Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSI104
CSI104
Uploaded by
Tâm Lê0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesThe document defines key terms related to computer history, binary logic, computer memory, sorting algorithms, programming languages, and data structures. It provides definitions for terms such as the Pascaline and Jacquard Loom as early computing devices, AND, OR, XOR, and NOT as binary logic operators, pages and segmentation as memory allocation techniques, insertion, selection, and bubble sort, procedural and object-oriented programming languages, and stacks and queues as data structures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to computer history, binary logic, computer memory, sorting algorithms, programming languages, and data structures. It provides definitions for terms such as the Pascaline and Jacquard Loom as early computing devices, AND, OR, XOR, and NOT as binary logic operators, pages and segmentation as memory allocation techniques, insertion, selection, and bubble sort, procedural and object-oriented programming languages, and stacks and queues as data structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesCSI104
CSI104
Uploaded by
Tâm LêThe document defines key terms related to computer history, binary logic, computer memory, sorting algorithms, programming languages, and data structures. It provides definitions for terms such as the Pascaline and Jacquard Loom as early computing devices, AND, OR, XOR, and NOT as binary logic operators, pages and segmentation as memory allocation techniques, insertion, selection, and bubble sort, procedural and object-oriented programming languages, and stacks and queues as data structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
1-9 A 17th-century computing machine that could perform addition and
subtraction was the ________
Pascaline
1-12 The first electronic special-purpose computer was called ________
ABC
1-13 One of the first computers based on the von Neumann model was called
________ .
EDVAC
1-14 The first computing machine to use the idea of storage and
programming was called ________ .
the Jacquard loom
4-11 ________ operator (s) takes two inputs to produce one output.
AND, OR, or XOR
4-12 The unary ________ operator inverts its single input.
NOT
4-13 ________ operator (s), if the input is two 0s, the output is 0.
In AND, OR, or XOR
4-14 ________ operator (s), if the input is two 1s, the output is 0.
In only XOR
4-15 For the binary AND operation, only an input of ________ gives an
output of 1.
two 1s
4-16 For the binary OR operation, only an input of ________ gives an output of 0.
two 0s
4-18 To flip all the bits of a bit pattern, make a mask of all 1s and then
________ the bit pattern and the mask.
XOR
4-19 To un-set (force to 0) all the bits of a bit pattern, make a mask of all 0s
and then ________ the bit pattern and the mask.
AND
4-20 To set (force to 1) all the bits of a bit pattern, make a mask of all 1s and then
________ the bit pattern and the mask.
OR
7-8 In paging, a program is divided into equally sized sections called________ .
pages
7-9 In ________ , the program can be divided into differently sized sections.
demand segmentation
7-10 In ________ , the program can be divided into equally sized sections called pages,
but the pages need not be in memory at the same time for execution.
demand paging
8-12 In ________ sort, the item that goes into the sorted list is always the first item in
the unsorted list.
insertion
8-13 In ________ sort, the smallest item from the unsorted list is swapped with the item
at the beginning of the unsorted list.
selection
8-14 In ________ sort, the smallest item moves to the beginning of the
unsorted list. There is no one-to-one swapping.
Bubble
FORTRAN is a(n) ________ language.
procedural
9-4 Pascal is a(n) ________ language.
. procedural
9-5 Java is a(n) ________ language.
object-oriented
9-6 LISP is a(n) ________ language.
functional
9-7 ________ is a common language in the business -environment.
COBOL
9-8 ________ is a popular object-oriented language.
Java
9-9 A ________ program can be either an application or an applet.
Java
9-10 LISP and Scheme are both ________ languages.
functional
9-11 Prolog is an example of a(n) ________ language.
Declarative
10-6 ________ is the breaking up of a large project into smaller parts.
Modularization
10-7 ________ is a measure of how tightly two modules are bound to each other.
Coupling
10-8 ________ between modules in a software system must be minimized.
Coupling
10-9 ________ between modules in a software system must be maximized.
Cohesion
12-2 A stack is a ________ structure.
LIFO
12-3 A (n) ________ list is also known as a queue.
FIFO
You might also like
- Excel VBA CodeDocument6 pagesExcel VBA CodemcmonizNo ratings yet
- Csapp 3e Solutions PDFDocument407 pagesCsapp 3e Solutions PDFame100% (1)
- hp11c15c EasycourseDocument260 pageshp11c15c EasycourseLuiz Carlos RodriguesNo ratings yet
- UGRD-ITE6102 Computer Programming 1 by EBDocument18 pagesUGRD-ITE6102 Computer Programming 1 by EBErbreth BiasNo ratings yet
- Informatica SenariosDocument26 pagesInformatica Senariossatish85cNo ratings yet
- HANA (High Performance Analytic Appliance)Document159 pagesHANA (High Performance Analytic Appliance)Mohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Table Both Are 2/2 Matrices But There Are Many Differences Between Table andDocument35 pagesStructure and Table Both Are 2/2 Matrices But There Are Many Differences Between Table andDittyAneeshNo ratings yet
- Abap On Hana by Sreedhar NotesDocument159 pagesAbap On Hana by Sreedhar NotesAshij100% (2)
- Mouse Using NumpadDocument17 pagesMouse Using NumpadTâm LêNo ratings yet
- Programming in Pascal: From simple Pascal programs to current desktop applications with Database DEV-PASCAL, LAZARUS AND PASCAL N-IDEFrom EverandProgramming in Pascal: From simple Pascal programs to current desktop applications with Database DEV-PASCAL, LAZARUS AND PASCAL N-IDENo ratings yet
- Unit 4 VE IT2 TestDocument1 pageUnit 4 VE IT2 Testوليد طه50% (2)
- SP Rao ABAP Project NotesDocument47 pagesSP Rao ABAP Project Noteskanakaraju vudata50% (2)
- Online Assessment AsrDocument3 pagesOnline Assessment AsrRAJBEERNo ratings yet
- Chap 01Document4 pagesChap 01se180287nguyenbaophucNo ratings yet
- SE - Kó 1 - CSI104Document18 pagesSE - Kó 1 - CSI104wtskaneNo ratings yet
- Class6 Technology Computers WorksheetDocument5 pagesClass6 Technology Computers WorksheetsjiaahhsusgshuNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu ôn tậpDocument47 pagesTài liệu ôn tậpnguyendaothien2003No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computing 2Document10 pagesFundamentals of Computing 2Bry PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- G7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 1 NEWDocument4 pagesG7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 1 NEWEbb Lian AninoNo ratings yet
- Practiceworksheet 1Document3 pagesPracticeworksheet 1AriesMascarhenasNo ratings yet
- Figure 9.1 - The Parallel PortDocument7 pagesFigure 9.1 - The Parallel PortRosanna AverillaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Interfacing To Switches and LED's ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLab 2 - Interfacing To Switches and LED's ObjectivesidkNo ratings yet
- CSC 202 (C Language Questions) PDFDocument30 pagesCSC 202 (C Language Questions) PDFDavid GbadamosiNo ratings yet
- Matlab Laboratory f19Document26 pagesMatlab Laboratory f19IsaacNo ratings yet
- CS101 Midterm2Document5 pagesCS101 Midterm2ali abbasNo ratings yet
- 22 Alex - Balashov Kamailio TriviaDocument24 pages22 Alex - Balashov Kamailio TriviaerminNo ratings yet
- CS401 TODAY Grand Quiz 2021 BY JUNAIDDocument16 pagesCS401 TODAY Grand Quiz 2021 BY JUNAIDsajidaruqaya760No ratings yet
- Using Valgrind:: Detecting Memory ErrorsDocument11 pagesUsing Valgrind:: Detecting Memory ErrorsGiridhar AddepalliNo ratings yet
- Handout Prog LangsDocument7 pagesHandout Prog Langsblosos69No ratings yet
- Oracle 8i ch23Document11 pagesOracle 8i ch23Venky PragadaNo ratings yet
- COMP111: Unix and Script Programming: The Hong Kong University of Science & TechnologyDocument20 pagesCOMP111: Unix and Script Programming: The Hong Kong University of Science & TechnologyKaycey JoNo ratings yet
- Grade9 UnittestDocument2 pagesGrade9 UnittestChristian ZapicoNo ratings yet
- EDC - Lab - 01 - Fall 2023Document15 pagesEDC - Lab - 01 - Fall 2023i222200 Muhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming: Lab Practical Week 4Document4 pagesFundamentals of Programming: Lab Practical Week 4Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- AssemblyDocument14 pagesAssemblyUnity of GamersNo ratings yet
- Ssignmen: Q.1: Choose The Correct WordDocument8 pagesSsignmen: Q.1: Choose The Correct WordEE PWDNo ratings yet
- Arid Agriculture University, RawalpindiDocument4 pagesArid Agriculture University, RawalpindiMehar FaizanNo ratings yet
- Jan Franco Glanc - MSP Pretests (1-2)Document2 pagesJan Franco Glanc - MSP Pretests (1-2)JanFrancoGlancNo ratings yet
- Exercises Basic Syntax PDFDocument1 pageExercises Basic Syntax PDFamitsinghNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design: Laboratory ManualDocument9 pagesDigital Logic Design: Laboratory ManualrabiasamadNo ratings yet
- DSP LabDocument40 pagesDSP LabSrinivasan KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Interfacing To Keypad and LCD ObjectivesDocument19 pagesLab 4 - Interfacing To Keypad and LCD ObjectivesidkNo ratings yet
- CMP4266 Week 4 Lab: Essential - To Be Completed Within The WeekDocument5 pagesCMP4266 Week 4 Lab: Essential - To Be Completed Within The WeekHassan Ali AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Program C E N (Batch Control Center and More... ) U S E R's G U I D EDocument6 pagesProgram C E N (Batch Control Center and More... ) U S E R's G U I D EegorNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: 8-Puzzle: Basic RequirementsDocument4 pagesAssignment 3: 8-Puzzle: Basic RequirementsA hNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture Notes (9/9/99) : Introductory InformationDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Lecture Notes (9/9/99) : Introductory InformationSahir MajeedNo ratings yet
- Activty 7 and 8Document11 pagesActivty 7 and 8Je ApigoNo ratings yet
- VerilogDocument80 pagesVeriloggenx142No ratings yet
- Simple Programming ProblemsDocument5 pagesSimple Programming ProblemsnikolasmerNo ratings yet
- 2011 Fall2017 Final NO SolutionsDocument12 pages2011 Fall2017 Final NO SolutionsVictor BuicaNo ratings yet
- Practicle FileDocument37 pagesPracticle FileabishekNo ratings yet
- AutomataDocument1 pageAutomataRose Mary Millan-Arellano VelascoNo ratings yet
- 7 Structured Query Language PDFDocument34 pages7 Structured Query Language PDFMitchell IngallNo ratings yet
- Exercises Basic Syntax PDFDocument1 pageExercises Basic Syntax PDFMimo MolioNo ratings yet
- Lab 12B Interfacing An NXM Keyboard To The 8051Document2 pagesLab 12B Interfacing An NXM Keyboard To The 8051M Rameez Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Guide PLX DAQDocument7 pagesGuide PLX DAQAlfonso Arellano CruzNo ratings yet
- ICP-Programming Assignment-IV PDFDocument3 pagesICP-Programming Assignment-IV PDFAbhijit AroopNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic SequanceDocument3 pagesArithmetic SequanceSisca DianaNo ratings yet
- Arid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi: Q.No. Marks ObtainedDocument5 pagesArid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi: Q.No. Marks ObtainedMehar FaizanNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument5 pagesComputer GenerationsTâm LêNo ratings yet
- How To Decide Which Data Model For Your ApplicationDocument2 pagesHow To Decide Which Data Model For Your ApplicationTâm LêNo ratings yet
- The Action of Loading OS Into RAM Is Called Booting or Start Up SequenceDocument1 pageThe Action of Loading OS Into RAM Is Called Booting or Start Up SequenceTâm LêNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document1 pageChapter 3Tâm LêNo ratings yet
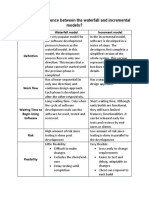
- What Is The Diference Between The Waterfall and Incremental ModelsDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Diference Between The Waterfall and Incremental ModelsTâm LêNo ratings yet
- Chap14 1473751047 598112Document46 pagesChap14 1473751047 598112Tâm LêNo ratings yet
- ThreadsDocument25 pagesThreadsTâm LêNo ratings yet
- ProcessesDocument17 pagesProcessesTâm LêNo ratings yet
- L1- Number Systems jhkj njn bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................vbhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................vbhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjhDocument32 pagesL1- Number Systems jhkj njn bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................vbhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................bhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjh .........................................................vbhagavad gita ............................... hgjbhbjhbjhbjhjbbjbkj jhj hbjhSaumith DahagamNo ratings yet
- Definitions of The Turing MachineDocument10 pagesDefinitions of The Turing Machinemaki ababiNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Arithmetic For ComputersDocument28 pagesUnit - Ii Arithmetic For ComputersAlexander Rueda OrduzNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument32 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsNikita Mittal50% (2)
- Kleen's TheoremDocument21 pagesKleen's TheoremAmmara Younas 3831-FBAS/BSCS/F18No ratings yet
- Implementation of Modified Booth Algorithm (Radix 4) and Its Comparison With Booth Algorithm (Radix-2)Document18 pagesImplementation of Modified Booth Algorithm (Radix 4) and Its Comparison With Booth Algorithm (Radix-2)THIRUCHANOORU SREENATHNo ratings yet
- HO - Thinking Like A Computer ScientistDocument62 pagesHO - Thinking Like A Computer ScientistJOHN PRINCE M COCAMASNo ratings yet
- TocDocument9 pagesTocAtul Barve100% (1)
- AOA-Paper SolutionsDocument68 pagesAOA-Paper SolutionsSahil KNo ratings yet
- Restoring DivisionDocument5 pagesRestoring DivisionAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Turing Machine BasicsDocument112 pagesTuring Machine Basicssanjay prabhuNo ratings yet
- C: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)Document3 pagesC: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)jayabaNo ratings yet
- 11 NewDocument30 pages11 Newnada abdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Daily Time Record Daily Time RecordDocument1 pageDaily Time Record Daily Time RecordasawwerNo ratings yet
- Recurrence Relations PDFDocument16 pagesRecurrence Relations PDFSrinivasaRao JJ100% (1)
- Anr 6.02 (60200005) 20221003 013523 1611174316Document18 pagesAnr 6.02 (60200005) 20221003 013523 1611174316EcaNo ratings yet
- Adder Cum SubtractorDocument4 pagesAdder Cum SubtractorCHERISMA100% (2)
- HW2 Questions (Theory of Computation) Due 09/26Document2 pagesHW2 Questions (Theory of Computation) Due 09/26Anonymous ZIO2lMmiNo ratings yet
- AutomataDocument5 pagesAutomataMorcilla IverNo ratings yet
- ch12 - Binary 2Document35 pagesch12 - Binary 2Snow WhiteNo ratings yet
- AND & Ampersand OR - Pipe NOT Tilde XOR CaretDocument5 pagesAND & Ampersand OR - Pipe NOT Tilde XOR CaretMohamed RayanyNo ratings yet
- TOCDocument12 pagesTOCYash SugandhiNo ratings yet
- NP Hard and NP Complete ProblemsDocument15 pagesNP Hard and NP Complete ProblemsAngu Vignesh GuruNo ratings yet
- Finite State TransducersDocument4 pagesFinite State TransducersAbhisek SarkarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Computation and Compiler Design: Module - 4Document69 pagesTheory of Computation and Compiler Design: Module - 4AdityaNo ratings yet
- CS402 Quiz-2 File by Vu Topper RMDocument56 pagesCS402 Quiz-2 File by Vu Topper RMM. KhizarNo ratings yet
- Mca AssignmentDocument27 pagesMca AssignmentArvind PokhariyaNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design Model Lab QuestionsDocument4 pagesCompiler Design Model Lab QuestionsKisan SakthiNo ratings yet
- Combinational CircuitDocument15 pagesCombinational CircuitTanmay HazraNo ratings yet