Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Frances Samson GianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Frances Samson GianCopyright:
Available Formats
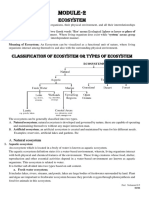
The Earth Ecosystem includes population, community,
habitat, and the environment.
Ecology 5. Biome
- branch of biology 6. Biosphere – is the world of life. Part of
- Primary focus is individual’s the earth where life operates.
(organisms) relationship with the
environment (physical sorrounding). The Ecosystem
- deals with what is outside of the - to the environment of life.
organism. - Living things interacting w/ non living
- Greek word “oikos” meaning environment.
household or home “logus” the study - self-sustaining, structural and
of. functional unit of biosphere.
- A multi disciplinary science - foundations of the Biosphere
- determine the health of the entire
Environment earth system.
- involves both living organisms and the - may be natural or artificial, land-based
non-living physical conditions. or water-based.
- a life supporting system.
- All life systems interact with the Ecosystem based on Region:
environment for food, shelter, growth *Terrestrial
and development. - Forest
- Grassland
LAWS OF ECOLOGY - Thundra
1. Everything is connected to everything else. - dessert
2. There is strength & stability in the unity of *Aquatic
differences. - Fresh water
3. Consumption must not exceed production. - Marine
4. Everything has a purpose.
Structure of Ecosystem
Ecological Organization and their level
(least to greatest)
1. Individual
2. Population – is a group of organisms
of the same kind.
3. Community – is a group of the
population living together in a given
place.
4. Ecosystem – the basic unit of ecology.
It refers to the interaction between the
organism and its environment. It
Chemoautotrophs - Food chain can be short or long
- include nitrogen fixing bacteria located depending on the number of
in the soil, iron oxidizing bacteria consumers involved.
located in the lava beds, and sulfur - Food chain is a pattern in nature in w/c
oxidizing bacteria located in deep sea living things eat and are eaten by
thermal vents. other living things.
Autotrophs - makes their own food - Food chains follow a single path as
Heterotrophs - gets energy from food they animals eat each other.
eat.
Saprotrophs - Get their food from dead
decaying matters ex: Fungi and yeast
Scavenger
- Eat dead animal for energy
- Starts the decomposing process
- Large animals and makes foods for
decomposers.
Decomposer
- Get energy by breaking down remains
of dead organisms
- Smaller organism
- Make nutrients for plants and animals
FOOD WEB
Feeding Relationship and Trophic Level
- consists of all the food chains in a
- Plants and animals are linked closely
single ecosystem.
in a food chain.
- Each living thing in an ecosystem is
- Food chain is formed when plants
part of multiple food chains
(producers) are eaten by animals
- All of the interconnected and
(herbivores) and these herbivores are
overlapping food chains in an
eaten by other animals called
ecosystem make up a food web.
carnivores.
You might also like
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Principles and Concept of EcosystemDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Concept of EcosystemJay Bianca Abera Alistado100% (1)
- LecturesDocument11 pagesLecturesMariel CampomanesNo ratings yet
- STS M4Document2 pagesSTS M4Jocel Rose TorresNo ratings yet
- ATE BINGmodule in ECOLOGYDocument7 pagesATE BINGmodule in ECOLOGYJaypeeRuizSomeraNo ratings yet
- 1st PPT - Forest EcologyDocument87 pages1st PPT - Forest EcologyMia KhufraNo ratings yet
- MST1 MidtermsDocument15 pagesMST1 MidtermsJam DomingoNo ratings yet
- Envisci ReviewerDocument16 pagesEnvisci ReviewerRosPapNo ratings yet
- Attributes-to-ecosystem-and-biodiversityDocument8 pagesAttributes-to-ecosystem-and-biodiversityGORDO, JANELLE L.No ratings yet
- Ge Elec 1 Prelim Reviewer: Module 1: Introduction To Ecosystem ECOSYSTEM First Appeared in ADocument11 pagesGe Elec 1 Prelim Reviewer: Module 1: Introduction To Ecosystem ECOSYSTEM First Appeared in AJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument23 pagesEnvi SciJeanelle Ledesma MarabutNo ratings yet
- 4.1 To 4.4 Ecosystems, Energy & Carbon Cycle (2023)Document147 pages4.1 To 4.4 Ecosystems, Energy & Carbon Cycle (2023)riorivfunNo ratings yet
- Biology Term 4Document6 pagesBiology Term 4ghfh9mn5f6No ratings yet
- Populations and CommunitiesDocument4 pagesPopulations and CommunitiesISABELITANo ratings yet
- Envisci Module 1 7Document11 pagesEnvisci Module 1 7Ruth MuldongNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM CONNECTIONSDocument86 pagesECOSYSTEM CONNECTIONSvishalNo ratings yet
- Envisci L3Document4 pagesEnvisci L3Hency Dapolano BautistaNo ratings yet
- PLNG Bwu PnyaDocument8 pagesPLNG Bwu Pnya1931989No ratings yet
- Ecology Review NotesDocument6 pagesEcology Review NotesMaKylah ClevelandNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument22 pagesExam 1 Study GuideoreldysNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - environmental sciencesDocument32 pagesTopic 1 - environmental sciencesJomari TawatNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE KEY TERMSDocument20 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE KEY TERMSFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Ecological RelationshipDocument19 pagesEcological RelationshipJoy PedrosaNo ratings yet
- 02 EcosystemDocument80 pages02 EcosystemNiladri BiswasNo ratings yet
- Week004 The EcosystemDocument6 pagesWeek004 The EcosystemEthan RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Components and InteractionsDocument31 pagesEcosystem Components and InteractionsBirraa TajuNo ratings yet
- EVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023Document11 pagesEVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023prakashnisha9741No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Ecological SystemDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Ecological SystemJudyAnIntongQuiroyNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology: Key Topics for Nutrition, Ecosystems & ClassificationDocument43 pagesCSEC Biology: Key Topics for Nutrition, Ecosystems & ClassificationMarcellus Lee100% (1)
- Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesOur Environmentraimaali220077No ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument2 pagesBiodiversityAkeisha PascuaNo ratings yet
- CPT 31Document7 pagesCPT 31Precious Collantes Quarteroz100% (1)
- Food ChainsDocument7 pagesFood ChainsAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Ecology HandoutDocument6 pagesEcology HandoutGabrielle Morgan100% (1)
- Concepts of The EcosystemDocument4 pagesConcepts of The EcosystemsandovalcelestineNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: An Ecosystem Is A Geographic AreaDocument9 pagesEcosystem: An Ecosystem Is A Geographic AreaAvon NayapalNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes!!Document10 pagesEcology Notes!!Raudha Athif100% (3)
- Ge Elect 103 Environmental Science: Amabel Marina C. Marcaida, Mase Assistant Professor 3Document22 pagesGe Elect 103 Environmental Science: Amabel Marina C. Marcaida, Mase Assistant Professor 3Paula Bianca DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EnviDocument8 pagesModule 1 EnviJimuel LadaoNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument67 pagesEnvironmental Studiesshu100% (1)
- Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEcosystems and BiodiversityRahul67% (3)
- Lesson 7 - EcosystemDocument28 pagesLesson 7 - EcosystemCRIS EDISON VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Definition PDFDocument2 pagesEcosystem Definition PDFJonas TenederoNo ratings yet
- Biotic, Abiotic, Ecological RelationshipDocument57 pagesBiotic, Abiotic, Ecological RelationshipSarah Mae Lequin ManzanasNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Functions by Prof AK YadavaDocument103 pagesEcosystem Functions by Prof AK Yadavabirudulavinod1No ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Ecological Concept: Prepared By: Dr. Arnel B. BeltranDocument32 pagesLesson 2: Ecological Concept: Prepared By: Dr. Arnel B. BeltranAlyssa Beatrice CuevoNo ratings yet
- Topic-2-EcologyDocument10 pagesTopic-2-EcologyJomari TawatNo ratings yet
- Biology: Chapter 1 Invitation To BiologyDocument9 pagesBiology: Chapter 1 Invitation To Biologyamstrghtr94No ratings yet
- 02 EcosystemDocument80 pages02 EcosystemHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life and Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Life and Earth ScienceRalph Francis GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesEcology Lecture NotesMarton Emile DesalesNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 CHY1002 TH VL2021220504796 Reference Material I 14-02-2022 KGS-EVSc-Module1Document164 pagesWINSEM2021-22 CHY1002 TH VL2021220504796 Reference Material I 14-02-2022 KGS-EVSc-Module1Captain ThejaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument27 pagesEnvironmental ScienceArijit SamantaNo ratings yet
- Unit II - ECOSYSTEMDocument56 pagesUnit II - ECOSYSTEMthusharaNo ratings yet
- 02 EcosystemDocument81 pages02 EcosystemSyed Mohd Raza TaqviNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering Module 1Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering Module 1Pamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document20 pagesUnit 1050 Shubham SainiNo ratings yet
- 11-Ecology Notes PDFDocument41 pages11-Ecology Notes PDFShubham MandalNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes: Species, Populations, Communities, EcosystemsDocument41 pagesEcology Notes: Species, Populations, Communities, EcosystemsManish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Basic CourseDocument97 pagesBasic CourseAhmed KhairyNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument11 pages1 PB PDFaldo surya pratamaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Acid-Related Disorders - SeminarDocument40 pagesTreatment of Acid-Related Disorders - SeminarZana Mohammed0% (1)
- CerebrumDocument26 pagesCerebrumsanthiyasandy100% (1)
- Cascade Control: 25.1 Master and Slave LoopsDocument10 pagesCascade Control: 25.1 Master and Slave Loopsdeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- SynonymsDocument14 pagesSynonymsMursal IbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Telangana Govt T-PRIDE Scheme GuidelinesDocument90 pagesTelangana Govt T-PRIDE Scheme GuidelinesitzprasuNo ratings yet
- ASME B36.10M-2004 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe StandardDocument2 pagesASME B36.10M-2004 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe StandardAmit BansalNo ratings yet
- Official All Things Turmeric PPT GuidebookDocument14 pagesOfficial All Things Turmeric PPT Guidebookapi-507527047No ratings yet
- Villamor Test - 2 PDFDocument18 pagesVillamor Test - 2 PDFLocrian IonianNo ratings yet
- Hooded Scarf Project From Warm Knits, Cool GiftsDocument4 pagesHooded Scarf Project From Warm Knits, Cool GiftsCrafterNews33% (3)
- Predicting Iron Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials With Arbitrary Voltage Supply An Engineering ApproachDocument9 pagesPredicting Iron Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials With Arbitrary Voltage Supply An Engineering Approachmayur isameNo ratings yet
- Aryatech Brochure IndiaDocument12 pagesAryatech Brochure IndiaHari RamNo ratings yet
- IC TDA-11115, TDA-11145 Service Manual enDocument24 pagesIC TDA-11115, TDA-11145 Service Manual enJeank Rivadeneyra50% (2)
- Structural Dyanmics-Anna University Q PaperDocument7 pagesStructural Dyanmics-Anna University Q PaperVijay AravindNo ratings yet
- ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 5 (2022) 367-379 PDFDocument13 pagesACS Appl. Energy Mater. 5 (2022) 367-379 PDFEdgar QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- McMahan Transpositions of Metaphor and Imagery in The Ga Avyūha and Tantric Buddhist PracticeDocument14 pagesMcMahan Transpositions of Metaphor and Imagery in The Ga Avyūha and Tantric Buddhist PracticeAnthony TribeNo ratings yet
- Christopher Pelling (Ed.) - Greek Tragedy and The Historian - Oxford University Press, USA (1997)Document278 pagesChristopher Pelling (Ed.) - Greek Tragedy and The Historian - Oxford University Press, USA (1997)rmvicentin100% (1)
- Aashto Lane Width PDFDocument1 pageAashto Lane Width PDFnywd806033No ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C03Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- Proposal For Mining Skill TrainingDocument31 pagesProposal For Mining Skill Trainingdwarka prasad100% (1)
- Cerebral PalsyDocument24 pagesCerebral PalsyUday Kumar100% (1)
- (Elsevier) The Influence of Circumferential Weld-Induced Imperfections On The Buckling of Silos ADocument12 pages(Elsevier) The Influence of Circumferential Weld-Induced Imperfections On The Buckling of Silos AMateo PaladinoNo ratings yet
- Fmea PC ProcessDocument2 pagesFmea PC Processsudeep_singh1No ratings yet
- Katalog Single Split Packaged AC 2015-2016 PanasonicDocument32 pagesKatalog Single Split Packaged AC 2015-2016 Panasonicdoris0% (1)
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument7 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelQuicksilverNo ratings yet
- Rev Quiz All PDFDocument46 pagesRev Quiz All PDFNota Belz82% (17)
- Is 1726 1991Document17 pagesIs 1726 1991RaykochiNo ratings yet
- Biosystems Engineering BS CurriculumDocument2 pagesBiosystems Engineering BS CurriculumAsiiimweNo ratings yet
- Kumiko Jigs Japanese Woodworking PDFDocument9 pagesKumiko Jigs Japanese Woodworking PDFJaime Montiel100% (1)