0% found this document useful (0 votes)
505 views7 pagesUpdated Question Bank-5
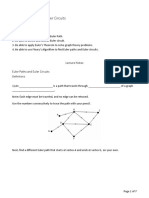
This document contains 35 questions related to the course "Discrete Mathematics" with topics including graphs, trees, coloring, and spanning trees. The questions range from basic definitions to more complex problems involving finding subgraphs, determining if graphs are isomorphic, finding Euler and Hamiltonian paths/circuits, coloring graphs using algorithms, and properties of trees.
Uploaded by
Dr. Sushant ShekharCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
505 views7 pagesUpdated Question Bank-5
This document contains 35 questions related to the course "Discrete Mathematics" with topics including graphs, trees, coloring, and spanning trees. The questions range from basic definitions to more complex problems involving finding subgraphs, determining if graphs are isomorphic, finding Euler and Hamiltonian paths/circuits, coloring graphs using algorithms, and properties of trees.
Uploaded by
Dr. Sushant ShekharCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd