Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respuestas Al Cambio Climático Durante El Holoceno Tardío
Respuestas Al Cambio Climático Durante El Holoceno Tardío
Uploaded by
David Carrión0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThis document discusses cultural responses to climate change during the Late Holocene period. It summarizes four case studies:
1) The Akkadian collapse in Mesopotamia around 4200 years ago due to drought caused by changes in ocean circulation and reduced water supply. This led to abandonment of agricultural plains and migration.
2) The Classic Maya collapse around 1200 years ago when their civilization declined after 200 years of arid conditions in the Yucatan.
3) The Moche IV-V transformation in coastal Peru around 1500 years ago when a 30-year drought caused migration to highlands due to the region's extreme aridity.
4) The Tiwanaku collapse in South
Original Description:
Respuestas de diferentes civilizaciones al cambio climático durante el Holoceno tardío
Original Title
Respuestas al cambio climático durante el Holoceno tardío
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses cultural responses to climate change during the Late Holocene period. It summarizes four case studies:
1) The Akkadian collapse in Mesopotamia around 4200 years ago due to drought caused by changes in ocean circulation and reduced water supply. This led to abandonment of agricultural plains and migration.
2) The Classic Maya collapse around 1200 years ago when their civilization declined after 200 years of arid conditions in the Yucatan.
3) The Moche IV-V transformation in coastal Peru around 1500 years ago when a 30-year drought caused migration to highlands due to the region's extreme aridity.
4) The Tiwanaku collapse in South
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageRespuestas Al Cambio Climático Durante El Holoceno Tardío
Respuestas Al Cambio Climático Durante El Holoceno Tardío
Uploaded by
David CarriónThis document discusses cultural responses to climate change during the Late Holocene period. It summarizes four case studies:
1) The Akkadian collapse in Mesopotamia around 4200 years ago due to drought caused by changes in ocean circulation and reduced water supply. This led to abandonment of agricultural plains and migration.
2) The Classic Maya collapse around 1200 years ago when their civilization declined after 200 years of arid conditions in the Yucatan.
3) The Moche IV-V transformation in coastal Peru around 1500 years ago when a 30-year drought caused migration to highlands due to the region's extreme aridity.
4) The Tiwanaku collapse in South
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Cultural Responses to Climate Change
During the Late Holocene
David Carrion|Yachay Tech University
ABSTRACT CULTURAL RESPONSES TO MODES AND
THE CLIMATIC MECHANISMS OF
Modern complex societies exhibit a marked
capacity to recover from interannual to decadent VARIATIONS OF THE LATE HOLOCENE
droughts. But, cultural responses to multidecanal
to multicultural droughts can only be addressed HOLOCENE CLIMATE
through the integration of detailed
archaeological and paleoclimate records. So, how Four studies illustrate past cultural
VARIABILITY
can we understand how and why climates responses to Holocene climate change: Multidecadal to
change? The answer use the following approach:
• Akkadian collapse. multicentury droughts
“Present is the key to understanding the past” marked Holocene climate
James Hutton • Classic Maya collapse. (last 11.700 years).
• Moche IV–V Transformation Droughts can be caused by
HISTORIC AND • Tiwanaku collapse.
the following factors.
PREHISTORIC DROUGHT • Water availability
• Changes in ocean
IN NORTH AMERICA
Akkadian
collapse
(Mesopotamia, circulation.
4200 calendar yr
Water availability.- Key climatic B.P.) • Solar irradiance.
determinant for drought. Produced by
aridification of • Volcanism.
Mesopotamia.
Several droughts presented in the Consequenses:
following years in USA: 1280, 1580 (”Great • Excess of
refugees at
Drought”), 1600 (“Megadroughts”), 1930 south
Mesopotamia
of
(“Dust Bowl”), 1951-1956 (six years Texas • Construction of
the "Repeller of
drought). the Amorites"
wall to prevent
the passage of
Abandonment of Akkadians to
the south.
Akkadian agricultural • Abandonment
plains. [Photo credit: H. of Akkadian B and C shows a temperature decay
Weiss/Yale University] agricultural starting in 4200 B.P. in the sub-polar Water availability is the principal factor
plains. Atlantic climate and subtropical that determine the existence of a drought
surface waters (“Holocene Event”). [Photo credit:
This fact caused the reduction of the https://pixabay.com/en/drought-aridity-
water supply of Mesopotamia. dry-earth-soil-780088/]
Classic Maya collapse
(Yucatan, 1200 Moche IV–V
Transformation
calendar yr B.P.) (coastal Peru, 1500
This civilization was calendar yr B.P. )
subjected to a period of The Peruvian coast
200 years of arid and is extremely arid,
highly evaporative therefore, depends
on the
conditions. Before that, precipitation. A 30
it was found at the top years of reduced
of development of regional
commercial networks, precipitation
urban centers, caused the
migration of the
construction of population to
monumental stelae and highlands. “Huaca de Sol” and other monuments were
advanced knowledge of abandonated by Moche people near 1500
astronomy and The number of sites dedicated to the B.P.. [Photo credit: sendautopica.com]
mathematics. construction of monuments in 1200 B.P.
indicate that the classic Mayan empire
collapsed at the peak of its cultural
development.
Brenner]
[Photo credit: M. CULTURAL
RESPONSES TO
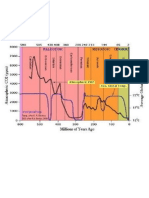
Color figures of USA represent 1280, 1584 and 1956
Tiwanaku collapse
(Bolivian-Peruvian Graphic suggest CLIMATE
Southwest United States droughts. altiplano, ca. 1000
calendar yr B.P.).
that a Tiwanaku
abandonment CHANGE
Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI), measures the coincides eith a
A multicentury multicentury What can we learn from this?
intensity, duration and spatial extent of a drought. It
interval of reduced interval of • Interannual droughts occur many times in a
goes from -5.0 (extreme drought) to +5.0 (extreme precipitation caused reduced determinate generation.
humidity conditions). the collapsed of high precipitation, as • Decenal droughts are repeated infrequently
determined by the over many generations.
1580 USA figure correspond to ”Great Drought”. The field cultivation and
ice accumulation • Multidecadal to multicentric scale droughts
black curves represent decadal average of drought. their urban and rural record at are much rarer nut natural.
The gray curves represent the full annual-resolution agricultural Quelccaya ice As it was seen, the culture of a civilization can
environments. Also core, at 200 km
record change according to the climate conditions.
produced a 10 m. fall northwest of Lake Therefore, we can conclude that our society has
at Titicaca lake level. Titicaca. great resilience and vulnerability to complex
environmental variability.
You might also like
- Net Zero Cloud Business Guide To Carbon AccountingDocument10 pagesNet Zero Cloud Business Guide To Carbon AccountingApple DevicesNo ratings yet
- Global Warming MisunderstoodDocument47 pagesGlobal Warming MisunderstoodLindsay Hackett85% (13)
- Final Exam AnswersDocument7 pagesFinal Exam Answersemilia5970% (1)
- Closson Et Al-2009-Earth Surface Processes and LandformsDocument14 pagesClosson Et Al-2009-Earth Surface Processes and LandformsUtku SütNo ratings yet
- Intro Basic Concepts PDFDocument57 pagesIntro Basic Concepts PDFGeorge KabaNo ratings yet
- KL-Climate Action Plan - MalaysiaDocument120 pagesKL-Climate Action Plan - MalaysiaMd. Majedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Kids Fight Climate Change: Act Now To Be A #2minutesuperhero Chapter SamplerDocument26 pagesKids Fight Climate Change: Act Now To Be A #2minutesuperhero Chapter SamplerCandlewick Press100% (1)
- Zim 169511Document176 pagesZim 169511Newton MutasaNo ratings yet
- Niversidad Acional de AN Gustin: E P I GDocument23 pagesNiversidad Acional de AN Gustin: E P I GHEBERT JHON RAFAEL AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Jaramilloetal 2019 PetrogenesisCombiaDocument18 pagesJaramilloetal 2019 PetrogenesisCombiaCristina DallosNo ratings yet
- The Depositional Environments and Tectonic Development of A Mesozoic Intra-Arc Basin, Atacama Region, ChileDocument14 pagesThe Depositional Environments and Tectonic Development of A Mesozoic Intra-Arc Basin, Atacama Region, Chilefo saldiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Canada's Geological HistoryRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- KadimaDocument29 pagesKadimajohn ngandouNo ratings yet
- Cu N ChileDocument4 pagesCu N ChilePedro Luis Trujillo HermitañoNo ratings yet
- 1991 - Mpodozis - Regional Setting Epithermal Gold Deposits ChileDocument14 pages1991 - Mpodozis - Regional Setting Epithermal Gold Deposits ChileArsennicneroNo ratings yet
- At4St11 - 003 - Singer Et Al - Laguna Del Maule Magma SystemDocument4 pagesAt4St11 - 003 - Singer Et Al - Laguna Del Maule Magma SystemAlejandro Barrientos MuñozNo ratings yet
- Muoz-Farasetal 2023Document21 pagesMuoz-Farasetal 2023Laura Quiroz LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Dunning Et Al. 2012 - Kax - and - Kol - Collapse - and - Resilience - in - Lowland - May PDFDocument7 pagesDunning Et Al. 2012 - Kax - and - Kol - Collapse - and - Resilience - in - Lowland - May PDFNayelitzin J. CanoNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Magmatisim and Uplift of MagmatisimDocument6 pagesAlkaline Magmatisim and Uplift of MagmatisimNirdesh Maravi 17164No ratings yet
- 6-Regional Setting of The Mahakam DeltaDocument11 pages6-Regional Setting of The Mahakam DeltaGita Putri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Geotectonic-4Document58 pagesGeotectonic-4Arieq ClasherNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Sedimentary Basin AnalysisDocument69 pagesLECTURE 2 - Sedimentary Basin AnalysisMichelle Maua JabaNo ratings yet
- 2006 Mountney PDFDocument35 pages2006 Mountney PDFLorenza FerrariNo ratings yet
- 3-4 - Evolution of Landforms and Geomorphic SystemsDocument51 pages3-4 - Evolution of Landforms and Geomorphic SystemsdaenielbuctuanonmNo ratings yet
- Morel Et Al. - 2003 - Lithology, Landscape Dissection and Glaciation Controls On Catchment Erosion As Determined by Cosmogenic Nuclides IDocument7 pagesMorel Et Al. - 2003 - Lithology, Landscape Dissection and Glaciation Controls On Catchment Erosion As Determined by Cosmogenic Nuclides ITifa AliNo ratings yet
- Geologic Events InfographicDocument1 pageGeologic Events InfographicpaullawrencepizzarramarasiganNo ratings yet
- Collot Et Al., 2005Document4 pagesCollot Et Al., 2005Ernesto YanezNo ratings yet
- Geologic Events InfographicDocument1 pageGeologic Events InfographicPaul Lawrence MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Aleman Al 1999 PetrolSystem MadreDeDios ThrustBelt PeruDocument25 pagesAleman Al 1999 PetrolSystem MadreDeDios ThrustBelt Peruchicha48No ratings yet
- Dynamic EarthDocument10 pagesDynamic Earthsaloni1anandNo ratings yet
- KT BoundaryDocument15 pagesKT Boundarymd anisur hoqueNo ratings yet
- 2007-Scholl-GSA-Crustal Recycling at Modern Subduction Zones Applied To The PastDocument24 pages2007-Scholl-GSA-Crustal Recycling at Modern Subduction Zones Applied To The Pastlee BlakeNo ratings yet
- AljojucacantonatriptiDocument6 pagesAljojucacantonatriptijazminnhalauraNo ratings yet
- Basins AnalysisDocument56 pagesBasins AnalysisBac mathNo ratings yet
- IIIb Milankovitch Cycles and The Ice AgesDocument9 pagesIIIb Milankovitch Cycles and The Ice AgesSam Beljon CatapusanNo ratings yet
- MatthewDocument37 pagesMatthew겟리껫나No ratings yet
- Reading A 400,000-Year Record of Earthquake Frequency For An Intraplate FaultDocument6 pagesReading A 400,000-Year Record of Earthquake Frequency For An Intraplate FaultAnirudh SabooNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: January 2003Document37 pagesVolcanoes: January 2003JupiterNo ratings yet
- Allock Et AlDocument9 pagesAllock Et Albyhz7wwdm4No ratings yet
- Hungerbuhler, 1997Document5 pagesHungerbuhler, 1997Milton Agustin GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Mercader Et Al 2012 - Cosmogenic Nuclide Age Constraints On MiDocument15 pagesMercader Et Al 2012 - Cosmogenic Nuclide Age Constraints On MiAstolfo AraujoNo ratings yet
- Peters Loss 2012Document4 pagesPeters Loss 2012VmanuloNo ratings yet
- Kaufman 2019 The Ediacaran-Cambrian TransitionDocument28 pagesKaufman 2019 The Ediacaran-Cambrian TransitionGg GNo ratings yet
- Henderson 1979 Cretaceous To Eocene Volcanic Arc Activity in The Andes of Northern EcuadorDocument13 pagesHenderson 1979 Cretaceous To Eocene Volcanic Arc Activity in The Andes of Northern EcuadorMilton Agustin GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time: A Story in The RocksDocument28 pagesGeologic Time: A Story in The RocksEddyleen LuzadaNo ratings yet
- DePalma Et Al 2019 A Seismically Induced Onshore Surge Deposit at The KG Boundary North DakotaDocument10 pagesDePalma Et Al 2019 A Seismically Induced Onshore Surge Deposit at The KG Boundary North DakotaMaría ChavarríaNo ratings yet
- Thouret 1999 Volcanic Geomorphology-An OverviewDocument37 pagesThouret 1999 Volcanic Geomorphology-An OverviewEdgardo Alvarez100% (1)
- Economic Potential of The Yucatan Block PDFDocument9 pagesEconomic Potential of The Yucatan Block PDFAlejandrothegeologistNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphy (Key Variables in Earth History) - Lecure 5Document6 pagesStratigraphy (Key Variables in Earth History) - Lecure 5Hani HamoudNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4B Geological HazardsDocument196 pagesMODULE 4B Geological HazardsAngelica Mathew50% (2)
- A Genetic Classification of Floodplains: GeomorphologyDocument28 pagesA Genetic Classification of Floodplains: Geomorphologyresacoxis9No ratings yet
- Introduction To Geology PDFDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Geology PDFAydan MustafayevaNo ratings yet
- 07 Paleo SealevelDocument30 pages07 Paleo Sealevelmuhammad affanNo ratings yet
- Roddaz Et Al 2002 TectonicsDocument23 pagesRoddaz Et Al 2002 Tectonicsammar oudyNo ratings yet
- The Changing EarthDocument52 pagesThe Changing EarthAnileydi Taveras JimenezNo ratings yet
- Sequence StratigraphyDocument3 pagesSequence StratigraphyKH13No ratings yet
- Earth and Planetary Science LettersDocument13 pagesEarth and Planetary Science LettersDanielNo ratings yet
- GEO-Eqs, Volcanism, Tsunamis For CamSur, Sorsogon TeachersDocument161 pagesGEO-Eqs, Volcanism, Tsunamis For CamSur, Sorsogon TeachersJane ErlanoNo ratings yet
- 2-How Basins Are Made 2Document177 pages2-How Basins Are Made 2Annisa 'd-tink' AzizahNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage PDFDocument4 pagesReading Passage PDFMushroom PhiliaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Piquer CongresoDocument3 pages2012 Piquer CongresoFelipe Eduardo Rojas VerasayNo ratings yet
- Cretaceous To Eocene Volcanic Arc Activity in The Andes Northern EcuadorDocument12 pagesCretaceous To Eocene Volcanic Arc Activity in The Andes Northern EcuadorMayra AvilaNo ratings yet
- The Timing of Magmatism and Ore FormatioDocument28 pagesThe Timing of Magmatism and Ore FormatioCarolina PerezNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and The Collapse of The Akkadian Empire Evidence From The Deep SeaDocument5 pagesClimate Change and The Collapse of The Akkadian Empire Evidence From The Deep SeaSongNo ratings yet
- Projected Changes in Seasonal Rainfall in The Mid-21 Century (2036-2065) For Northern Samar Relative To 1971-2000Document7 pagesProjected Changes in Seasonal Rainfall in The Mid-21 Century (2036-2065) For Northern Samar Relative To 1971-2000Earl VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Tu Dong Nghia Global WarmingDocument1 pageTu Dong Nghia Global WarmingNguyễn HòaNo ratings yet
- TitleDocument2 pagesTitledaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Earth-Toned Colors Illustrative Science and History Geologic Time Scale Educational PresentationDocument11 pagesEarth-Toned Colors Illustrative Science and History Geologic Time Scale Educational PresentationJohn Enrick ManuelNo ratings yet
- Protected Cultivation and Secondary Agriculture: Agricultural EngineeringDocument2 pagesProtected Cultivation and Secondary Agriculture: Agricultural Engineeringaditya singhNo ratings yet
- Climate Health-5th May 2023Document6 pagesClimate Health-5th May 2023Ramaiah Kannirajan Arumugam PillaiNo ratings yet
- Environment Article 1 Threat of Climate Change 28 Feb 2022Document3 pagesEnvironment Article 1 Threat of Climate Change 28 Feb 2022Amita RajeevNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Human Strategy (S (P)Document2 pagesClimate Change and Human Strategy (S (P)Nagendra Prasad0% (1)
- Since The Industrial RevolutionDocument3 pagesSince The Industrial Revolutionim.dawood121No ratings yet
- Climate Change Data - Climate Change Indicators DashboardDocument9 pagesClimate Change Data - Climate Change Indicators DashboardSuresh MohanNo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 14064-1-2019Document58 pagesBS en Iso 14064-1-2019pirjoNo ratings yet
- Empirical Project - Assignment - GuideDocument16 pagesEmpirical Project - Assignment - Guidesergio carrasco romeroNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On "Climate Change Mitigation and Strategies: Global Perspectives"Document23 pagesTerm Paper On "Climate Change Mitigation and Strategies: Global Perspectives"KirataNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts RegisterDocument1 pageEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Registerมิตร อันมาNo ratings yet
- Ted Talk About Climate ChangeDocument1 pageTed Talk About Climate ChangeEris MolenoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint Calculation Ed 4 ENG - v2Document13 pagesCarbon Footprint Calculation Ed 4 ENG - v2trader123No ratings yet
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change) : SpeechDocument2 pagesIPCC (Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change) : SpeechKristia AnagapNo ratings yet
- Objectives For Studying The TopicDocument6 pagesObjectives For Studying The Topichvntech42No ratings yet
- Revision Class - Reported Speech and ConditionalsDocument4 pagesRevision Class - Reported Speech and ConditionalsInés MonllorNo ratings yet
- Literary Review 1Document7 pagesLiterary Review 1api-542796089No ratings yet
- 7.2 Climate Change CausesDocument15 pages7.2 Climate Change CausesSanskar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cop 28Document2 pagesCop 28tewet66169No ratings yet
- Assignment Climate Change and Its Impact On Agriculture: An OverviewDocument9 pagesAssignment Climate Change and Its Impact On Agriculture: An OverviewKomal SaraogiNo ratings yet
- Wgiiar5 Chap6 FinalDocument74 pagesWgiiar5 Chap6 FinalMercedes PrietoNo ratings yet
- Evs Project Climatic ChangesDocument6 pagesEvs Project Climatic Changesvansh gandhiNo ratings yet