Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Science
Research Science
Uploaded by
Alexes Alyza CañeteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Science
Research Science
Uploaded by
Alexes Alyza CañeteCopyright:
Available Formats
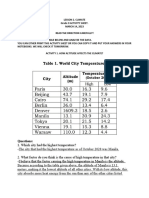
Latitude is the distance north or south of the equator.
It is one of the factors affecting
climate, for as the latitude increases, the smaller the angle at which the sun's rays
strike the surface, causing it to experience low temperatures. On the other hand, the
bigger the angle at which the sun's rays strike the surface, the higher the temperature
it experiences. Therefore, when the area is farther from the equator, the air
temperature is lower. The air temperature rises as one gets closer to the equator.
Altitude, also called as true altitude," is the distance above sea level. It is one of the
factors affecting climate, for we all know that the Earth's surface absorbs heat energy
from the sun. When the surface warms up, it diffuses and warms the atmosphere,
transferring some of the heat to the upper layers of the atmosphere. Therefore, the
layers of atmosphere closest to the Earth's surface, or low altitude areas, receive more
heat energy and are typically warmer compared to layers of atmosphere in higher
altitude areas, like mountainous places.
Topography describes the physical or natural features of an area of land. It is one of
the factors affecting climate because it influences wind patterns and weather patterns.
Mountains are one of the topographic features that we have, and mountainous areas
greatly affect the precipitation in certain places. The side of the mountain toward
which the wind blows is called the windward side. Here, the wind is blocked by the
mountain, forcing it to move upward. Water vapor then condenses and forms clouds,
resulting in precipitation on the windward side. On the other side of the mountain,
called the leeward side, cold air mass starts to absorb heat and becomes warm and
dry. thus making the leeward side dry and having less precipitation.
Bodies of water refer to any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth.
It is one of the factors affecting climate for large bodies of water like oceans because
they store solar radiation and distribute heat around the globe, having the ability to
alter the temperature and weather. When molecules are heated, they evaporate, which
causes an increase in temperature and humidity, forming rain and storms that are then
carried by trade winds. Which is why, like tropical countries, they mostly experience
rainfall and storms because of the tropical oceans surrounding them. Tropical oceans
receive more direct solar energy from the sun, causing more evaporation and leading
to more precipitation.
Distance from the ocean is one of the factors affecting climate because landmasses
heat up more quickly than water bodies as they receive solar radiation from the sun
but also lose heat more quickly than water. So, in hot seasons, especially at daytime,
the sea or ocean remains cooler than the continent and therefore reduces the
temperatures of adjacent lands. In cold seasons and at night, the sea remains warmer
and therefore raises the temperatures of places close to it. Therefore, we can say that
the sea moderates the climate of the coastal areas by keeping the temperatures neither
too high nor too low.
Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater
driven by gravity, wind (the Coriolis Effect), and water density. It is one of the factors
affecting climate because it acts like a conveyor belt, transporting warm water and
precipitation from the equator toward the poles and cold water from the poles back to
the tropics. This concludes that currents regulate the global climate, helping
counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth's surface.
Gases, particularly greenhouse gases, trap heat in the earth's atmosphere. It is one of
the factors affecting climate that humans burning fossil fuels and other harmful gases
absorb solar energy and keep heat close to Earth's surface rather than letting it escape,
causing the temperature to go higher and leading to global warming.
A monsoon is a seasonal change in the direction of the prevailing, or strongest, winds
of a region. It is one of the factors affecting climate, for it causes wet and dry seasons
that are affected by this throughout mostly tropical countries or countries and
continents lying on or near the equator. Summer monsoons happen when large land
masses heat up. The heat from these land masses causes the air atop the land masses
to heat up and rise through the atmosphere. This creates an area of low pressure that
pulls in cooler, moist air, creating the right conditions for the heavy rains of the
summer monsoons. And vice versa, during winter monsoons, water off the shore of a
land mass heats up and rises, creating an area of low pressure that pulls in dry air from
over the land mass down towards the water.
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Q4 Science 8 Module 6Document18 pagesQ4 Science 8 Module 6Alexes Alyza Cañete100% (1)
- Music: Quarter 4 - Module 4: Traditional Asian Theater MusicDocument15 pagesMusic: Quarter 4 - Module 4: Traditional Asian Theater MusicAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Climate Grade 9 ActivityDocument5 pagesClimate Grade 9 ActivityAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Science MapDocument2 pagesScience MapAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Science News Casting ScriptDocument6 pagesScience News Casting ScriptAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Music PTDocument3 pagesMusic PTAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 LM CONTENT 1Document185 pagesScience Grade 9 LM CONTENT 1Alexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- MUSIC OF THE ROMANTIC ERA AutosavedDocument15 pagesMUSIC OF THE ROMANTIC ERA AutosavedAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Cleopatra and Mark AntonyDocument41 pagesCleopatra and Mark AntonyAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Creative Reporting 10 DiligenceDocument1 pageCreative Reporting 10 DiligenceAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Subject OrientationDocument11 pagesSubject OrientationAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Arts of The Neoclassical and Romantic PeriodsDocument22 pagesArts of The Neoclassical and Romantic PeriodsAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- The Climate BoothDocument2 pagesThe Climate BoothAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Chinese CuisineDocument2 pagesChinese CuisineAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document4 pagesScience 9Alexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ModalsDocument25 pagesLesson 2 ModalsAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Destination Spots in ChinaDocument6 pagesDestination Spots in ChinaAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Orientation 2022 2023Document6 pagesEarthquake Orientation 2022 2023Alexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 2:: Japanese and Korean Face and Mask Painting (Cont... )Document19 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 2:: Japanese and Korean Face and Mask Painting (Cont... )Alexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 4Document27 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 4Alexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 3 - Module 7: Nature of Emerging and Re-Emerging DiseaseDocument15 pagesHealth: Quarter 3 - Module 7: Nature of Emerging and Re-Emerging DiseaseAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet
- English NotesDocument7 pagesEnglish NotesAlexes Alyza CañeteNo ratings yet