Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science and Technology
Science and Technology
Uploaded by
Rudra Kumar VermaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science and Technology
Science and Technology
Uploaded by
Rudra Kumar VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
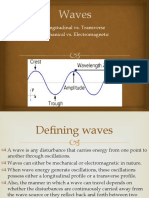
WAVE
Wave is a disturbance.
Waves are of two types-
Mechanical- Need a medium to travel. (Solid, liquid, gas) Ex- Sound waves
Non-Mechanical- No medium required. Can travel in vacuum. Ex- Light
Mechanical waves are of two types-
Transverse waves- Transverse waves cause the medium to move perpendicular to the
direction of the wave. Ex- Wave in string.
Longitudinal waves- Longitudinal waves cause the medium to move parallel to the
direction of the wave. Ex- Sound waves
Sound-
Mechanical longitudinal wave.
Solid>Liquid>Gas
5300>1500>332 m/s
Stiffness is directly proportional to speed.
Density ( V=1/√d)
Al>Fe>Au
Speed is directly proportional to temperature.
Speed is directly proportional to humidity.
Pressure has no effect.
0 degree- 332m/s
22
Wavelength- Wavelength is the distance between identical points (adjacent crests) in the
adjacent cycles of a waveform signal propagated in space or along a wire.
Frequency- Number of oscillations per unit time. (f) or (v)
Time period- T=1/f.
Amplitude- Amplitude, in physics, the maximum displacement or distance moved by a point
on a vibrating body or wave measured from its equilibrium position. It is equal to one-half
the length of the vibration path.
Audible frequency- 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
Below 20 Hz- Infrasound
Above 20000 Hz- Ultrasonic
You might also like
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer in ScienceJosh Deinille ManarinNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Waves NotesDocument23 pagesCharacteristics of Waves Notesapi-449002661No ratings yet
- Chapter 71 Simple Harmonic Motion and WavesDocument6 pagesChapter 71 Simple Harmonic Motion and WavesasdfNo ratings yet
- MY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesDocument12 pagesMY SO Waves Notes Powerpoint - Property of WavesFirdaus Kamal BahrinNo ratings yet
- Vakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodDocument21 pagesVakev Physics Term 2 L5 Els&sodvigiraneza0No ratings yet
- A Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesDocument5 pagesA Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesMercy PaduaNo ratings yet
- Waves - Lecture 1Document45 pagesWaves - Lecture 1Hisham MohamedNo ratings yet
- Wave TermsDocument1 pageWave TermsMary Rose RemedioNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument46 pagesWave Motionalingig.cleonnyNo ratings yet
- Waves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDocument40 pagesWaves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingGellirose S. Bantayan100% (1)
- WavesDocument21 pagesWavesVincent AkintoluNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- Waves As A Carrier of EnergyDocument39 pagesWaves As A Carrier of EnergyDaisy DuronNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesIfrah ZiaNo ratings yet
- Physics For The Life SciencesDocument11 pagesPhysics For The Life Sciencesnawaf2016errorNo ratings yet
- WAVES AROUND YOU (Grade 7 q3)Document23 pagesWAVES AROUND YOU (Grade 7 q3)Genelyn BorjaNo ratings yet
- VibrationDocument15 pagesVibrationDesy SafitriNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument31 pagesWavesstefone cenizaNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument13 pagesWavesGrace Adrianne BacayNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Properties of WavesDocument24 pagesThe Nature and Properties of WavesMeryl PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Techniques-1Document62 pagesUltrasound Techniques-1yahyaNo ratings yet
- WAVESjsjDocument4 pagesWAVESjsjtinotaku58No ratings yet
- MYP4 Physics Waves and Calculations PPT Intro (18266)Document22 pagesMYP4 Physics Waves and Calculations PPT Intro (18266)Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- ch11 2Document90 pagesch11 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Wave and SoundDocument38 pagesWave and SoundCorazon JacksonNo ratings yet
- Wave MachanicsDocument30 pagesWave MachanicsMahadi Hasan SakilNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound UPDATEDDocument42 pagesWaves and Sound UPDATEDGEORGE MATHIASNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument14 pagesWave MotionPraveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World CommunicatesDocument5 pagesPhysics Half-Yearly Notes by Dillon Halder The World Communicatesuhhwot100% (1)
- Anatomy of A WaveDocument28 pagesAnatomy of A WaveAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument37 pagesWavesmohammed issaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Travelling WavesDocument36 pages4.2 Travelling WavesXavierNo ratings yet
- 8.1a Properties - of - WavesDocument31 pages8.1a Properties - of - WavesNoel John UmallaNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties: Secondary 3 PhysicsDocument13 pagesGeneral Wave Properties: Secondary 3 PhysicsShakil MalikNo ratings yet
- The World Communicates James SaraDocument11 pagesThe World Communicates James SaraJames coleNo ratings yet
- Waves: Presented By: Md. Sumon Hossain - Zannatul Naim Lemon - Shovan Sarkar - Shovan Samaddar - Robiul IslamDocument16 pagesWaves: Presented By: Md. Sumon Hossain - Zannatul Naim Lemon - Shovan Sarkar - Shovan Samaddar - Robiul IslamMD. SUMON HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument6 pagesWave NotesVittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- Presentation On WavesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Wavesmaqsood ahmadNo ratings yet
- Properties of Waves: AdditionalsDocument2 pagesProperties of Waves: AdditionalsJason Doctolero HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionRocking Himanshu21No ratings yet
- Oscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumDocument2 pagesOscillation of Energy: An Oscillation That Travels Through A MediumApril Joy Gelilang PulgaNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument36 pagesWavesjomelleann.pasolNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument11 pagesSound WavesshenxxvNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument17 pagesWaveJevanthe Miguel ObusanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 8 Waves: DR - SalmaDocument45 pagesLecture - 8 Waves: DR - SalmaMuhammad TajammulNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Waves ExplainedDocument14 pagesWaves ExplainedRohinKanjiNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of WavesDocument14 pagesGeneral Characteristics of WavesAjay G RNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Properties of WavesDocument19 pagesThe Nature and Properties of Waves7-SAL 2022No ratings yet
- Waves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingDocument72 pagesWaves: Presented By: Ms. Evalyn Suyat-CapindingKristina C IbonNo ratings yet
- Waves and Their Applications PDFDocument14 pagesWaves and Their Applications PDFprimalNo ratings yet
- Basic Wave PhenomenaDocument43 pagesBasic Wave Phenomena李彊No ratings yet
- Idebe Physics 4 1Document147 pagesIdebe Physics 4 1May Nang'onde75% (8)
- 015 WaveDocument31 pages015 WaveChris john AlfilerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Wave (Form 5)Document29 pagesChapter 1 - Wave (Form 5)kcnjojo91% (11)
- BuDocument15 pagesBubreycariganNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics NotesLegend RR3No ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet