plane of the body and right
and left part.
(Median /
medsagittal) section. o Cut along a horizontal plane,
dividing the body and organ into
superior and inferior parts.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
o The walls of the body cavities and
Body Cavities: the surface of internal organs are in
o Dorsal body cavity contact with membranes.
o Ventral cavity
Parietal serous membrane:
Dorsal Body Cavity: o Layer that lines the walls of the
o Encloses the organs of the nervous cavities.
system, the brain and spinal cord.
Subdivision: Visceral serous membrane:
o Cranial Cavity: Brain o The layer covering the internal
o Vertebral Canal: Spinal cord organs.
o Covered by membranes
(meninges) Two membranes are separated by a thin
film of serous fluid produced by the
Ventral Body Cavity: membranes.
o Viscera As organs move around in the cavities, the
2 major subdivision: combination of serous fluid and smooth
o Thoracic cavity serous membranes reduces friction.
o Abdominopelvic cavity
Thoracic cavity: Thoracic Cavity Membranes
o More superior to the
abdominopelvic cavity.
o Heart and lungs
Subdivided:
o Two lateral pleural cavities
o Medial mediastinum
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Enclosed by abdominal muscles:
Abdominal cavity
o Stomach
o Intestines
o Liver
o Spleen Pericardial Cavity
o Heart
Pelvic cavity:
o Below pelvis. Parietal pericardium
o Urinary bladder o Parietal serous membrane.
o Urethra
o Rectum (Large intestine) Visceral pericardium.
o Reproductive organs o Visceral serous membrane.
Serous Membranes of the Ventral Body Pericardial cavity
Cavity o The space between the two
pericardial membranes and is filled
with pericardial fluid.
o Pleural Cavities
Serous membranes:
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
with peritoneal fluid
o In addition to covering organs, a
double-folded sheet of visceral
peritoneum attaches the digestive
organs at certain points to the
posterior abdominopelvic cavity
wall.
o These regions of double-folded
visceral peritoneum are called
mesenteries.
Parietal pleura o The mesenteries also provide a
o The parietal serous membrane lining pathway for nerves and blood
the pleural cavities. vessels to reach the digestive organs
Visceral pleura
o Visceral serous membrane covering o The most notable mesenteric
the lungs. structure is an enormous pouch
Pleural cavity containing adipose tissue that is
o Space between the two pleural suspended from the inferior border
membranes and is filled with pleural of the stomach.
fluid.
o Some abdominal organs are tightly
adhered to the posterior body wall
Peritoneal Cavity and are covered by peritoneum only
o Liver on their peritoneal cavity side.
o Digestive organs
Reproductive organs o These organs have a retroperitoneal
location and include the kidneys,
ureters, adrenal glands, a large
portion of the pancreas, parts of the
large intestine, and the urinary
bladder.
Inflammation of the serous membranes:
Pericarditis
o An inflammation of the pericardium.
Pleurisy:
o An inflammation of the pleura.
Peritonitis
o An inflammation of the peritoneum.
Parietal peritoneum.
o Serous membrane in the peritoneal
cavity.
o The space between the two serous
membranes is the specific location
of the peritoneal cavity and is filled
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
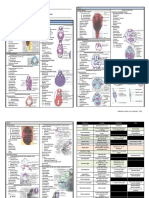
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Specializations of the plasma
o A cell is composed primarily of membrane include microvilli (which
four elements carbon, hydrogen, increase the absorptive surface area)
oxygen, and nitrogen plus many and cell junctions (desmosomes, tight
trace elements. Living matter is junctions, and gap junctions).
over 60 percent water. The major
building material of the cell is The cytoplasm is where most cellular
protein. activities occur. Its fluid substance, the
o Cells vary in size from microscopic cytosol, contains inclusions, stored or
to over a meter in length. Shape inactive materials in the cytoplasm (fat
reflects function. For example, globules, water vacuoles, crystals, and
muscle cells have a long axis to the like) and specialized bodies called
allow shortening. organelles, each with a specific
function. For example, mitochondria are
Anatomy of a Generalized Cell sites of ATP synthesis, ribosomes are sites
Cells have three major regions: of protein synthesis, and the Golgi
Nucleus apparatus packages proteins for export
Cytoplasm from the cell. Lysosomes carry out
Plasma membrane. intracellular digestion, and peroxisomes
disarm dangerous chemicals in the cells.
The nucleus, or control center, directs Cytoskeletal elements function in
cell activity and is necessary for cellular support and motion. The
reproduction. centrioles play a role in cell division and
The nucleus contains genetic material form the bases of cilia and flagella.
(DNA), which carries instructions for
synthesis of proteins. Cell Physiology
All cells exhibit irritability (the ability to
The plasma membrane encloses the respond to stimuli), digest foods, excrete
cytoplasm and acts as a wastes, and are able to reproduce,
semipermeable barrier to the grow, move, and metabolize.
movement of substances into and out
of the cell. Transport of substances through the cell
It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer membrane:
containing proteins, sugars, and a. Passive processes include diffusion
cholesterol. The water-impermeable and filtration.
lipid portion forms the basic membrane (1) Diffusion is the movement of a
structure. The proteins (many of which substance from an area of its higher
are glycoproteins) act as enzymes or concentration to an area of its lower
carriers in membrane transport, form concentration. It occurs because of
membrane channels, provide receptor kinetic energy of the molecules
sites for hormones and other chemicals, themselves; no ATP is required. The
or play a role in cellular recognition and diffusion of dissolved solutes through the
interactions during development and plasma membrane is simple diffusion.
immune reactions. The diffusion of water across the plasma
membrane is osmosis. Diffusion that
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
requires a protein channel or carrier is a. Hypertonic solutions contain more
facilitated diffusion. solutes (and less water) than do cells. In
these solutions, cells lose water by
Filtration is the movement of substances osmosis and crenate.
through a membrane from an area of
high hydrostatic pressure to an area of b. Hypotonic solutions contain fewer
lower fluid pressure. In the body, the solutes (and more water) than do the
driving force of filtration is blood cells. In these solutions, cells swell and
pressure. may rupture (lyse) as water rushes in by
osmosis.
b. Active processes (active transport c. Isotonic solutions, which have the
and vesicular transport) use energy same soluteto-solvent ratio as cells,
(ATP) provided by the cell. cause no changes in cell size or shape.
(1) In active transport, substances are
moved across the membrane against 4. Cell division has two phases, mitosis
an electrical or a concentration (nuclear division) and cytokinesis
gradient by proteins called solute (division of the cytoplasm).
pumps. This accounts for the transport of
amino acids, some sugars, and most a. Mitosis begins after DNA has been
ions. replicated (during interphase); it consists
of four stages—prophase, metaphase,
(2) The two types of ATP-activated anaphase, and telophase.
vesicular transport are exocytosis and The result is two daughter nuclei, each
endocytosis. identical to the mother nucleus.
Exocytosis moves secretions and other b. Cytokinesis usually begins during
substances out of cells; a membrane- anaphase and progressively pinches
bounded vesicle fuses with the plasma the cytoplasm in half.
membrane, ruptures, and ejects its Cytokinesis does not always occur; in
contents to the cell exterior. such cases, binucleate or multinucleate
cells result.
Endocytosis, in which particles are taken
up by enclosure in a plasma membrane c. Mitotic cell division provides an
sac, includes phagocytosis (uptake of increased number of cells for growth
solid particles), pinocytosis (uptake of and repair.
fluids), and the highly selective
receptor-mediated endocytosis. 5. Protein synthesis involves both DNA
In the latter, membrane receptors bind (the genes) and RNA.
with and internalize only selected target
molecules. a. A gene is a segment of DNA that
carries the instructions for building one
3. Osmotic pressure, which reflects the protein. The information is in the
solute concentration of a solution, sequence of bases in the nucleotide
determines whether cells gain or lose strands. Each three-base sequence
water. (triplet) specifies one amino acid in the
protein.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
Grind hard, Search for your inspiration and have fun (Walwal after)!!
God bless! Good luck future RMT
Mr.Pseudocute,RMT
b. Messenger RNA carries the 5. Tissue repair (wound healing) may
instructions for protein synthesis from the involve regeneration, fibrosis, or both. In
DNA (gene) to the ribosomes. regeneration, the injured tissue is
Transfer RNA transports amino acids to replaced by the same type of cells.
the ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA forms In fibrosis, the wound is repaired with
part of the ribosomal structure and helps scar tissue. Epithelia and connective
coordinate the protein building process. tissues regenerate well. Mature cardiac
muscle and nervous tissue are repaired
by fibrosis.
PART II: BODY TISSUES
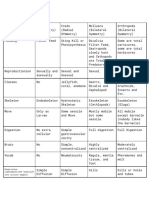
1. Epithelium is covering, lining, and PART III: DEVELOPMENTAL ASPECTS
glandular tissue. OF CELLS AND TISSUES
Its functions include protection,
absorption, and secretion. Epithelia are 1. Growth by cell division continues
named according to number of layers through puberty. Cell populations
(simple, stratified) and cell shape exposed to friction (such as epithelium)
(squamous, cuboidal, and columnar). replace lost cells throughout life.
Connective tissue remains mitotic and
2. Connective tissue is the supportive, forms repair (scar) tissue. With some
protective, and binding tissue. It is exceptions, muscle tissue becomes
characterized by the presence of a amitotic by the end of puberty, and
nonliving, extracellular matrix (ground nervous tissue becomes amitotic shortly
substance plus fibers) produced and after birth.
secreted by the cells; it varies in amount Injury can severely handicap amitotic
and consistency. Fat, ligaments and tissues.
tendons, bones, and cartilage are all
connective tissues or connective tissue 2. The cause of aging is unknown, but
structures. chemical and physical insults, as well as
genetic programming, have been
3. Muscle tissue is specialized to proposed as possible causes.
contract, or shorten, which causes
movement. There are three types 3. Neoplasms, both benign and
skeletal (attached to the skeleton), cancerous, represent abnormal cell
cardiac (in the heart wall), and smooth masses in which normal controls on cell
(in the walls of hollow organs). division are not working. Hyperplasia
(increase in size) of a tissue or organ
4. Nervous tissue is composed of irritable may occur when tissue is strongly
cells called neurons, which are highly stimulated or irritated. Atrophy
specialized to receive and transmit (decrease in size) of a tissue or organ
nerve impulses, and supporting cells occurs when the organ is no longer
called neuroglia. Neurons are important stimulated normally.
in control of body processes. Nervous
tissue is located in nervous system
structures—brain, spinal cord, and
nerves.
These notes are not to be shared or reproduced without my permission.
You might also like
- 1 Medical TerminologyDocument6 pages1 Medical TerminologyFatzie MendozaNo ratings yet
- ALHS 1090 Final Exam WorksheetDocument18 pagesALHS 1090 Final Exam WorksheetCesilia Martinez Castro0% (1)
- Basic Word Structure (MT)Document19 pagesBasic Word Structure (MT)leapphea932No ratings yet
- PrefixDocument3 pagesPrefixFlorilyn CabezoNo ratings yet
- 353 Med Terminology PDFDocument5 pages353 Med Terminology PDFNicole NicholsonNo ratings yet
- HOSA Prep-3Document1 pageHOSA Prep-3Tryhard PremedNo ratings yet
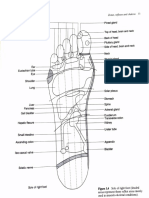
- Reflex Areas Palms and FootDocument5 pagesReflex Areas Palms and Footdonald duckNo ratings yet
- Ashap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Document1 pageAshap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Lorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Nema TableDocument3 pagesNema Tableanon_574497805No ratings yet
- Entomology: Harsh HemananiDocument17 pagesEntomology: Harsh HemananiThe DeofelNo ratings yet
- Families AnimaliaDocument1 pageFamilies Animaliaimranminhas2006No ratings yet
- Q CY9qjeEemJ1w4LYV5qDg - Useful Biological Prefixes and SuffixesDocument3 pagesQ CY9qjeEemJ1w4LYV5qDg - Useful Biological Prefixes and SuffixesPaula Andrea Melo ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Prefixes Which Can Be Used As Combining Forms in Compounded WordsDocument7 pagesPrefixes Which Can Be Used As Combining Forms in Compounded WordsNikkhil PatilNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminolgieeeesDocument5 pagesMedical TerminolgieeeesJeenah Yvet Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Frog AtlasDocument16 pagesFrog AtlasJAYHANNE PSYCHE MONDIANo ratings yet
- Derivation (Structural Analysis)Document2 pagesDerivation (Structural Analysis)Klein LibaoNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument4 pagesPoriferachildicuNo ratings yet
- Biowords v2Document3 pagesBiowords v2Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PhyiosologyDocument111 pagesAnaphy PhyiosologyArmanNo ratings yet
- SuffixesDocument3 pagesSuffixesgrgicosNo ratings yet
- Cockroach - Endgame Handwritten and SupernotesDocument27 pagesCockroach - Endgame Handwritten and Supernotesmansilamba1006No ratings yet
- Study PDFDocument4 pagesStudy PDFk0mmon.wwwwNo ratings yet
- Midterm Worksheet ALHS 1090 AssignmentDocument13 pagesMidterm Worksheet ALHS 1090 AssignmentElijah HallNo ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- Prs 8Document2 pagesPrs 8Lê Thùy VânNo ratings yet
- Prefijos - Lista Prefijo Definición EjemploDocument6 pagesPrefijos - Lista Prefijo Definición EjemploLuciano BerlassoNo ratings yet
- Reflexology Association of Canada - Foot Chart: Plantar ViewDocument1 pageReflexology Association of Canada - Foot Chart: Plantar ViewprabhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Salient Summary IntroDocument16 pages2 Salient Summary Introjmmos207064No ratings yet
- Medical Prefixes and SuffixesDocument12 pagesMedical Prefixes and SuffixesKrishnanunni KLNo ratings yet
- Varma 1st Exam NotesDocument7 pagesVarma 1st Exam NotesKarthick KanagarajNo ratings yet
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Frog EmbryoCHRISTIAN LOYD ARUPENo ratings yet
- Medical Term List PDFDocument21 pagesMedical Term List PDFAntonSusantoNo ratings yet
- Species Tab.Document13 pagesSpecies Tab.Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton LabelingDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton Labelingadriana blanco galianoNo ratings yet
- Prefixes PDFDocument5 pagesPrefixes PDFChristian100% (2)
- Primary SurveyDocument1 pagePrimary SurveyAmzar SaniNo ratings yet
- 78338-Anatomy of The Oral Cavity Pharynx and Larynx - SchuknechtDocument6 pages78338-Anatomy of The Oral Cavity Pharynx and Larynx - SchuknechtvldNo ratings yet
- Cap 17 Raices Sist Nervioso y CondcutaDocument2 pagesCap 17 Raices Sist Nervioso y CondcutaSandra OrtizNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument4 pagesMedical TerminologyDr Shreshta Reddy KNo ratings yet
- Common Affixes and Their Meanings: PrefixesDocument2 pagesCommon Affixes and Their Meanings: PrefixesKim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- Midterm Worksheet ALHS 1090 AssignmentDocument13 pagesMidterm Worksheet ALHS 1090 Assignmentariannaprice787No ratings yet
- Normal Ob 1Document14 pagesNormal Ob 1Dairyl TagaroNo ratings yet
- Prefixes, Suffixes, and StemsDocument6 pagesPrefixes, Suffixes, and Stemssonickemet100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemRANGSINEE SUWANNASUKNo ratings yet
- Language of Science: PREFIX LIST BeginningsDocument4 pagesLanguage of Science: PREFIX LIST BeginningsjmunozbioNo ratings yet
- Bank Soal AMSA Youth ProjectDocument24 pagesBank Soal AMSA Youth ProjectTuti Awwaliah27No ratings yet
- PSR 202Document115 pagesPSR 202Arpita ArpiNo ratings yet
- Endoskeleton of The ChickenDocument20 pagesEndoskeleton of The ChickenJoachimNo ratings yet
- Para Notes (Dev)Document4 pagesPara Notes (Dev)Miiwhh SoneNo ratings yet
- Prefixes in Medical TerminologyDocument7 pagesPrefixes in Medical Terminologyalerp07100% (1)
- UPPER LIMB - 4 The Anatomical SnuffboxDocument1 pageUPPER LIMB - 4 The Anatomical SnuffboxDhananjay hyalijNo ratings yet
- Greek and Latin ComparisonsDocument9 pagesGreek and Latin ComparisonsNatalie UrquhartNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Review BoxDocument2 pagesReview BoxJack MandelNo ratings yet
- Terrminology For - Henderson - Appendix Prefixes and SuffixesDocument5 pagesTerrminology For - Henderson - Appendix Prefixes and SuffixesEng Spasii GeemNo ratings yet
- Prefixes & SuffixesDocument5 pagesPrefixes & Suffixescurly perkyNo ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder AnatomyDocument10 pagesUrinary Bladder AnatomyprinceNo ratings yet