Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anomalies of The Placenta and Umbilical Cord
Uploaded by
Ayessa D. Rosalita100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
19 views2 pagesThe document summarizes several common anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord, including placenta succenturiata (extra lobes), placenta circumvallata (chorion covering), battledore placenta (off-center cord insertion), velamentous cord insertion, vasa previa (blood vessels under cervix), short and long umbilical cords, umbilical cord knot, and nuchal cord (cord around neck). Many of these anomalies can lead to complications for the fetus such as bleeding, distress, growth restriction, and mortality. The placenta and cord are always examined after birth to check for any anomalies.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anomalies-of-the-placenta-and-umbilical-cord
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes several common anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord, including placenta succenturiata (extra lobes), placenta circumvallata (chorion covering), battledore placenta (off-center cord insertion), velamentous cord insertion, vasa previa (blood vessels under cervix), short and long umbilical cords, umbilical cord knot, and nuchal cord (cord around neck). Many of these anomalies can lead to complications for the fetus such as bleeding, distress, growth restriction, and mortality. The placenta and cord are always examined after birth to check for any anomalies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
19 views2 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and Umbilical Cord
Uploaded by
Ayessa D. RosalitaThe document summarizes several common anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord, including placenta succenturiata (extra lobes), placenta circumvallata (chorion covering), battledore placenta (off-center cord insertion), velamentous cord insertion, vasa previa (blood vessels under cervix), short and long umbilical cords, umbilical cord knot, and nuchal cord (cord around neck). Many of these anomalies can lead to complications for the fetus such as bleeding, distress, growth restriction, and mortality. The placenta and cord are always examined after birth to check for any anomalies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
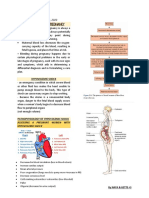
Anomalies of the Placenta
Anomalies of the Placenta
• The placenta and cord are always examined for the 3. Battledore Placenta The cord is inserted
presence of anomalies after birth. marginally rather than centrally.
• The normal placenta weighs approximately 500 g
Signs and Symptoms Complications
and is 15 to 20 cm in diameter and 1.5 to 3.0 cm
• Vaginal bleeding • Fetal distress
thick. • Low amniotic fluid • Low birth weight
• Its weight is approximately one sixth that of the • Preterm Labor
fetus.
• A placenta may be unusually enlarged in women
with diabetes. 4. Velamentous Insertion of the Cord
• In certain diseases, such as syphilis or Is a situation in which the cord, instead of
erythroblastosis, the placenta may be so large that entering the placenta directly, separates into
it weighs half as much as the fetus. small vessels that reach the placenta by
• If the uterus has scars or a septum, the placenta spreading across a fold of amnion.
may be wide in diameter because it was forced to
Signs and Symptoms Complications
spread out to find implantation space.
• PROM • Fetal distress
Anomalies of the Placenta • Vaginal bleeding • Intrauterine growth
• Low birth weight restriction (IUGR)
1. Placenta Succenturiata: Placenta
Succenturiata is a placenta that has one or more
5. Vasa Previa The umbilical vessels of a
accessory lobes connected to the main placenta by
velamentous cord insertion cross the Cervical OS
blood vessels.
and therefore deliver before the fetus.
Signs and Symptoms Complications
Signs and Symptoms Complications
• Vaginal bleeding • Increase Maternal
• PROM • Fetal hemorrhage
• Abdominal pain Mortality and Morbidity
• Vaginal bleeding • Chorioamnionitis
• Preterm Labor • Postpartum Hemorrhage
• Low birth weight • Respiratory distress
• Postpartum Infection
syndrome
2. Placenta Circumvallata The fetal side of the
placenta is covered to some extent with chorion. The 5. Vasa Previa Is an unusually deep
umbilical cord enters the placenta at the usual attachment of the placenta to the uterine
midpoint, and large vessels spread out from there. myometrium so deeply the placenta will not
loosen and deliver.
Signs and Symptoms Complications
• Vaginal bleeding • No abnormalities were Signs and Symptoms Complications
• Inhibited fetal growth associated but presence • PROM • Fetal hemorrhage
• Premature rupture of should be noted. • Vaginal bleeding • Chorioamnionitis
membrane • Low birth weight • Respiratory distress
syndrome
Anomalies of the Umbilical Cord
omalieof the
• Umbilical cord connects the baby to the mother’s Umbilical Cord Knot
placenta. Definition: An umbilical cord knot happens when
• It contains three vessels which are two arteries and your baby moves around in a manner that
one vein (AVA). causes a loop in the cord as if it were tied.
Signs and Symptoms Complications
• Decreased fetal movement • Fetal Distress
Anomalies of the Umbilical Cord • Abnormal fetal heart rate • Low birth
• Meconium-stained weight
amniotic fluid • Infant
1. Two Vessel Cord: Two Vessel Cord or Single mortality
Umbilical Artery is an umbilical anomaly in which
there is an absence of one umbilical artery
surrounding the fetal bladder.
Signs and Symptoms Complications
• There aren't any • Low birth weight
signs or symptoms • Trisomy 18
associated with the • Infant mortality
condition.
2. Unusual Cord Length:
• Normal cord length is 30-70cm, averagely 50cm
• Short cord: <30cm is defined as short cord, may
lead to fetal distress, placental abruptio, prolonged
labor
• Long cord: >80cm is defined as long cord, higher
occurrence of cord around neck, cord around
body, cord knot, cord prolapse and cord
compression.
Nuchal Cord
Definition: This happens when the baby’s umbilical
cord wraps around their neck or body.
Signs and Symptoms Complications
• Decreased fetal movement • Infant mortality
• Abnormal fetal heart rate • Fetal distress
• Meconium-stained • Meconium
amniotic fluid. aspiration
You might also like
- Labor and Delivery TopicsDocument44 pagesLabor and Delivery TopicsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- CHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramDocument3 pagesCHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramCassey Anne100% (1)
- Degree of Question Difficulty 4 3 2Document13 pagesDegree of Question Difficulty 4 3 2icy431No ratings yet
- Physiology of ParturitionDocument85 pagesPhysiology of ParturitionDark MomentzNo ratings yet
- Community DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCommunity DiagnosisFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Ob 100 RatioDocument13 pagesOb 100 RatioJUANJOSEFOXNo ratings yet
- Fetal MalpresentationDocument83 pagesFetal MalpresentationArianJubaneNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Lec 3 - The High Risk Prenatal ClientDocument16 pagesNCM 108 - Lec 3 - The High Risk Prenatal ClientNicole TomlinsonNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference?: EINC (Ma'am Nera Galan)Document2 pagesWhat Is The Difference?: EINC (Ma'am Nera Galan)Angeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- Physical and Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument35 pagesPhysical and Physiological Changes in PregnancyAYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Test Drill OBDocument8 pagesTest Drill OBViviane Ńíáshéè Basod100% (1)
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument39 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRena VilNo ratings yet
- 1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraDocument9 pages1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraGrace OrdameNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections StisDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Stisapi-646865632No ratings yet
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument8 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Three Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal DevelopmentmellowlilydeeNo ratings yet
- OB Exam 11 A AnswerDocument14 pagesOB Exam 11 A AnswerDianeNo ratings yet
- (OBS) 3.08b Sexually Transmitted Diseases in Pregnancy - Bongala (Nov 30)Document18 pages(OBS) 3.08b Sexually Transmitted Diseases in Pregnancy - Bongala (Nov 30)Gerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting Pregnancy: (Tuberculosis & STD)Document64 pagesDiseases Affecting Pregnancy: (Tuberculosis & STD)Cyrelle Jen TorresNo ratings yet
- Complications in PregnancyDocument81 pagesComplications in PregnancyTia TahniaNo ratings yet
- 3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborDocument105 pages3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesFetal Growth and DevelopmentAngel Shaina VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NCM 237-Course-OutlineDocument2 pagesNCM 237-Course-OutlineKhibul LimNo ratings yet
- 107 Answer KeyDocument8 pages107 Answer KeyKryzza LeizellNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument23 pagesABORTIONCristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- MalpresentationDocument37 pagesMalpresentationLovely SarangiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Action (10 Files Merged)Document277 pagesAbnormal Uterine Action (10 Files Merged)Liji GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing (PIH, GDM, HELLP Syndrome, Eclampsia and Pre-Eclampsia)Document6 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing (PIH, GDM, HELLP Syndrome, Eclampsia and Pre-Eclampsia)PAULINE BERNICE BAGUIONo ratings yet
- FC Insertion and RemovalDocument30 pagesFC Insertion and RemovalAngel Alexa Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Internal Examination: Leslie L. Paguio BSN 3-CDocument26 pagesInternal Examination: Leslie L. Paguio BSN 3-CLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaDocument72 pagesPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaEsa SthaNo ratings yet
- ObgynDocument14 pagesObgynJan Crizza Dale R. Franco100% (1)
- Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument70 pagesIntrapartal ComplicationsRose AnnNo ratings yet
- 3 (OB Cases)Document267 pages3 (OB Cases)Sharyl Plan SarominesNo ratings yet
- September 2023 Part 3Document238 pagesSeptember 2023 Part 3Fatinha Lucia FC Pinto100% (1)
- First Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionDocument4 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- Fetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnDocument21 pagesFetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnEsther Ellise Abundo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingLei Ortega68% (25)
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument4 pagesBleeding During PregnancyCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- High Risk Prenatal CareDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Prenatal CareKatherine Gayle GuiaNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument14 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyJezrael PueblosNo ratings yet
- Elzohry+Exam LabsDocument88 pagesElzohry+Exam Labsnaira100% (5)
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument74 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageApex College of Nursing100% (1)
- High - Risk PregnancyDocument110 pagesHigh - Risk PregnancyAndre DityaNo ratings yet
- NCM QuizDocument7 pagesNCM QuizKyla Marie NabongNo ratings yet
- 18 - Oligohydramnios and PolyhydramniosDocument3 pages18 - Oligohydramnios and PolyhydramniosSu OoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Management (Part 4)Document17 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 4)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- MCNDocument12 pagesMCNIan CarodanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument20 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Management (Part 5)Document36 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 5)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Midwifery CurriculumDocument2 pagesMidwifery Curriculuminvictus044650% (2)
- Obstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Document12 pagesObstructed Labor: Basliel E. (MD)Asteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- MalpresentationDocument19 pagesMalpresentationHanelie B. AldeaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric NursingDocument2 pagesObstetric NursingKaren Joyce Costales Magtanong100% (1)
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument92 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentMelissa Diego-sarmiento100% (1)
- Skills Delivery TeachingDocument84 pagesSkills Delivery TeachingRandyNo ratings yet
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocument6 pagesPostpartum ComplicationsALCANTARA ALYANNANo ratings yet
- MCP NCP Benefits SlidesDocument13 pagesMCP NCP Benefits SlidesJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Operative ObstetricsDocument4 pagesOperative Obstetricssarguss14100% (3)
- Mcn. ReviewerDocument18 pagesMcn. ReviewerjeyNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Rle ClinicalDocument20 pagesNCM 109 Rle ClinicalBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Fanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- How Do Organism ReproduceDocument40 pagesHow Do Organism ReproduceNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Empowering Growing Families With Affordable Fertility TreatmentsDocument9 pagesEmpowering Growing Families With Affordable Fertility TreatmentsOma FertilityNo ratings yet
- CasesDocument37 pagesCasesZakaria FarahNo ratings yet
- ANM SyllabusDocument9 pagesANM SyllabusMonica ZineNo ratings yet
- Star PackageDocument24 pagesStar PackagePrsdeepNo ratings yet
- Montero, Karen Patricia P. - Legal OpinionDocument8 pagesMontero, Karen Patricia P. - Legal OpinionKaren MonteroNo ratings yet
- Morning Report 9-9-14Document9 pagesMorning Report 9-9-14Rian Segal HidajatNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term Biology Note For WK 8 - WK 10 Grade 11.Document23 pages1ST Term Biology Note For WK 8 - WK 10 Grade 11.Adeola YusufNo ratings yet
- KHFA 2018 19 Popular Version Report FinalDocument96 pagesKHFA 2018 19 Popular Version Report FinalgramedincNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument9 pagesAbortionmendato marcabanNo ratings yet
- Safe Sex Is The Best Sex PowerpointDocument21 pagesSafe Sex Is The Best Sex Powerpointapi-284351148No ratings yet
- Saint Louis University School of Nursing: Combined Injectable Contraceptives NCM 107A-RDDocument8 pagesSaint Louis University School of Nursing: Combined Injectable Contraceptives NCM 107A-RDKyle FelixNo ratings yet
- Nlna 301-360Document133 pagesNlna 301-360Sashi0% (1)
- Benign Gynecologic LesionsDocument10 pagesBenign Gynecologic LesionsJefelson Eu Palaña NahidNo ratings yet
- Embryo Transfer: Paula Curtin Paula - Curtin@mtu - IeDocument12 pagesEmbryo Transfer: Paula Curtin Paula - Curtin@mtu - IePaula SteeleNo ratings yet
- Bab 15 T4Document7 pagesBab 15 T4annurkhaliesyaqaisaraNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffIvory PlatypusNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 GE-USDocument6 pagesUnit 2 GE-USAlgin ArolladoNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of The RH LawDocument1 pageSWOT Analysis of The RH LawAsirante LumenNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12 - EditedDocument17 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12 - Editedharveylenseena2006No ratings yet
- Applied Nutritionppt Unit 1Document42 pagesApplied Nutritionppt Unit 1zia urrehmanNo ratings yet
- Mpharm Year 2 Gastrointes Nal Tract Example MCQ'SDocument8 pagesMpharm Year 2 Gastrointes Nal Tract Example MCQ'SManish JainNo ratings yet
- GE Voluson E10 Ultrasound Machine Brochure 2Document9 pagesGE Voluson E10 Ultrasound Machine Brochure 2Carlos GarciaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument94 pagesEndocrineSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction-L11 (2.0)Document78 pagesHuman Reproduction-L11 (2.0)Upal PramanickNo ratings yet
- SynchronizationDocument15 pagesSynchronizationShahzad Hur BalouchNo ratings yet