Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geography p2 Memo Nov 2019 English
Uploaded by
Samkele SibiyaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography p2 Memo Nov 2019 English
Uploaded by
Samkele SibiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL
SENIOR CERTIFICATE
NOVEMBER 2019
GRADE 10
GEOGRAPHY P2
MARKING GUIDELINE
MARKS: 75
This marking guideline consists of 12 pages.
2 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
GENERAL INFORMATION ON VRYHEID
The town of Vryheid in KwaZulu-Natal Province lies southward along the R33 in the valley at
the foot of the Zungwini Mountain. It is the centre of coal mining and cattle farming in the
district and being an old town with a historical past, there are a number of national monuments
in the town. Decisive battles were fought in the vicinity during the Anglo Boer War.
Coordinates: 27° 46′ 3″ S, 30° 47′ 9″ E
[Source: https://www.google.co.za/images]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2019) GEOGRAPHY P2 3
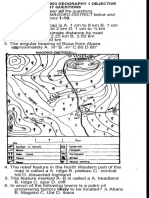
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
The questions below are based on the 1 : 50 000 topographic map 2730DD
VRYHEID, as well as the orthophoto map of a part of the mapped area. Various
options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the
answer and write only the letter (A–D) in the block next to each question (1.1–1.15).
1.1 The type of scale evident on the orthophoto map is a ...
A line scale.
B ratio scale.
C word scale.
B
D Richter scale.
1.2 The contour interval of the topographic map is …
A 20 m.
B 10 m.
A
C 15 m.
D 20 km.
1.3 The 1 : 50 000 scale of the topographic map is ... than that of the orthophoto
map.
A 5 times smaller
B 5 times larger
A
C 50 times smaller
D 50 times larger
1.4 The index number of the map sheet southwest of Vryheid on the topographic
map is …
A 2730 BB.
B 2731 CC.
C
C 2730 BA.
D 2731 AA.
1.5 The distance of the line labelled D on the topographical map is ...
A 2,1 km
B 0,21 km
B
C 21 km
D 210 km
Copyright reserved Please turn over
4 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
1.6 The height of an index contour line labelled Y, in block D6 on the topographic
map is ...
A 1 120 m.
B 1 100 m.
C 1 200 m.
B
D 1 050 m.
1.7 The man-made feature found at grid reference 27⁰48′35′′S / 30⁰47′40′′E is
a(n) ...
A dam.
B valley.
C
C excavation.
D mine dump.
1.8 The evidence that mining has taken place in block F1 is the presence of …
A a river.
B roads.
C
C mine dumps.
D excavations.
1.9 The land use in block A6 is for the following activities:
A Mining and fishing
B Diggings and excavation
C
C Cultivation and diggings
D Dams and diggings
1.10 The altitude shown by the trigonometrical station in block G2 is …
A 365 m.
B 1 190 m.
D
C 365 km.
D 1 218,3 m.
1.11 The true bearing of trigonometrical beacon number 103 in block D4 from
trigonometrical beacon number 381 in block B5 is …
A 300°.
B 067°.
B
C 275°.
D 090°.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2019) GEOGRAPHY P2 5
1.12 If you travel south-westerly on main road R33 from the police station in
block C2 in Vryheid along Route 33 on the topographic map, you are going
to ...
A Hlobane.
B Paulpietersberg.
C Kingsley.
C
D Tinta Drift.
1.13 The area in block E1 is largely covered by ...
A buildings.
B woodlands.
C dams.
B
D sports fields.
1.14 Refer to both the orthophoto and topographic map. The feature labelled 7 on
the orthophoto map is a ...
A police station.
B school.
C hotel.
B
D hospital.
1.15 The water extraction feature in block A3 on the topographic map is a ...
A weir.
B wind pump.
C dam.
B
D furrow.
(15 x 1) [15]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
6 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
SECTION B: MAPWORK CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
QUESTION 2
2.1 Refer to the orthophoto map.
2.1.1 Measure and calculate the distance between points 1 and 2 in
kilometres.
Distance = cm/scale x 100 000
3,4 cm √ /10 000 x 100 000 [Range: 3,3–3,5 cm]
= 34 km √ [Range: 33–35 km]
(2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Calculate the area covered by the orthophoto map (also indicated by a black
rectangular box on the topographic map). Use the formula:
AREA = LENGTH x WIDTH
Length = 8,2 cm √ x 0,5 [8,1 cm–8,3 cm]
= 4,1 km √
Width = 5,8 cm √ x 0,5 [5,7 cm–5,9 cm]
= 2,9 km √
Area = 4,1 x 2,9
= 11,89 km2 √ [Range = 11,5–12,24 km2]
(5 x 1) (5)
2.3 Refer to block G3 on the topographic map. Identify trigonometrical beacon
number 60 and spot height 1395.
2.3.1 Is the slope between the two features named above steep or gentle?
Steep √
(1 x 1) (1)
2.3.2 Support your answer in QUESTION 2.3.1 above.
Contour lines are closely spaced. √√
Land rises sharp over short distance. √√
Trig beacon 60 is on a hill top √√ [Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
2.3.3 Work out the difference in height between trigonometrical beacon
number 60 and spot height 1395.
1 430,9 m – 1 395 m √ = 35,9 m √
(2 x 1) (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2019) GEOGRAPHY P2 7
2.4 Calculate the magnetic declination of the map for the present year.
Difference in years: 2019 – 1997 = 22 √ years
Mean annual change: 6′ √ West
Total change: 22 x 6′ = 132′W (1° = 60′)
= 2⁰ 12′ √ W
Magnetic declination: 19° 38′ + √ 2⁰ 12′
= 21° 50′ WTN √ (5 x 1) (5)
2.5 Refer to the contour lines below which depict a landform found in blocks F4/5
on the topographic map (between spot heights 1274 in F4 and 1368 in F5) to
answer the questions that follow.
2.5.1 Draw a simple free-hand (not to scale) cross section of the landform
shown by the contour lines from A to B.
√ correct shape of cross section
√ different height of hills
√ saddle not touching ground level
(2 x 1) (2)
2.5.2 Name the landform that is depicted by the cross section in
QUESTION 2.5.2 above.
Saddle / butte / pointed butte √ [Any ONE]
(1 x 1) (1)
[20]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
8 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
QUESTION 3: MAP AND PHOTO APPLICATION AND INTERPRETATION
3.1 Refer to block D4 on the topographic map.
3.1.1 Name the activity that is practised at A.
Excavation √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.1.2 Describe how the activity named in QUESTION 3.1.1 above can be
hazardous (harmful) to the environment and people’s activities.
The landscape loses shape √√
It leads to land degradation/desertification √√
Top soil/fertile soil with nutrients is lost √√
Land loses importance for cultivation √√
Plant and animal species are lost by clearing vegetation √√
It facilitates soil erosion √√ [Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Refer to the table below together with the topographic map to answer the
questions that follow.
VRYHEID WEATHER BY MONTH / WEATHER AVERAGES
December
September
November
February
January
October
March
August
April
June
May
July
Avg. Temperature 21 21 20 18,1 15,2 12,8 12,8 15 16,9 18,7 19,6 20,6
(°C)
Precipitation / 148 123 100 43 22 11 13 20 43 92 122 149
Rainfall (mm)
3.2.1 What was the mean monthly temperature for June?
12,8 degrees Celsius √/12,8 °C
(1 x 1) (1)
3.2.2 State the month in which Vryheid receives its highest rainfall.
December √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.2.3 Calculate the mean annual temperature range for Vryheid.
21 °C – 12,8 °C √ = 8,2 °C √
(2 x 1) (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2019) GEOGRAPHY P2 9
3.2.4 Vryheid receives less than average rainfall. Provide TWO pieces of
evidence from the map showing that Vryheid receives seasonal
rainfall.
Presence of non-perennial rivers √
Wind pumps √
Reservoirs √ [Any TWO]
(2 x 1) (2)
3.3 Refer to the topographic map.
3.3.1 Name any recreational activity in block C2.
Golf/golf driving √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.3.2 Identify any ONE tourist attraction in the Vryheid mapped area.
Hotels √√
Golf driving / Golf course √√
Dams/Fishing/Boating √√
Mountain viewing / Besterkop / Esikhuma / Skaapkoppie / Lancaster
Hill / Hiking / Vryheid Nature Reserve √√
National monuments √√ [Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Name the feature labelled 6 on the orthophoto map.
Power lines √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.5 Refer to the Klipfontein Dam on the topographic map.
3.5.1 Mention the main river that supplies the dam with water.
Besterspruit river √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.5.2 A man was canoeing in the Klipfontein Dam moving from Inkamana
(block D5) towards the damwall (block D6). Determine the direction
the man was heading in.
Southwards/South √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.5.3 Suggest TWO possible ways in which Inkamana (block D5) and the
neighbouring settlements would benefit from the Klipfontein Dam.
Water for domestic/Recreation/Irrigation/Farming/Fishing √
Cooling temperatures in summer √
Job creation / Tour guides √
Agricultural projects √ [Any TWO]
(2 x 1) (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
10 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
3.5.4 Give ONE reason why people at Inkamana would consider the dam
as a threat to their lives during flooding.
Dam water can overspread causing flood into the settlement √√
They are located on a lower ground √√
Mosquitos in summer causing malaria disease √√
Unclean water especially in dry seasons causing cholera √√
[Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
3.6 Refer to the landform in block B/C6.
3.6.1 The feature represented by the contour lines crossed by line E is a/an
(spur/valley).
Valley √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.6.2 Support your answer to QUESTION 3.6.1 above.
Contours are pointing to higher ground √√
Presence of a river along the marshes √√ [Any ONE] (2)
(1 x 2)
3.7 Refer to the orthophoto map.
3.7.1 Choose the correct answer from the options between brackets:
The orthophoto map is derived from a (high oblique / vertical aerial)
photograph.
Vertical aerial √
(1 x 1) (1)
3.7.2 Describe the difference between an oblique and vertical photograph.
In vertical photographs the camera is perpendicular / vertical above
the earth’s surface / taken from the air √√
In oblique photographs the camera is tilted/slanting at an angle √√
Objects behind high features like hills or buildings are obscured/
hidden in oblique √√
Objects below appear from their roof top √√
Scale varies within the same photographs in oblique / Objects in the
foreground appear larger than those in the background √√
The scale is nearly the same for vertical photographs √√
[Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
[25]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
(EC/NOVEMBER 2019) GEOGRAPHY P2 11
QUESTION 4: GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS)
4.1 Refer to FIGURE 4.1 below which shows parts of a GIS component system
and how it operates to answer the following questions.
FIGURE 4.1
4.1.1 Define the term geographical information systems (GIS).
Is a computer-based tool of doing work √
Is a computer-based technique of gathering, manipulating, storing
and retrieving information for doing work. √
(1 x 1) (1)
4.1.2 Name any FOUR components of GIS.
Software √/Users √/Procedures or Methods √/Data √/Network √
[Any FOUR]
(4 x 1) (4)
4.1.3 From FIGURE 4.1 above, name any ONE hardware device that is
used for:
(a) Capturing information into the system
Scanner/Keyboard √
(b) Storing information in the system.
Image server/CPU/Tape back-up/File server √
(c) Connecting the system to a network
Network cable/Modem √
(3 x 1) (3)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
12 GEOGRAPHY P2 (EC/NOVEMBER 2019)
4.2 Explain the importance of using GIS in today’s fast changing world.
Computers are faster / cheaper / efficient √√
More information is coming into the world √√
The world’s problems exist in a geographical context √√
GIS can be used in daily lives, e.g. choosing a nearby school √√
[Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
4.3 Refer to block D3 on the topographic map.
4.3.1 State ONE example of each of the following types of features in block
D3.
(a) Area/(Polygon): Excavation/Recreation ground/Lakeside
settlements/Cemetary √ [Any ONE]
(b) Line/(Arc): Arterial Road/Secondary road/Power
line/Track/hiking trail/River √ [Any ONE]
(c) Point/(Node): Buildings/School/Trigonometrical beacon/
Trees √ [Any ONE]
(3 x 1) (3)
4.4 Refer to the area on the top north-western part of the orthophoto map. Explain
why it would be wise for the surveyors to use remote sensing in collecting
data from that area.
Not accessible by roads/no roads leading there √√
It can be dangerous to go there because of snakes and wild animals √√
Landscape is too steep, forested and unreachable √√
Remote sensors can easily reach unreachable places from a distance √√
[Any ONE]
(1 x 2) (2)
[15]
TOTAL: 75
Copyright reserved Please turn over
You might also like
- Gr11 Geog p2 n16 Memo EngDocument10 pagesGr11 Geog p2 n16 Memo EngThato MotlhabaneNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY P2 GR11 QP NOV 2019 - Eng DDocument24 pagesGEOGRAPHY P2 GR11 QP NOV 2019 - Eng Dhlolothabo818No ratings yet
- Mapwork Task Memo Grade 10 2023Document11 pagesMapwork Task Memo Grade 10 2023zinhlecolette35100% (1)
- Geography P2 Feb-March 2010 Memo EngDocument10 pagesGeography P2 Feb-March 2010 Memo Engashleighmutsvani7No ratings yet
- Geography P2 Mapwork Memorandum PDFDocument10 pagesGeography P2 Mapwork Memorandum PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document15 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Lethabo MoropaNo ratings yet
- Geog p2 Gr11 - Qp-Eng VryheidDocument11 pagesGeog p2 Gr11 - Qp-Eng VryheidRhulani MaluksNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 Nov 2016 Memo EngDocument14 pagesGeography P2 Nov 2016 Memo EngBRYAN BONAPARTEE SHINGANGENo ratings yet
- Geography P2 Feb-March 2014 Memo EngDocument9 pagesGeography P2 Feb-March 2014 Memo EngZamambo MkhizeNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document12 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Thandiweh MwabaNo ratings yet
- Geog p2 Memo Eng Nov 2012Document10 pagesGeog p2 Memo Eng Nov 2012jaftarampyapediNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 Nov 2018 EngDocument15 pagesGeography P2 Nov 2018 EngmrtwvilakaziNo ratings yet
- Louis Trichardt MG Grade 11 MapworkDocument8 pagesLouis Trichardt MG Grade 11 MapworkmogomotsanavNo ratings yet
- Geography p2 Gr10 QP Nov 2018 EngDocument13 pagesGeography p2 Gr10 QP Nov 2018 EngAndzaniNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 10Document9 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 10shanolkersNo ratings yet
- Geography P1 May-June 2023 EngDocument20 pagesGeography P1 May-June 2023 Engtanielliagreen0No ratings yet
- Geography P2 Nov 2016 EngDocument15 pagesGeography P2 Nov 2016 Engmpanzanandisa4No ratings yet
- Geography P2 Feb-March 2016 EngDocument14 pagesGeography P2 Feb-March 2016 Engsndumiso373No ratings yet
- Geography P2 May-June 2017 Eng PDFDocument13 pagesGeography P2 May-June 2017 Eng PDFdan danny0% (1)
- Geography P2 Feb-March 2018 EngDocument13 pagesGeography P2 Feb-March 2018 Engbenjaminlocke2.1No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document16 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Thembelani ThempeliNo ratings yet
- Geography P1 Nov 2022 Eng PDFDocument20 pagesGeography P1 Nov 2022 Eng PDFSipho MthiNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 May-June 2022 EngDocument17 pagesGeography P2 May-June 2022 EngrukieymNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 Nov 2022 EngDocument19 pagesGeography P2 Nov 2022 Engamber45ngewuNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 May-June 2022 EngDocument17 pagesGeography P2 May-June 2022 EngshlotseNo ratings yet
- Geography P2 Nov 2020 EngDocument16 pagesGeography P2 Nov 2020 EngAlfa VutiviNo ratings yet
- Sir Medora Nav 2 TQDocument3 pagesSir Medora Nav 2 TQuyawakokoNo ratings yet
- Geography p2Document19 pagesGeography p2mosupiamogelang55No ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY P2 GR12 QP SEPT2023 - EnglishDocument29 pagesGEOGRAPHY P2 GR12 QP SEPT2023 - Englishymadikane38No ratings yet
- Geog Specimen MCDocument28 pagesGeog Specimen MCBranson Kaution Peters II100% (1)
- Grade 9: Senior PhaseDocument10 pagesGrade 9: Senior PhaseLyndelle MoyoNo ratings yet
- SBA02 Task002b Mapwork TaskDocument5 pagesSBA02 Task002b Mapwork TaskZhezakho MbizoNo ratings yet
- 2024 GR12 MG Mapwork TestDocument13 pages2024 GR12 MG Mapwork Testmxolisingcobo059No ratings yet
- EC Geography Grade 12 September 2023 P2 and MemoDocument41 pagesEC Geography Grade 12 September 2023 P2 and Memomabelenglehlohonolo3No ratings yet
- CSEC Geography Specimen Paper 01Document13 pagesCSEC Geography Specimen Paper 01Ashleigh JarrettNo ratings yet
- NG Chart General Questions 6p 58qDocument6 pagesNG Chart General Questions 6p 58qpaoloNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 NSC Geography P2 (English) Preparatory Examination Question PaperDocument17 pagesGrade 12 NSC Geography P2 (English) Preparatory Examination Question Papernthakotebza629No ratings yet
- Geog 20-21 S1 CT1 PDFDocument10 pagesGeog 20-21 S1 CT1 PDF1F-17 Li Jasmine Tin YanNo ratings yet
- English Test Question Grade 4 Part 2Document26 pagesEnglish Test Question Grade 4 Part 2Czar Julius MalasagaNo ratings yet
- Geography P1 Nov 2023 EngDocument19 pagesGeography P1 Nov 2023 Engbenjaminlocke2.1No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document26 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12Mussa AthanasNo ratings yet
- Igeo 2022 MMTDocument10 pagesIgeo 2022 MMTfizarputra23No ratings yet
- Geo 2003iiDocument3 pagesGeo 2003iialmightyfavouriteNo ratings yet
- Map Reading Skills - Booklet p.9-15Document7 pagesMap Reading Skills - Booklet p.9-15Lai Sum YinNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Refer To The Following Diagram Showing A River and Its EnvironsDocument13 pages1-5 Refer To The Following Diagram Showing A River and Its EnvironsNeree100% (1)
- Geography Paper 1 MockDocument17 pagesGeography Paper 1 MockOwen KaputulaNo ratings yet
- Zoom in Mapskills Grade 11: Task 1: VelddrifDocument6 pagesZoom in Mapskills Grade 11: Task 1: VelddrifJaryd GovenderNo ratings yet
- B. C. Peta Geologi D. Peta Persebaran Gunung E. Peta Jalur TransportasiDocument6 pagesB. C. Peta Geologi D. Peta Persebaran Gunung E. Peta Jalur TransportasiYullia PuTriNo ratings yet
- Cadastral Survey Questions...Document7 pagesCadastral Survey Questions...sureshNo ratings yet
- 4024 Y12 SP 2Document20 pages4024 Y12 SP 2Mansoor MithaiwalaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Mapwork Task Option 1 Memo ErmeloDocument8 pagesGrade 11 Mapwork Task Option 1 Memo Ermelozinhlecolette3550% (2)
- DTCP/19: Town Country Planning (Post Diploma STD.)Document40 pagesDTCP/19: Town Country Planning (Post Diploma STD.)Breaking dawnNo ratings yet
- Geo Gr9 QP Nov2016 EngDocument10 pagesGeo Gr9 QP Nov2016 EngNick BredenkampNo ratings yet
- Geografi 2022Document10 pagesGeografi 2022Aklil IlfaniNo ratings yet
- Strange Aeons - 05 - What Grows Within - Interactive Maps PDFDocument4 pagesStrange Aeons - 05 - What Grows Within - Interactive Maps PDFcojanat436No ratings yet
- Alejandro 2 - Refresher MATH PDFDocument2 pagesAlejandro 2 - Refresher MATH PDFAlliah Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Prometheus PDFDocument12 pagesPrometheus PDFFernán OteroNo ratings yet
- PrometheusDocument12 pagesPrometheusjamesgmccreaNo ratings yet
- Topographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsFrom EverandTopographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsNo ratings yet
- Late Prehistoric Fortifications in Europe: Defensive, Symbolic and Territorial Aspects From The Chalcolithic To The Iron Age.Document256 pagesLate Prehistoric Fortifications in Europe: Defensive, Symbolic and Territorial Aspects From The Chalcolithic To The Iron Age.David AbellaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Plate BoundariesDocument44 pagesLesson 1. Plate BoundariesMa’am Diana V.No ratings yet
- Researching The Hybrid Geographies of Climate (Popke, 2016)Document5 pagesResearching The Hybrid Geographies of Climate (Popke, 2016)Manuel SalasNo ratings yet
- Escape From Tenopia 3 Terror On KabranDocument75 pagesEscape From Tenopia 3 Terror On KabranLopinNo ratings yet
- Lundy 1974 Rock Art of NW CoastDocument363 pagesLundy 1974 Rock Art of NW CoastMarina ElliottNo ratings yet
- Did The Chinese Discover America?Document6 pagesDid The Chinese Discover America?Mary LinNo ratings yet
- Spice Route and The Kerala CoastDocument14 pagesSpice Route and The Kerala CoastSundeep AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Merchant Shipping Act 1983 PDFDocument181 pagesMerchant Shipping Act 1983 PDFAsifNo ratings yet
- Why Ram Setu Must Be Saved???Document5 pagesWhy Ram Setu Must Be Saved???Sushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- Adverb StoryDocument2 pagesAdverb StoryJaja Carlina100% (2)
- Met o MergedDocument31 pagesMet o MergedJhun Clyde DabasolNo ratings yet
- Standing StonesDocument10 pagesStanding StonesViktor NybergNo ratings yet
- Libro 1Document8,303 pagesLibro 1EstebanGarzonNo ratings yet
- New York City Sinking Four Millimeters A Year 8 e 9 AnosDocument2 pagesNew York City Sinking Four Millimeters A Year 8 e 9 AnosGabriela LimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - A Geographer's World: Section Notes VideoDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - A Geographer's World: Section Notes VideoBrian Jay GimanNo ratings yet
- Geography of Drones - Definition and Significance in Geography - MundoGEODocument4 pagesGeography of Drones - Definition and Significance in Geography - MundoGEORicardo Javier Garnica PeñaNo ratings yet
- Tumkur Taluk Covid-19 Travellers DetailsDocument3 pagesTumkur Taluk Covid-19 Travellers DetailsEmran AhmedNo ratings yet
- Converging Currents of GlobalizationDocument40 pagesConverging Currents of GlobalizationJuliean Torres AkiatanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Create A Civilization Project ExampleDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Create A Civilization Project ExampleMatthewNo ratings yet
- Current Editions of Sailing Directions: NP Title Edition WeekDocument3 pagesCurrent Editions of Sailing Directions: NP Title Edition Weeksrikant pNo ratings yet
- Final Control Points For Drone SurveyDocument2 pagesFinal Control Points For Drone SurveyGIS GmapNo ratings yet
- Mapping Subnautica - All CoordinatesDocument13 pagesMapping Subnautica - All CoordinatesJosh HighNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Stream Flow Measurement and HydrographDocument73 pagesChapter Four: Stream Flow Measurement and HydrographErmias EmiruNo ratings yet
- Ixgeo - Practice. Paper-1Document12 pagesIxgeo - Practice. Paper-1Satya brataNo ratings yet
- BSS MEMO March 19Document4 pagesBSS MEMO March 19Dhesigan PillayNo ratings yet
- Where in The World - Southern & Eastern AsiaDocument3 pagesWhere in The World - Southern & Eastern AsiaNevaeh ChrispinNo ratings yet
- 1.10 Study AreaDocument7 pages1.10 Study AreaBarnabas UdehNo ratings yet
- Anglao and Aran SummaryDocument1 pageAnglao and Aran SummaryEldi CastroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisPriscilia LewerissaNo ratings yet
- Louis Trichardt MG Grade 11 MapworkDocument8 pagesLouis Trichardt MG Grade 11 MapworkmogomotsanavNo ratings yet