Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics of Investment 6
Uploaded by
Gerico MagbagOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics of Investment 6
Uploaded by
Gerico MagbagCopyright:
Available Formats
MATHEMATICS OF INVESTMENT
MODULE NO. 6
A. LESSON
LEARNING OBJECTIVE TOPIC
• Solve worded problems on • Amortization
amortization.
B. DISCUSSION
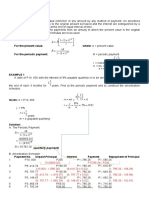
Amortization is a means of repaying a debt by series of equal payments at equal time interval.
The periodic payments form an annuity in which the present value is the principal of an interesting-
bearing debt. Hence we use the following annuity formulas:
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
𝐴 = 𝑅( )
𝑖
𝐴𝑖
𝑅=
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
Where: A – principal
R – periodic payment
i – interest per period
n – total number of payments periods
Examples:
1. An obligation of P21,000 with interest of 8% compounded semi-annually must be paid at the
end of every 6 months for 4 years.
a. Find the size of periodic payment.
b. Find the remaining liability just after making the 5th payment.
c. Prepare the amortization table.
SOLUTION:
A = P21,000 m = 2 i = 0.04 j = 8% t = 4 years n=8
a. Find the size of periodic payment.
𝐴𝑖
𝑅=
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
(21,000)(0.04)
𝑅= = 𝑷𝟑, 𝟏𝟏𝟗. 𝟎𝟖
1 − (1 + 0.04)−8
MODULE NO.6: MATHEMATICS OF INVESTMENT A.Y. 2021-2022
Page 1 of 4
b. Find the remaining liability just after making the 5th payment.
The remaining liability after the 5th payment is the present value of the remaining periodic
payments.
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
𝐴 = 𝑅( )
𝑖
1 − (1 + 0.04)−3
𝐴 = 3,119.08 ( ) = 𝑷𝟖, 𝟔𝟓𝟓. 𝟕𝟑
0.04
d. Amortization schedule.
Period Balance Payment Interest Paid Payment for
Principal
1 P21,000.00 P3,119.18 P840.00 P2,279.08
2 18,720.92 P3,119.18 748.84 2,370.24
3 16,350.68 P3,119.18 654.03 2,465.05
4 13,885.63 P3,119.18 555.43 2,563.65
5 11,321.98 P3,119.18 452.88 2,666.20
6 8,655.78 P3,119.18 346.23 2,772.85
7 5,882.93 P3,119.18 235.31 2,883.76
8 2,999.16 P3,119.18 119.97 2,999.11
Total P24,952.64 P3,953.10 P21,000*
*The actual value is P20,999.94. This is due to rounding error.
Discussion of the amortization table.
First Column: PERIOD
This pertains to the number of payments indicated in the problem.
Second Column: BALANCE
MODULE NO.6: MATHEMATICS OF INVESTMENT A.Y. 2021-2022
Page 2 of 4
The first balance is the amount of the principal. The second amount in the balance
column can be computed by subtracting the Payment for principal from the previous balance.
Ex: P21,000 – 2,279.08 = P18,720.92
P18,720.92 – 2,370.24 = P16,350.68
Third Column: PAYMENT
This is the computed periodic payment.
Fourth Column: INTEREST PAID
This is computed by multiplying the balance by the value of i.
Ex: P21,000 x 0.04 = P840
P18,720.92 x 0.04 = P748.84
Fifth Column: PAYMENT FOR PRINCIPAL
This is computed by subtracting the INTEREST PAID from the PAYMENT.
Ex: P3,119.08 – 840 = P2,279.08
P3,119.08 – 748.84 = P2,370.24
The total for the last column which is the PAYMENT FOR THE PRINCIPAL should be
equal to the given principal in the problem.
C. REFERENCES
Young, F. (2009). Mathematics of Investment Made Simple. Rex Book Store
Sirug, W. (2014). Mathematics of Investment. Mindshapers Co., Inc.
Altares, P. et. al., (2007). Mathematics of Investment. Rex Book Store
MODULE NO.6: MATHEMATICS OF INVESTMENT A.Y. 2021-2022
Page 3 of 4
Name: Year/Program/Major: Score:
D. EVALUATION
Answer the following:
1. A debt of P70,000.00 with 8% converted quarterly must be paid at the end of every 3 months
for 3 years.
a. Find the size of each payment.
b. Find the remaining liability after the 4th payment.
c. Construct the amortization schedule.
2. Nikko borrows a certain sum with interest at 9% compounded semi-annually. The obligation
will be discharged by paying P7,000 every end of 6 months for 4 years.
a. What is the present value of Nikko’s debt?
b. How much of his 3rd payment is interest and how much goes to repayment of principal?
c. Prepare the amortization table.
3. A loan of P140,000 bearing a 15% interest converted annually is to be amortized with equal
yearly payments for 10 years.
a. Find the size of each payment.
b. What should the outstanding liability be just after 4th payment?
c. Construct the amortization schedule.
4. Aster borrows P360,000. She plans to amortize her debt with equal quarterly payments for 2
years. Interest is allowed at 11% converted quarterly.
a. Find the quarterly cost of her debt.
b. By how much is the debt reduced by the 3rd payment?
c. Construct the amortization schedule.
5. A loan of P100,000 with interest at 10% converted quarterly will be settled by paying P12,000
at the end of every 3 months.
a. How many payments amounting P12,000 will be made?
b. What final smaller payment is needed?
c. Construct the amortization schedule.
MODULE NO.6: MATHEMATICS OF INVESTMENT A.Y. 2021-2022
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- E.eco. Module 6 Amortization and Sinking FundsDocument8 pagesE.eco. Module 6 Amortization and Sinking FundsjemjemgarciaaNo ratings yet
- 8B Financial Mathematics (B)Document17 pages8B Financial Mathematics (B)enn ennNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment FinalsDocument78 pagesMathematics of Investment FinalsLuisa Mae N. MahenerNo ratings yet
- Skinning FundsDocument12 pagesSkinning FundsNehemia T MasiyaziNo ratings yet
- BM2.MOD4 HandoutDocument9 pagesBM2.MOD4 HandoutPollie Jayne ChuaNo ratings yet
- MATH103-ch5 and chp7Document53 pagesMATH103-ch5 and chp7merlin otemakumiNo ratings yet
- MOI Chapter IV Amortization and Sinking Funds UpdatedDocument23 pagesMOI Chapter IV Amortization and Sinking Funds UpdatedGabriel LagranaNo ratings yet
- MOI Lesson FinalsDocument78 pagesMOI Lesson FinalsPie CanapiNo ratings yet
- MOI - Chapter IV - Amortization and Sinking Funds - UpdatedDocument23 pagesMOI - Chapter IV - Amortization and Sinking Funds - UpdatedPatricia MallariNo ratings yet
- FINMAN1 Module5Document10 pagesFINMAN1 Module5Jayron NonguiNo ratings yet
- Week 4 General Annuity Take AwayDocument9 pagesWeek 4 General Annuity Take AwayJohn Daniel AntolinNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Simple and Compound InterestsDocument22 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Simple and Compound InterestsEldon Kim RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Online Corporate Finance I Practice Exam 1 SolutionDocument14 pagesOnline Corporate Finance I Practice Exam 1 SolutionTien DuongNo ratings yet
- Amortization and Sinking FundsDocument46 pagesAmortization and Sinking FundssaneconNo ratings yet
- MOI 4.1 Amort and SFDocument11 pagesMOI 4.1 Amort and SFBaekhyun ByunNo ratings yet
- I I R A Ia R J: Lesson 4: AmortizationDocument4 pagesI I R A Ia R J: Lesson 4: AmortizationArcanus LorreynNo ratings yet
- Math of FinanceDocument10 pagesMath of FinanceJhon Mhark GarinNo ratings yet
- CMP Lecture 7 Construction EconomicsDocument22 pagesCMP Lecture 7 Construction EconomicsGebriel UbananNo ratings yet
- 8 Simple InterestDocument19 pages8 Simple InterestMsloudy VilloNo ratings yet
- 8 Simple InterestDocument19 pages8 Simple Interestdhaniro.salinasNo ratings yet
- N 228, PV - $1,100, FV $13,438 Compute I: Solutions To TVM Practice Set IIDocument5 pagesN 228, PV - $1,100, FV $13,438 Compute I: Solutions To TVM Practice Set IIMohamedNo ratings yet
- Math 108 Chapter 4 Amortization and Sinking FundDocument6 pagesMath 108 Chapter 4 Amortization and Sinking FundMary Jane Aguinaldo100% (2)
- Present Value of An Annuity Amortization (3.4)Document11 pagesPresent Value of An Annuity Amortization (3.4)wanderingbutterflyNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 53 stacksNo ratings yet
- GM Q4 LAS-16 (Week4)Document8 pagesGM Q4 LAS-16 (Week4)Ymma Bravo MalanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Financial MathematicsDocument23 pagesLecture 2 Financial MathematicsAlexis ParrisNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Brooks, (2013) Chapters 3, 4Document49 pagesTime Value of Money: Brooks, (2013) Chapters 3, 4DiannaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: I.2 Learning ActivitiesDocument6 pagesGeneral Mathematics: I.2 Learning ActivitiesAndrea InocNo ratings yet
- 5mfz SampleDocument46 pages5mfz SampledutersNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Amortization and Sinking FundDocument24 pagesLesson 5 Amortization and Sinking FundEdgardo SeriloNo ratings yet
- Note Amort ExampleDocument27 pagesNote Amort ExampleSukmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of InvestmentsDocument9 pagesMathematics of InvestmentsJohndee Mozart Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Q2 Week 4 1Document11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Q2 Week 4 1Santos, Mart Czendric Y.No ratings yet
- Math 11 Gen Math Q2-Week 3Document20 pagesMath 11 Gen Math Q2-Week 3Eloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Business Math: Interest On Mortgage, Amortization, Services, Utilities, Deposits, and LoansDocument12 pagesBusiness Math: Interest On Mortgage, Amortization, Services, Utilities, Deposits, and Loansmikasa ackerman100% (1)
- Chapter-5-Annuity-Due FinalDocument29 pagesChapter-5-Annuity-Due Finaledwin dumopoy100% (1)
- LAS 6 InterestsDocument6 pagesLAS 6 Interestschad lowe villarroyaNo ratings yet
- 5 3 NotesDocument7 pages5 3 Notesapi-301176378No ratings yet
- Simple and Compound Interest-NotesDocument30 pagesSimple and Compound Interest-NotesTrexie MerivelesNo ratings yet
- L1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesL1 Introductionwhyvictoria0812No ratings yet
- The Time Value of Money - Annuities and Other TopicsDocument78 pagesThe Time Value of Money - Annuities and Other TopicsTaqiya NadiyaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Peirson 11e CH 3Document24 pagesBusiness Finance Peirson 11e CH 3RitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Amortization and NPVDocument3 pagesLecture 7 - Amortization and NPVChristin Me LocsinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Finance: Section 4 Present Value of An Annuity AmortizationDocument20 pagesMathematics of Finance: Section 4 Present Value of An Annuity AmortizationHAFIAZ MUHAMMAD IMTIAZNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Simple and Compound InterestsDocument21 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Simple and Compound InterestsThegame1991ususus100% (1)
- Sinking Fund and Amortization: OP PMT X IDocument10 pagesSinking Fund and Amortization: OP PMT X IKhevin NetflixNo ratings yet
- MATHINVS - Simple Annuities 3.3Document10 pagesMATHINVS - Simple Annuities 3.3Kathryn SantosNo ratings yet
- Genmath Q2 W1-8Document60 pagesGenmath Q2 W1-8lui yangyangNo ratings yet
- Maths Final orDocument5 pagesMaths Final ortemedebereNo ratings yet
- Ps Bonds SolutionsDocument20 pagesPs Bonds SolutionsnazNo ratings yet
- 7.-SLM Bus - Math Q1 W9Document11 pages7.-SLM Bus - Math Q1 W9Sir AronNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument49 pagesTime Value of MoneyAlison ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: University of Eastern Philippines College of EngineeringDocument34 pagesEngineering Economy: University of Eastern Philippines College of EngineeringFrqnz AyasivNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Simple InterestsDocument7 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Simple InterestsClaire BalatucanNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument6 pagesAnnuitymasyatiNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Document15 pagesBusiness Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Divina Grace Rodriguez - Librea100% (1)
- Amortisations and Sinking FundsDocument7 pagesAmortisations and Sinking FundsChari TawaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document65 pagesChapter 4WK LamNo ratings yet