Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Threats
Uploaded by
Ismaeel SheikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Threats
Uploaded by
Ismaeel SheikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Network threats:
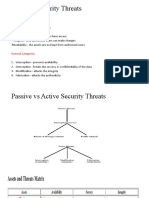
- Passive attack = data is monitored whilst it is travelling on a network, any sensitive information if intercepted.
They may use software’s like packet sniffers. – passive attacks = hard to detect, best defence = data encryption
- Active attack = network is attacked with malware – main defence = firewall
- Insider attack = person in an organisation exploits their network access to steal info.
- Brute force = automated software produces possible passwords combinations – defence = locking an account
after multiple failed password attempts
- Denial of service attack (DoS) – hacker tries to stop users from accessing a part of a network. – Most DoS involve
flooding a network with traffic – makes the network slow
- Malware = malicious software installed on someone’s device without consent
- Typical malware actions = deleting/ modifying files, locking files (encrypts files and holds them ransom), spyware
(secretly monitors user actions)
- Virus’ – attach themselves to certain files (e.g. .exe),
- Worms – self-replicating virus’ – spread quickly – exploit weaknesses in network securities.
- Trojans – malware disguised as legit software – don’t replicate
Weak points in secure systems:
- People: social engineering = method of gaining sensitive info through influencing people, usually employees of
large companies
- Common form of social engineering = scam calls
- Phishing = social engineering – when criminals send email/texts to people claiming to be from a legit business
SQL injections:
- Networks that use databases are vulnerable to this attack. SQL = structured query language
- SQL injection = pieces of SQL typed into a websites input box – revealing sensitive info
Example:
Website lets you view your account info if u enter your password. – if the websites SQL does not have a strong
input validation, then someone may be able to enter some SQL code that lets them access other people’s
account info.
Penetration testing = Systems are tested for vulnerabilities to reveal any weaknesses in the system which can be
fixed.
Antimalware = Avast, McAfee, Malwarebytes
Firewall = An application that prevents unauthorised connections to and from the Internet.
User access levels = a large company or school, many people will be using computers on the same network. A
network manager will normally control the level of access people have to the network. General users will not have
the ability to download any software they want or to make changes to any part of the system, as that could affect
other users.
Encryption is the process of encoding data or a message so that it cannot be understood by anyone other than its
intended recipient.
Physical security – login USBS, covering your pin etc.
You might also like
- Cyber Crime ResearchDocument14 pagesCyber Crime ResearchJay VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Security+ Notes v.2Document70 pagesSecurity+ Notes v.2sabiyNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument44 pagesSummaryDominique Eijansantos100% (1)
- THREATSDocument10 pagesTHREATSF19BA110Mehrose FatimaNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Performance AnalysisDocument39 pagesSAP ABAP Performance AnalysisBrahim KaddafiNo ratings yet
- Security in NetworkingDocument8 pagesSecurity in NetworkingAdhithya KannanNo ratings yet
- Your System's Sweetspots: CEO's Advice on Basic Cyber Security: CEO's Advice on Computer ScienceFrom EverandYour System's Sweetspots: CEO's Advice on Basic Cyber Security: CEO's Advice on Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- COSC 6301 - Computer Security Threats - and - VulnerabilitiesDocument52 pagesCOSC 6301 - Computer Security Threats - and - VulnerabilitiesmailtosiscoNo ratings yet
- Ben's Security+ NotesDocument22 pagesBen's Security+ NotesIftaKharulIslamArnobNo ratings yet
- ITEC 1010 Final Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesITEC 1010 Final Exam ReviewKelvin KongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Khánh LyNo ratings yet
- Data SecurityDocument31 pagesData SecurityRoy GichukiNo ratings yet
- LO1 Asset and Security Threat Week 02Document40 pagesLO1 Asset and Security Threat Week 02kaung kyaw zaNo ratings yet
- EC301: Computer Network Fundamental: Chapter 6: Basic SecurityDocument27 pagesEC301: Computer Network Fundamental: Chapter 6: Basic SecurityAyu WafaNo ratings yet
- Lectu Er TwoDocument32 pagesLectu Er TwoAbdurahman awilNo ratings yet
- Running Head: COMPUTER SECURITYDocument6 pagesRunning Head: COMPUTER SECURITYNining ArlianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Security and CryptographyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Security and CryptographyBensonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7Carleen Grace DeleonNo ratings yet
- 03 - CO1-ethical Hacking TerminologiesDocument53 pages03 - CO1-ethical Hacking TerminologiesWoyNo ratings yet
- Dire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesDire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceAhadu techNo ratings yet
- Hacking BasicsDocument18 pagesHacking BasicsdavidcseNo ratings yet
- UCR Security GlossaryDocument7 pagesUCR Security GlossaryulliisseessNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Network Security BasicsDocument7 pagesLecture 1 - Network Security BasicsHillary AyabeiNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Cloud Security - Part2Document25 pagesUnit - V Cloud Security - Part2shinderohann02No ratings yet
- SecurityDocument3 pagesSecuritygirma wodajoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Khánh LyNo ratings yet
- Isaa Assignment 1Document4 pagesIsaa Assignment 1SANKALP MUKIM 20BDS0128No ratings yet
- It Security Procedures and Guidelines: Adrija SenDocument33 pagesIt Security Procedures and Guidelines: Adrija SenSaket AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Web Definitions: Example For Active and Passive AttackDocument7 pagesWeb Definitions: Example For Active and Passive AttackJanaka VidurindaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 GlossaryDocument2 pagesModule 1 GlossaryDominique EijansantosNo ratings yet
- Module 2 System Security (Jerick Zen Sildo, Marc Sanchez)Document13 pagesModule 2 System Security (Jerick Zen Sildo, Marc Sanchez)Junel SildoNo ratings yet
- Computer Security and Safety (Pt.1)Document9 pagesComputer Security and Safety (Pt.1)jhammyNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Cyber SecurityDocument40 pagesUnit - II Cyber SecurityRitesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Computer Security - Quick GuideDocument43 pagesComputer Security - Quick GuideSampath DarshanaNo ratings yet
- 1.6 SecurityDocument30 pages1.6 SecurityVIJAYA PRABA PNo ratings yet
- Mama ArbDocument4 pagesMama ArbMarian SolivaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security CEHDocument5 pagesCyber Security CEHSridhar PNo ratings yet
- EssentialDocument1 pageEssentialKLNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CybersecutityDocument4 pagesIntroduction To CybersecutityMihaelaNo ratings yet
- Security and CommunicationDocument31 pagesSecurity and CommunicationDickson MusoniNo ratings yet
- Describe The Costs Associated With ActionsDocument22 pagesDescribe The Costs Associated With ActionsAlleyNo ratings yet
- NSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENDocument6 pagesNSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENitachi uchihaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Intruders Virus FirewallDocument93 pagesCh5 Intruders Virus FirewallHai LeNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CyberSecurityDocument7 pagesUnit-1 CyberSecurityGopi Krishna stylish foreverNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking - TerminologiesDocument4 pagesEthical Hacking - TerminologiesmihirmmbNo ratings yet
- Database SecurityDocument23 pagesDatabase Securityabel dequinaNo ratings yet
- Security Management in An ICT EnvironmentDocument75 pagesSecurity Management in An ICT EnvironmenttalalNo ratings yet
- CYBERSECURITYDocument41 pagesCYBERSECURITYDominique EijansantosNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument3 pagesViruseshs_sanadhyaNo ratings yet
- Rahul Singh 21csmsa109Document18 pagesRahul Singh 21csmsa109cst01sm4311No ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Threats and AttacksDocument51 pagesLec 4 - Threats and AttacksgNo ratings yet
- CSS4-Q1 Module 2Document10 pagesCSS4-Q1 Module 2Lielanie NavarroNo ratings yet
- RamakrishnaDocument3 pagesRamakrishnadurgarajesh800No ratings yet
- Network Security ThreatsDocument16 pagesNetwork Security Threatsdipu2kNo ratings yet
- Module 5-OsDocument25 pagesModule 5-Oscreations400abNo ratings yet
- CNS NotesDocument51 pagesCNS NotesSalva TanveerNo ratings yet
- Welcome This Comprehensive Ethical Hacking CourseDocument7 pagesWelcome This Comprehensive Ethical Hacking CoursevarshaNo ratings yet
- No Technology That's Connected To: The Internet Is Unhackable.Document9 pagesNo Technology That's Connected To: The Internet Is Unhackable.zeenia ahmedNo ratings yet
- Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Informatics and Computing Computer Science ProgramDocument37 pagesJimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Informatics and Computing Computer Science ProgramTaaddalaa HabteeNo ratings yet
- TerminologyDocument1 pageTerminologyKLNo ratings yet
- Cyber Attacks On Operating Systems Can Take Various Form1Document3 pagesCyber Attacks On Operating Systems Can Take Various Form1Idrissa SalehNo ratings yet
- Advance ExcelDocument40 pagesAdvance ExcelSaurabh SainiNo ratings yet
- IoT WiFi Based Data Logger With Device ControlDocument3 pagesIoT WiFi Based Data Logger With Device ControlwallraNo ratings yet
- LiteWave Switch DatasheetDocument3 pagesLiteWave Switch Datasheetpaul esparagozaNo ratings yet
- Ni Teststand: Getting Started With TeststandDocument89 pagesNi Teststand: Getting Started With TeststandAnwarNo ratings yet
- Installation and Configuration of LansweeperDocument46 pagesInstallation and Configuration of LansweeperGansari GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networksankit_coolheadNo ratings yet
- P and ID HandsbookDocument30 pagesP and ID HandsbookYohannes GebreNo ratings yet
- 40104diDocument6 pages40104dimariastalinNo ratings yet
- Connecting To The S7 PLCDocument4 pagesConnecting To The S7 PLCEmerson Gomes ToledoNo ratings yet
- Crash ReportDocument56 pagesCrash ReportIoan MesarosNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 Solution V2Document6 pagesAssignment-4 Solution V2Junaid MandviwalaNo ratings yet
- LIC Lecture 4.voltage Reference MaterialsDocument3 pagesLIC Lecture 4.voltage Reference MaterialsMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- DNP Profile - RTU To Master Rev1Document16 pagesDNP Profile - RTU To Master Rev1mato3848No ratings yet
- Acer Iconia Tab A3-A10 - Compal - La-A791p - r0.2 - Schematics PDFDocument29 pagesAcer Iconia Tab A3-A10 - Compal - La-A791p - r0.2 - Schematics PDFbobbiNo ratings yet
- HopeRF RF-EVB Manual V1.21Document15 pagesHopeRF RF-EVB Manual V1.21Biswa MisraNo ratings yet
- SG DriverDocument18 pagesSG Driverhary123No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: UNIT-4 Digital Fundamentals & Logic GatesDocument37 pagesDigital Electronics: UNIT-4 Digital Fundamentals & Logic GatesvishnuNo ratings yet
- CA. 7.1 Cloud Computing (17-18)Document16 pagesCA. 7.1 Cloud Computing (17-18)Kaushal KapureNo ratings yet
- Lakshya Polytechnic Plan. Execute. Achieve: Unit - 03 Sensors and Hardware For Iot SensorsDocument27 pagesLakshya Polytechnic Plan. Execute. Achieve: Unit - 03 Sensors and Hardware For Iot SensorsHimanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- HP 250 G1 Notebook PC - Spare Parts - HP® Customer SupportDocument15 pagesHP 250 G1 Notebook PC - Spare Parts - HP® Customer SupporthoracioNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Multilayer AHB Busmatrix For ARM: E. Raja, K.V. RamanaDocument4 pagesImplementation of Multilayer AHB Busmatrix For ARM: E. Raja, K.V. RamanaAnonymous pHi4dXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Software and Software Engineering: Sanjay Kumar Computer Science Department The ICFAI University DehradunDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Software and Software Engineering: Sanjay Kumar Computer Science Department The ICFAI University DehradunGaurav TyagiNo ratings yet
- The Raspberry Pi Glossary: Page 1Document3 pagesThe Raspberry Pi Glossary: Page 1TigauClaudiuNo ratings yet
- EEE303-Week01 - Number Systems, VerilogDocument87 pagesEEE303-Week01 - Number Systems, VerilogSaif YusufNo ratings yet
- 2 Lecture 2 - Strings and FunctionsDocument33 pages2 Lecture 2 - Strings and FunctionsReuel Patrick CornagoNo ratings yet
- Software 4 Model Answer Papers From 2019 To 2022Document27 pagesSoftware 4 Model Answer Papers From 2019 To 2022tapstaps902No ratings yet
- Veil - FrameworkDocument2 pagesVeil - FrameworkMtech MasterNo ratings yet
- Acer V193W Service Guide (For NT68167)Document49 pagesAcer V193W Service Guide (For NT68167)DaNo ratings yet
- Cinelerra User ManualDocument207 pagesCinelerra User Manualo_dimitrovNo ratings yet