Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASSESSMENT
Uploaded by
Zerimar Adawe Dulnuan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesOriginal Title
ASSESSMENT.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesASSESSMENT
Uploaded by
Zerimar Adawe DulnuanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
SCIENTIFIC
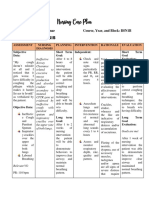
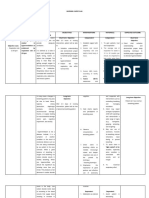
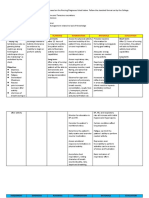
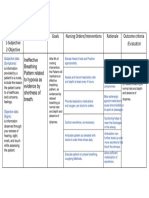
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
EXPLANATION
Subjective: Ineffective It is considered Goal: Dependent Goal met:
breathing the state in which After 4hrs of Monitor v/s To assist in The patient will
“Nahihirapan pattern the rate, depth, nursing creating an achieve
huminga ang timing, rhythm, or interventiona accurate effective
anak ko” as pattern of the pt will breath diagnosis and breathing
verbalized by the breathing is normally monitor pattern as
patient altered. When effectiveness evidenced by
the breathing of medical respiratory rates
Objective: pattern is treatment between 12 to
ineffective, the Assess and Provide for 20 breaths per
Breath body will likely record baseline data minutes, oxygen
sounds not get enough respiratory rate in evaluating saturation
noted: oxygen to the every 4 hrs respiratory between 88 to
Wheezes cells. Respiratory function 92%, and
failure may be verbalize ease
Irregular correlated with Observe Provide you of breathing.
breathing variations in breathing with greater
respiratory rate, pattern sense of
V/S taken as abdominal and mental clarity
follows: thoracic patterns. it can also
help you
Breathing pattern sleep better,
T: 36.8 alteration may digest food
P: 103 also transpire in more
R: 24 several efficiently
BP: 90/60 circumstances improve your
from heart failure, body, immune
hypoxia, airway response and
obstruction, reduce stress
diaphragmatic levels
paralysis, Auscultate Presence of
infection, breath sounds adventitious
neuromuscular breath
impairment, sounds may
trauma or indicate
surgery resulting developing
in Assess the complications
musculoskeletal client the use For patients
impairment and of relaxation relieve
pain, cognitive technique heaviness of
impairment and breath
anxiety, diabetic Assist and
ketoacidosis, demonstrate Leads to early
uremia, thyroid deep breathing identification
dysfunction, and coughing and treatment
peritonitis, drug exercises of impending
overdose, AIDS, respiratory
acute alcohol failure
withdrawal,
cardiac surgery,
cholecystectomy, Independent
liver cirrhosis, Administer the
craniocerebral prescribed To treat
trauma, disc antibiotics bacterial
surgery, medications infection if
lymphomas, this is the
renal dialysis, underlying
seizure cause of the
disorders, spinal patient’s
cord injuries, pleural
mechanical effusion.
ventilatory Prepare the
assistance, and patient for tube Tube
pleural toracsotomy or thoracostomy
inflammation. chest drain includes
insertion thoracentesis
and the
placement of
a draining
tube to the
pleural space
to drain the
excess fluid.
It may take
several days
before the
tube is
removed. On
the other
hand, a
pleural drain
insertion
involves long
term drain for
chronic
pleural
effusion. Both
are minimally
invasive
Prepare the procedures.
patient for For effusions
surgery as not relieved
ordered by drainage
or pleural
sclerosis,
surgery may
be warranted
and they are
divided into
two: Video
assisted
thorascopic
surgery
(VATS) – a
minimally
invasive
procedure
involving 1 to
3 small
incisions
under scope
guidance and
the
introduction of
sclerosing
agent to
prevent
pleural
effusion build-
upTraditional
thoracotomy
(open
thoracic
surgery) –
performed
thru a 6-8
incision into
the chest
cavity to
evacuate
infected
tissue and
remove
fibrous build-
up causing
pleural
effusions.
A variety of
medication
are prepared
Perform to manage
nasotracheal specific
suctioning as problems
necessary most promote
specially if clearance of
cough airway
ineffective secretions
and may
reduce airway
resistance
You might also like
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Impaire Spontaneous VentilationDocument4 pagesImpaire Spontaneous VentilationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveKristel PunoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- NCP 1 1Document10 pagesNCP 1 1Samantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Asthma Attack Nursing Care Plan for Married Female PatientDocument5 pagesAsthma Attack Nursing Care Plan for Married Female PatientMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Airway Clearance StrategiesDocument4 pagesAirway Clearance Strategiescammel ramos100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationDivine ParagasNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- CASE SCENARIO and NCPDocument14 pagesCASE SCENARIO and NCPBeverly PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument7 pagesName and Classification of DrugMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Careplan 1Document11 pagesCareplan 1ligaba1559No ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- Task 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesTask 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTine SabaulanNo ratings yet
- Defining CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesDefining CharacteristicsAngel MayNo ratings yet
- Bautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemDocument4 pagesBautista - 3 Way Bottle SystemKatherine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- Valeriano, NCPDocument4 pagesValeriano, NCPVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Care of the Patient with Respiratory DisorderDocument1 pageCare of the Patient with Respiratory DisorderSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- NCP For Scenario BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP For Scenario Breathingmy moznNo ratings yet
- NCP and FDARDocument3 pagesNCP and FDARReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- (SOB) Care PlanDocument1 page(SOB) Care Planshatha faisal100% (1)
- Gr.4 NCP Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesGr.4 NCP Health AssessmentAlessandro MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Daniel P. Soriano BSN 4A Activity 3: Pediatric Nursing Health Assessment and Nursing Care Plan ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDaniel P. Soriano BSN 4A Activity 3: Pediatric Nursing Health Assessment and Nursing Care Plan ObjectivesChezka MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP)Sha PinedaNo ratings yet
- Improve Cardiac Output Through Nursing InterventionsDocument8 pagesImprove Cardiac Output Through Nursing InterventionsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDocument5 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Pulmo Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPulmo Nursing Care PlanVincent RoyNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalDocument59 pagesGroup 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalChristian Angelo LeonorNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT OF INEFFECTIVE AIRWAY CLEARANCEDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT OF INEFFECTIVE AIRWAY CLEARANCEtflorenzNo ratings yet
- Viray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDDocument3 pagesViray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDJezzy VeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- NCP, Drug StudyDocument9 pagesNCP, Drug StudyTresha CaliboNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Pedia)Document5 pagesNursing Care Plan (Pedia)JA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessement Diagnosis Goals and Desired Outcomes Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessement Diagnosis Goals and Desired Outcomes Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationJoshua Selwyn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (2)Document18 pagesNursing Care Plan (2)Layo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- Micro Lab#24Document2 pagesMicro Lab#24رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)Document25 pagesGroup 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)christelNo ratings yet
- NCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaDocument3 pagesNCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 pagesBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaNo ratings yet