0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageUnderstanding Modal Verbs
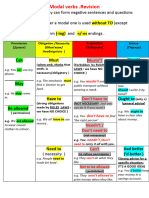
The document discusses modal verbs and their meanings and uses. It outlines that modal verbs can express suggestions and advice using "should" or criticism using "should not". It notes the difference between "should" expressing an obligation and "ought to" expressing expected behavior. Additionally, it mentions modal verbs like "can", "could", "may", and "might" express ability, possibility, permission and speculation while "must", "have to" express obligation and necessity and their negatives express lack of obligation or necessity. Finally, it highlights the difference between "mustn't" meaning prohibited versus "don't" meaning not required.
Uploaded by
Bent AlbrechtCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views1 pageUnderstanding Modal Verbs
The document discusses modal verbs and their meanings and uses. It outlines that modal verbs can express suggestions and advice using "should" or criticism using "should not". It notes the difference between "should" expressing an obligation and "ought to" expressing expected behavior. Additionally, it mentions modal verbs like "can", "could", "may", and "might" express ability, possibility, permission and speculation while "must", "have to" express obligation and necessity and their negatives express lack of obligation or necessity. Finally, it highlights the difference between "mustn't" meaning prohibited versus "don't" meaning not required.
Uploaded by
Bent AlbrechtCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd