Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Revalidaur PDF
Uploaded by
Riemer, Jheaz LheyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Revalidaur PDF
Uploaded by
Riemer, Jheaz LheyCopyright:
Available Formats
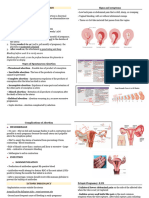
Bleeding disorders 2nd trimester
1st trimester 1. H-mole
- fertilized egg develops into a mass of cysts,
1. Abortion
rather than a fetus
- less than 500 grams
- H-moles high hCG, mgmt. is hysterectomy
- if less than 20 weeks it is called abortus (removal of uterus and cervix)
Types of abortion - Gestational Trophoblastic disease (group of
rare tumors that develop in the cells that would
- missed (fetus dies in the womb but is not normally form the placenta during pregnancy)
expelled)
- Choriocarcinoma (develops from the cells that
- threatened (vaginal bleeding occurs before 20 would normally form the placenta and produce
weeks of gestation but the cervix is still closed the hCG, malignant and can quickly spread to
and the fetus is still viable) other organs, may occur years after h-mole,
- complete (all the products of conception are cancerous)
expelled from the uterus) - Invasive moles (abnormal cells grow into the
- Incomplete (some but not all the products of muscle layer of the uterus)
conception are expelled)
2. Incompetent Cervix
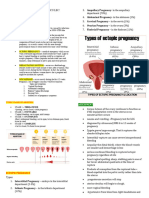
2. Ectopic - 4 – 5.2 cm is the normal ± 2 cm
- cervix is dilated/open
- ampulla is the most common site (80-90%) - no mucus plug (barrier to prevent bacteria
- ovarian - fimbriae - cervical from entering the uterus)
- 3cm up no cerclage
- isthmus - interstitial - must check for infection before doing cerclage
- indomethacin therapy
- Cullen’s sign (bluish tinge in the umbilicus)
- avoid sex for 2 weeks
- abdominal pain radiating to the shoulder (phrenic Types of cerclages
nerve) - Shirodkar (permanent)
- McDonalds (temporary)
- rigid/stiff abdomen
- Assisted reproduction
3rd trimester
- GIFT (Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer)
1. Placenta Previa (Abnormal implantation)
- sperm cell is added to meet/fertilize - 34 weeks
the egg - development of lower uterine segment
- resolution of placenta previa
- IVF (in Vitro Fertilization) - tocolytics given
- egg is already fertilized Types
- complete - partial
- salpingostomy – di tinatahi for healing/repairing - marginal - low lying
- salpingectomy – tinatahi *Deliver the baby is the mother has severe
bleeding regardless of gestation
* If the mother has minimal bleeding but the
baby is premature promote bed rest
* If the mother has minimal bleeding but the
baby is full term, deliver the baby
2. Abruptio Placenta (Normal implantation)
- happens in endometrium
- prone to hypovolemic shock
- covert (concealed, dark red bleeding), middle
is detached
- overt (bright red bleeding) sides are detached
- tocolytics given
- uterine apoplexy (Couvelaire)
- blood in myometrium (thick middle
muscular layer of the uterus wall
responsible for the movements of the
uterus during childbirth. Its main
function is to induce uterine
contractions to help during labor and
delivery)
- purple uterus
- ischemia (blood flow (and thus
oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a
part of the body)
You might also like
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Growing FetusDocument4 pagesChapter 9 The Growing FetusCarrie ANo ratings yet
- Emed - OB Part 1Document6 pagesEmed - OB Part 1Princess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Reproductive SystemRose Kathreen Quintans AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders During Pregnancy 1.threatened MiscarriageDocument12 pagesBleeding Disorders During Pregnancy 1.threatened MiscarriageKish Gabriel100% (1)
- REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (Scie)Document6 pagesREPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (Scie)Michaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument6 pagesMaternalBlessed Glaiza MarianoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization NCM107Document9 pagesFertilization NCM107Jasmin NatocNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Previa Vs AbruptioDocument1 pagePrevia Vs AbruptioJamaica QuetuaNo ratings yet
- Feb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118Document9 pagesFeb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118HANNAH BANGKILINGNo ratings yet
- h1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesDocument11 pagesh1 Reproductive Physiology Course Summary NotesHoney BaseriNo ratings yet
- NOTES 1st Sem P FDocument6 pagesNOTES 1st Sem P FReaNo ratings yet
- MCN Notes 2Document26 pagesMCN Notes 2Rogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- RevkeDocument11 pagesRevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Maternal (Finals)Document8 pagesMaternal (Finals)Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument5 pagesNOTESMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument43 pagesMaternal and Child NursingSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Reproductive Systemsamanthagracem3No ratings yet
- Fertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyDocument9 pagesFertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyjisooNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyDocument13 pagesNCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec - Chapter 3Document18 pagesMCN Lec - Chapter 3David LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Complications of Intrapartum and Post PartumDocument8 pagesComplications of Intrapartum and Post PartumMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Ncm213 Unit 1Document12 pagesNcm213 Unit 1Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- NCM 101Document8 pagesNCM 101Bing58No ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BDocument14 pagesComplications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Pregnancy and Delivery: Lecture On Pathological Anatomy For The 3-rd Year StudentsDocument35 pagesPathology of Pregnancy and Delivery: Lecture On Pathological Anatomy For The 3-rd Year StudentsRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocument47 pagesA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Caring For The Family During Pregnancy: Ischemic PhaseDocument11 pagesCaring For The Family During Pregnancy: Ischemic PhaseDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Reproductive System-ReviewerDocument6 pagesReproductive System-ReviewerAdrian Faiz VillenaNo ratings yet
- Infertility PDFDocument3 pagesInfertility PDFdharshiniNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction NotesZelNo ratings yet
- Week1 Menstrual or Reproductive Cycle Signs of Pregnancy 1Document25 pagesWeek1 Menstrual or Reproductive Cycle Signs of Pregnancy 1FEVI KATE IGTOSNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Child Print 1-10Document11 pagesMaternity and Child Print 1-10ZYRHIL ANANONo ratings yet
- Perinatal PeriodDocument3 pagesPerinatal PeriodApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahDocument33 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document21 pagesDay 1Ahmed DorghamNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Summary (Modifications) - AnasayaDocument15 pagesModule 8 Summary (Modifications) - Anasayafroosedd777No ratings yet
- Mohammad Sami نسائية وتوليدDocument25 pagesMohammad Sami نسائية وتوليدlianausinNo ratings yet
- CN DystociaDocument7 pagesCN DystociaAlbert Francis BialaNo ratings yet
- Ncma 217 MidtermsDocument15 pagesNcma 217 MidtermsCharmaine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFDocument29 pagesPlacenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFPamela Marie Cope100% (1)
- XII-Bio - Last Minute Revision Study MaterialDocument18 pagesXII-Bio - Last Minute Revision Study MaterialghjNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumanDocument32 pagesReproduction in HumanJorifNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument11 pagesMaternal and Child NursingKSY JanedoeNo ratings yet
- MCN Topic 1 Basic ConceptsDocument7 pagesMCN Topic 1 Basic ConceptsDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesUnit 12 Reproductive SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Repro NotesDocument19 pagesRepro NotesAsh-Lee HugginsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in AnimalsdiegocmakoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Female System: by Dr.H.Gusbakti, MSC, PKK, Aifm Professor of PhysiologyDocument44 pagesReproductive Female System: by Dr.H.Gusbakti, MSC, PKK, Aifm Professor of PhysiologyRizki YulianaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemChester Yting Pe Benito100% (1)
- Maternal Midterm TransesDocument24 pagesMaternal Midterm TransesTaegyu IS SAILING Periodt.No ratings yet
- Blastocyst ANA 205Document27 pagesBlastocyst ANA 205Ogundipe olorunfemiNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsDocument19 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet