Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Jas Per0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pagePneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs, making it difficult to breathe and causing symptoms like cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Pneumonia can range from mild to severe depending on factors like the cause and a person's age and health. Treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral drugs along with supportive care, while prevention includes vaccines and maintaining good health.
Original Description:
Original Title
pneumonia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs, making it difficult to breathe and causing symptoms like cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Pneumonia can range from mild to severe depending on factors like the cause and a person's age and health. Treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral drugs along with supportive care, while prevention includes vaccines and maintaining good health.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pagePneumonia
Uploaded by
Jas PerPneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs, making it difficult to breathe and causing symptoms like cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. It is usually caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Pneumonia can range from mild to severe depending on factors like the cause and a person's age and health. Treatment involves antibiotics or antiviral drugs along with supportive care, while prevention includes vaccines and maintaining good health.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
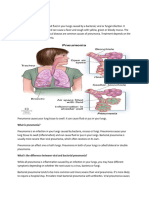
Pneumonia is an infection that physical examination, and diagnostic
inflames the air sacs in one or both tests, such as chest X-rays and
lungs. It is typically caused by bacteria, laboratory tests to identify the specific
viruses, or fungi. When a person organism causing the infection.
develops pneumonia, the air sacs in Treatment for pneumonia often
the lungs may fill with fluid or pus, involves antibiotics for bacterial
making it difficult to breathe and pneumonia or antiviral medications for
causing symptoms such as cough, viral pneumonia, along with supportive
fever, chest pain, and difficulty care to relieve symptoms and promote
breathing. recovery.
Pneumonia can range from mild to Prevention of pneumonia can be done
severe, and its severity depends on through vaccination against certain
various factors, including the type of organisms, such as pneumococcal
organism causing the infection, the vaccines and influenza vaccines,
overall health of the individual, and practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding
their age. Certain groups, such as close contact with individuals who
infants, young children, older adults, have respiratory infections, and
and individuals with weakened maintaining overall good health
immune systems, are at a higher risk through a balanced diet and regular
of developing complications from exercise.
pneumonia.
Common causes of pneumonia
include Streptococcus pneumoniae
bacteria, influenza viruses, respiratory
syncytial virus (RSV), and Mycoplasma
pneumoniae bacteria. Pneumonia can
be acquired in various settings,
including community-acquired
pneumonia (CAP), which is acquired
outside of a healthcare setting, or
hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP),
which occurs during a hospital stay.
There is also a type of pneumonia
called aspiration pneumonia, which
develops when foreign matter, such as
food or liquids, is inhaled into the
lungs.
Pneumonia is typically diagnosed
through a combination of symptoms,
You might also like
- Clinical PresentationDocument54 pagesClinical PresentationSêrâphîm HâdíNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia With Pleural EffusionDocument24 pagesPneumonia With Pleural EffusionMund CheleNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung. It Is Often Characterized AsDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung. It Is Often Characterized AsBettina Gem M. PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 3Document8 pagesPneumonia 3janinecasilenNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPneumoniasamtaynbNo ratings yet
- Classification: PneumoniaDocument2 pagesClassification: PneumoniaAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- What Is Pneumonia?: Patient EducationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Pneumonia?: Patient EducationDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaMargaret EricksonNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedDocument7 pagesPneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedHannah YtacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1Ayro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: DR Abdul Ghani WaseemDocument20 pagesPneumonia: DR Abdul Ghani WaseemFarwaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaDocument21 pagesAddis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaCheru DugaseNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The AlveoliDocument3 pagesPneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The AlveolimakkosetteNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia, BronchiolitisDocument65 pagesPneumonia, BronchiolitisYemata HailuNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: MicroorganismsDocument11 pagesSigns and Symptoms: MicroorganismsReni April AnaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An: ClinicalDocument13 pagesPneumonia Is An: ClinicaldfgsfsfssdNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia and GastroentiritisDocument3 pagesPneumonia and Gastroentiritismarie100% (5)
- Acute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)Document58 pagesAcute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)api-19916399No ratings yet
- Name: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikDocument37 pagesName: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikChintiya PutriNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is A Serious Infection of The Lungs in Which The AirDocument1 pagePneumonia Is A Serious Infection of The Lungs in Which The AirErdem EzerNo ratings yet
- Definition of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesDefinition of PneumoniaEmylia Ananda PutriNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Nelson 20 EdDocument43 pagesPediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Nelson 20 EdRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument8 pagesPneumoniaNader Smadi100% (2)
- Pneumonia Is Caused by VirusesDocument6 pagesPneumonia Is Caused by VirusesrayshahNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400Document37 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400fatima chrystelle nuñalNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument10 pagesPneumoniaJohn Philip M. Lacas RNNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia WrittenDocument12 pagesPneumonia WrittenFereli Joy SupanNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPneumoniaCeleste Parin Procopia KardinNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument18 pagesPneumoniaFryam Bells100% (1)
- 3 PneumoniaDocument17 pages3 PneumoniaMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument10 pagesPneumoniaKarylle ZairahNo ratings yet
- 1 Running Head: Disease Report On Causes and Prevention of PneumoniaDocument4 pages1 Running Head: Disease Report On Causes and Prevention of PneumoniawaweruhNo ratings yet
- Nasarullahkhan Mazari 70-Phae-2k17Document8 pagesNasarullahkhan Mazari 70-Phae-2k17Kashif BalochNo ratings yet
- REQ - PneumoniaDocument6 pagesREQ - PneumoniaAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 PneumoniaDocument7 pagesActivity 2 PneumoniaKyle AndrewNo ratings yet
- Practice Essentials: View Media GalleryDocument22 pagesPractice Essentials: View Media GalleryAza Patullah ZaiNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 pagesBroncho PneumoniamarkkkkkkkheeessNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DisordersDocument9 pagesRespiratory System Disordersasop06No ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children What Is Pneumonia in Children?Document7 pagesPneumonia in Children What Is Pneumonia in Children?Sandra GabasNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument13 pagesPneumoniaRobelNo ratings yet
- NOTES (Pneumonia & Lobectomy)Document6 pagesNOTES (Pneumonia & Lobectomy)Kim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Classification: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument15 pagesClassification: Community-Acquired PneumoniaHASLINDANo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: By: Muhamad Irwan Faizal (714.6.2.0539)Document13 pagesPneumonia: By: Muhamad Irwan Faizal (714.6.2.0539)irwanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is AnDocument9 pagesPneumonia Is Ansandro2000No ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: MicroorganismsDocument4 pagesSigns and Symptoms: MicroorganismsNikki P. NarteNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- S. Pneumoniae Produces Local Edema That Aids in The Proliferation of Organisms and TheirDocument7 pagesS. Pneumoniae Produces Local Edema That Aids in The Proliferation of Organisms and TheirKadek Soga Prayaditya PutraNo ratings yet
- LP IgdDocument15 pagesLP IgdMaya sabrinaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionmcvirgo014100% (1)
- 17 PneumoniaDocument30 pages17 PneumoniaCabdiNo ratings yet
- Cap HR With PTBDocument6 pagesCap HR With PTBReese Alessandra GandulfoNo ratings yet
- PCAP HandoutDocument1 pagePCAP HandoutCherr NollNo ratings yet
- Common DiseasesDocument7 pagesCommon DiseasesAlter BadonNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument9 pagesBroncho Pneumoniamunie munieNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaalyanadayritNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orDocument6 pagesPneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orOtrebron BatisanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: PneumoniaDocument45 pagesTopic 1: PneumoniaNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Air Borne DiseasesDocument3 pagesAir Borne DiseasesMuhammad Anwar GulNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (Lrtis) BronchitisDocument11 pagesLower Respiratory Tract Infections (Lrtis) BronchitisAhmed Gh Al-zechrawiNo ratings yet