Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM (Q.) - 30-04-23 e
Uploaded by
Vishal Kumar 5504Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM (Q.) - 30-04-23 e
Uploaded by
Vishal Kumar 5504Copyright:
Available Formats
www.escholars.
in
Date: 30-04-2023
CA Intermediate
Financial Management & Economics for Finance
Test Paper
Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100
STRICT INSTRUCTIONS Otherwise, your paper will not be checked.
1) Write your Name, Registered email Id, Phone number and State at the top of the answer sheet
before starting the paper.
2) UPLOADING THE ANSWER SHEET:
✓ Take images of answer sheet in VERTICAL FORM (not horizontal).
✓ Make PDF of all images in sequence using the App CAM SCANNER or any other App.
✓ Upload it before time.
✓ Be HIGHLY careful while uploading the answer sheet. Once you wrongly uploaded the
answer sheet, you will not be able to rectify it.
3) All the questions are mandatory.
Q. Questions Marks
No. Section – A (Financial Management)
1.
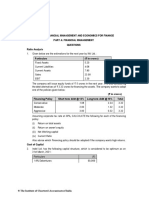
a) Alpha Ltd. has furnished the following information: 5
✓ Earning Per Share (EPS) ₹4
✓ Dividend payout ratio 25%
✓ Market price per share ₹ 50
✓ Rate of tax 30%
✓ Growth rate of dividend 10%
The company wants to raise additional capital of ₹10 lakhs including debt of ₹4 lakhs.
The cost of debt (before tax) is 10% up to ₹2 lakhs and 15% beyond that. Compute
the after tax cost of equity and debt and also weighted average cost of capital.
b) Kanoria Enterprises wishes to evaluate two mutually exclusive projects X and Y. The 5
particulars are as under:
Project X (₹) Project Y (₹)
Initial Investment 1,20,000 1,20,000
Estimated cash inflows (per annum for 8 years)
Pessimistic 26,000 12,000
Most Likely 28,000 28,000
Optimistic 36,000 52,000
The cut off rate is 14%. The discount factor at 14% are:
Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Discount factor 0.877 0.769 0.675 0.592 0.519 0.456 0.400 0.351 0.308
Advise management about the acceptability of projects X and Y.
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 1
www.escholars.in
c) Y Limited requires ₹50,00,000 for a new project. This project is expected to yield 5
earnings before interest and taxes of ₹10,00,000. While deciding about the financial
plan, the company considers the objective of maximizing earnings per' share. It has
two alternatives to finance the project - by raising debt ₹5,00,000 or ₹20,00,000 and
the balance, in each case, by issuing Equity Shares. The company's share is currently
selling at ₹300, but is expected to decline to ₹250 in case the funds are borrowed in
excess of ₹20,00,000. The funds can be borrowed at the rate of 12 percent upto
₹5,00,000 and at 10 percent over ₹5,00,000. The tax rate applicable to the company
is 25 percent.
Which form of financing should the company choose?
d) The following is the information of XML Ltd. relate to the year ended 31-03-2018: 5
Gross Profit 20% of Sales
Net Profit 10% of Sales
Inventory Holding period 3 months
Receivable collection period 3 months
Non-Current Assets to Sales 1:4
Non-Current Assets to Current Assets 1:2
Current Ratio 2:1
Non-Current Liabilities to Current Liabilities 1:1
Share Capital to Reserve and Surplus 4:1
Non-current Assets as on 31st March, 2017 ₹ 50,00,000
Assume that:
i) No change in Non-Current Assets during the year 2017-18
ii) No depreciation charged on Non-Current Assets during the year 2017-18.
iii) Ignoring Tax
You are required to Calculate cost of goods sold, Net profit, Inventory, Receivables
and Cash for the year ended on 31st March, 2018
2. From the following information, find out missing figures and REWRITE the balance 10
sheet of Mukesh Enterprise.
Current Ratio = 2:1
Acid Test ratio = 3:2
Reserves and surplus = 20% of equity share capital
Long term debt = 45% of net worth
Stock turnover velocity = 1.5 months
Receivables turnover velocity = 2 months
You may assume closing Receivables as average Receivables.
Gross profit ratio = 20%
Sales is ₹21,00,000 (25% sales are on cash basis and balance on credit basis) Closing
stock is ₹40,000 more than opening stock.
Accumulated depreciation is 1/6 of original cost of fixed assets. Balance sheet of the
company is as follows:
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 2
www.escholars.in
Liabilities (₹) Assets (₹)
Equity Share Capital ? Fixed Assets (Cost) ?
Reserves & Surplus ? Less: Accumulated. Depreciation ?
Long Term Loans 6,75,000 Fixed Assets (WDV) ?
Bank Overdraft 60,000 Stock ?
Creditors ? Debtors ?
Cash ?
Total ? Total ?
3. Indel Ltd. has the following capital structure, which is considered to be optimum as 10
on 31st March, 2021:
Particulars (₹)
14% Debentures 60,000
11% Preference shares 20,000
Equity Shares (10,000 shares) 3,20,000
4,00,000
The company share has a market price of ₹47.20. Next year dividend per share is 50%
of year 2020 EPS. The following is the uniform trend of EPS for the preceding 10 years
which is expected to continue in future.
Year EPS (₹) Year EPS (₹)
2011 2.00 2016 3.22
2012 2.20 2017 3.54
2013 2.42 2018 3.90
2014 2.66 2019 4.29
2015 2.93 2020 4.72
The company issued new debentures carrying 16% rate of interest and the current
market price of debenture is ₹96.
Preference shares of ₹18.50 (with annual dividend of ₹2.22 per share) were also
issued. The company is in 30% tax bracket.
A) CALCULATE after tax:
i) Cost of new debt
ii) Cost of new preference shares
iii) New equity share (assuming new equity from retained earnings)
B) CALCULATE marginal cost of capital when no new shares are issued.
C) DETERMINE the amount that can be spent for capital investment before new
ordinary shares must be sold, assuming that the retained earnings for next year’s
investment is 50 percent of earnings of 2020.
D) COMPUTE marginal cost of capital when the fund exceeds the amount calculated
in (C), assuming new equity is issued at ₹ 40 per share?
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 3
www.escholars.in
4. MT Ltd. has been operating its manufacturing facilities till 31.3.2021 on a single shift 10
working with the following cost structure:
Per unit (₹)
Cost of Materials 24
Wages (out of which 60% variable) 20
Overheads (out of which 20% variable) 20
64
Profit 8
Selling Price 72
As at 31.3.2021 with the sales of ₹17,28,000, the company held:
(₹)
Stock of raw materials (at cost) 1,44,000
Work-in-progress (valued at prime cost) 88,000
Finished goods (valued at total cost) 2,88,000
Sundry debtors 4,32,000
In view of increased market demand, it is proposed to double production by working
an extra shift. It is expected that a 10% discount will be available from suppliers of
raw materials in view of increased volume of business. Selling price will remain the
same. The credit period allowed to customers will remain unaltered. Credit availed
from suppliers will continue to remain at the present level i.e. 2 months. Lag in
payment of wages and overheads will continue to remain at one month.
You are required to CALCULATE the additional working capital requirements, if the
policy to increase output is implemented, to assess the impact of double shift for long
term as a matter of production policy.
5.
a) Rambo Limited Has 1,00,000 equity shares outstanding for the year 2022. The 6
current market price of the shares is ₹100 each. Company is planning to pay dividend
of ₹10 per share. Required rate of return is 15%. Based on Modigliani-Miller
approach, calculate the market price of the share of the company when the
recommended dividend is 1) declared and 2) not declared.
How many new shares are to be issued by the company at the end of the year on the
assumption that net income for the year is ₹40 Lac and the investment budget is
₹50,00,000 when dividend is declared, or dividend is not declared.
PROOF that the market value of the company at the end of the accounting year will
remain same whether dividends are distributed or not distributed.
b) CALCULATE the level of earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) at which the EPS 4
indifference point between the following financing alternatives will occur.
i) Equity share capital of ₹60,00,000 and 12% debentures of ₹40,00,000.
Or
ii) Equity share capital of ₹40,00,000, 14% preference share capital of ₹20,00,000
and 12% debentures of ₹40,00,000.
Assume the corporate tax rate is 35% and par value of equity share is ₹100 in each
case.
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 4
www.escholars.in
6.
a) State four tasks involved to demonstrate the importance of good Financial 4
Management.
b) Explain Electronic Cash Management System. 4
c) Define Internal Rate of Return (IRR) 2
Or
Explain in brief the following bonds: 2
i) Callable Bonds
ii) Puttable Bonds
Section – B (Economics for Finance)
1. From the following data calculate (a) Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost, and (b) 5
Gross Domestic Product at Market price.
Items ₹ (in Crores)
Gross national product at factor cost 6150
Net exports (−) 50
Compensation of employees 3,000
Rent 800
Interest 900
Profit 1,300
Net indirect taxes 300
Net domestic capital formation 800
Gross domestic capital formation 900
Factor income to abroad 80
2. i) How real GDP is a better measure of economic well-being? Explain. 2
ii) Illustrate with an example the redistribution effect of a tax and transfer policy. 3
3. i) The government decides to levy up to ₹ 20,500/ per flight from private airlines 3
on major routes in order to fund an ambitious regional connectivity scheme
which seeks to connect small cities by air and to make flying more affordable for
the masses. Critically, examine the implications of this policy on the airlines
market.
ii) Define Common Access Resources. Why they are over-used? Explain. 2
4. i) What criteria are used to distinguish between pure and impure public goods? 2
ii) Which type of Government interventions are applied for correcting information 3
failure.
5. i) Explain the objectives of Fiscal Policy. 2
ii) Distinguish between ‘pump priming’ and ‘compensatory spending’ 3
6. a) 2
i) Calculate velocity of money
Money Supply 5000 billion
Price = 110 billion
Volume of transaction = 200
ii) What will be the outcome if volume of transactions increases to225?
b) Calculate liquidity aggregate L2 when the following information is given- 3
Particulars ₹ (in crore)
Term deposits with term lending institutions 750
Term borrowing by refinancing institutions 450
All deposits with post office savings banks 1320
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 5
www.escholars.in
Term deposits with refinancing institutions 590
Certificate of deposits issued by FIs 290
Public deposits of non-banking financial companies 450
M3 2650
National saving certificates 240
7. i) How is the behaviour of central bank in economy reflected? Explain. 3
ii) What is the major idea behind Mercantilist’s view of trade? 2
8. a) The price index for exports of Country A in year 2012 (2000 base-year) was 116.1 3
and the price index for Country A’s imports was 120.2 (2000 base- year).
i) What do these figures mean?
ii) Calculate the index of terms of trade for Country A.
iii) How do you interpret the index of terms of trade for Country A?
b) What do you mean by anti-dumping duties? 2
888 888 0402 support@escholars.in 6
You might also like
- J8. CAPII - RTP - June - 2023 - Group-IIDocument162 pagesJ8. CAPII - RTP - June - 2023 - Group-IIBharat KhanalNo ratings yet
- CPA 10 - Financial ManagementDocument10 pagesCPA 10 - Financial ManagementAbby KiweewaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Quarterly Examination Q FINALDocument11 pagesClass 12 - Quarterly Examination Q FINALsubbuNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper 2: Financial Management & Economics for FinanceDocument6 pagesMock Test Paper 2: Financial Management & Economics for FinanceMayank RajputNo ratings yet
- RTP Dec 2021 Cap II Group IIDocument106 pagesRTP Dec 2021 Cap II Group IIRoshan KhadkaNo ratings yet
- 05 Challenger Series FM All ChaptersDocument26 pages05 Challenger Series FM All Chapterssujalpratapsingh71No ratings yet
- CA Intermediate Mock Test Eco FM 16.10.2018 EM Only QuestionDocument6 pagesCA Intermediate Mock Test Eco FM 16.10.2018 EM Only QuestionTanmayNo ratings yet
- SFM New Sums AddedDocument78 pagesSFM New Sums AddedRohit KhatriNo ratings yet
- FM MTP MergedDocument330 pagesFM MTP MergedAritra BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Paper 8 Financial Management & Economics For Finance PDFDocument5 pagesPaper 8 Financial Management & Economics For Finance PDFShivam MittalNo ratings yet
- Cost of Capital Analysis & Project AppraisalDocument2 pagesCost of Capital Analysis & Project AppraisalAmitNo ratings yet
- GTU MBA Semester 2 Financial Management Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesGTU MBA Semester 2 Financial Management Exam QuestionsAmul PatelNo ratings yet
- FM RTP Merge FileDocument311 pagesFM RTP Merge FileAritra BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument6 pages© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiatilokiNo ratings yet
- MBA 5109 - Financial Management (MBA 2020-2022)Document6 pagesMBA 5109 - Financial Management (MBA 2020-2022)sreekavi19970120No ratings yet
- BBA-V 551 Subjective Dec 2016Document2 pagesBBA-V 551 Subjective Dec 2016Saif ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam FM Summer 2021Document2 pagesFinal Exam FM Summer 2021AAYAN FARAZNo ratings yet
- 8) FM EcoDocument19 pages8) FM EcoKrushna MateNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2: Strategic Financial Management Questions Sensitivity AnalysisDocument27 pagesPaper - 2: Strategic Financial Management Questions Sensitivity AnalysisRaul KarkyNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem-FM - Model QP by Srijita Datta and Arunangsu Das Sarma-26Apr2020Document15 pages6th Sem-FM - Model QP by Srijita Datta and Arunangsu Das Sarma-26Apr2020Kashish GroverNo ratings yet
- Subject: Financial Management: Faculty: Dr. Sitangshu KhatuaDocument4 pagesSubject: Financial Management: Faculty: Dr. Sitangshu KhatuaMittal Kirti MukeshNo ratings yet
- 48 17228rtp Ipcc Nov09 Paper3bDocument33 pages48 17228rtp Ipcc Nov09 Paper3bemmanuel JohnyNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation QuestionsDocument9 pagesEquity Valuation Questionssairaj bhatkarNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT EXAMDocument6 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT EXAMsubhasis mahapatraNo ratings yet
- CA Final Paper 2Document32 pagesCA Final Paper 2MM_AKSINo ratings yet
- Paper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Section - A: Financial ManagementDocument27 pagesPaper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Section - A: Financial ManagementSakshi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- MTP Oct. 2018 FM and Eco QuestionDocument6 pagesMTP Oct. 2018 FM and Eco QuestionAisha MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure Problems SolvedDocument6 pagesCapital Structure Problems SolvedArundhathi MNo ratings yet
- FM Smart WorkDocument17 pagesFM Smart WorkmaacmampadNo ratings yet
- ABM 801 Financial Management Question BankDocument9 pagesABM 801 Financial Management Question BankneetamoniNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper - II for Intermediate (New) Group - II Paper 8A: Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesMock Test Paper - II for Intermediate (New) Group - II Paper 8A: Financial ManagementHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Firm Value Through Optimal Financing DecisionsDocument16 pagesMaximizing Firm Value Through Optimal Financing DecisionsTanmay AroraNo ratings yet
- Financial Management-1Document6 pagesFinancial Management-1chelseaNo ratings yet
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument26 pages© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaChandana RajasriNo ratings yet
- SFM RTP Nov 22Document16 pagesSFM RTP Nov 22Accounts PrimesoftNo ratings yet
- FM Eco 100 Marks Test 1Document6 pagesFM Eco 100 Marks Test 1AnuragNo ratings yet
- 1. Rajdhani College FM Assignment finalDocument6 pages1. Rajdhani College FM Assignment finalayushkorea52629No ratings yet
- Question No. 1 Is Compulsory. Attempt Any Four Questions From The Remaining Five Questions. Working Notes Should Form Part of The AnswerDocument5 pagesQuestion No. 1 Is Compulsory. Attempt Any Four Questions From The Remaining Five Questions. Working Notes Should Form Part of The AnswerItikaa TiwariNo ratings yet
- RTP CA Final New Course Paper 2 Strategic Financial ManagemeDocument26 pagesRTP CA Final New Course Paper 2 Strategic Financial ManagemeTusharNo ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument3 pagesCost of CapitalkimjethaNo ratings yet
- Ca Final Strategic Financial Management Full Test 1 May 2022 Test Paper 1644507041Document12 pagesCa Final Strategic Financial Management Full Test 1 May 2022 Test Paper 1644507041itaxkgcNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Doc-401 FIM - 24042016113313Document10 pagesAssignment - Doc-401 FIM - 24042016113313Ahmed RaajNo ratings yet
- 44956mtpbosicai Final QP p2Document7 pages44956mtpbosicai Final QP p2Shubham SurekaNo ratings yet
- FM - Assignment Batch 19 - 21 IMS IndoreDocument3 pagesFM - Assignment Batch 19 - 21 IMS IndoreaskjdfaNo ratings yet
- 4201 (Previous Year Questions)Document13 pages4201 (Previous Year Questions)Tanjid MahadyNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Questions Cover Financial, Treasury and Forex ManagementDocument5 pagesFinal Examination Questions Cover Financial, Treasury and Forex ManagementKaran NewatiaNo ratings yet
- 73153bos58999-p8Document27 pages73153bos58999-p8Sagar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Part A: Financial Management Questions Ratio AnalysisDocument29 pagesPaper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Part A: Financial Management Questions Ratio AnalysisBharat NotnaniNo ratings yet
- Financial Decision MakingDocument4 pagesFinancial Decision MakingHarsh DedhiaNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument7 pagesCapital StructurePrashanth MagadumNo ratings yet
- February 2017 Subject: Financial Management 2 FM: 100 Program: BBA Semester V PM: 50 Subject Code: BBK2233 Time: 3hrsDocument3 pagesFebruary 2017 Subject: Financial Management 2 FM: 100 Program: BBA Semester V PM: 50 Subject Code: BBK2233 Time: 3hrsAditi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Paper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Part A: Financial Management Questions Ratio AnalysisDocument29 pagesPaper - 8: Financial Management and Economics For Finance Part A: Financial Management Questions Ratio AnalysisEFRETNo ratings yet
- Cost of capital tutorialDocument3 pagesCost of capital tutorialNhi HoangNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII SUMMER HOLIDAY HOMEWORK ALL MERGEDDocument97 pagesCLASS XII SUMMER HOLIDAY HOMEWORK ALL MERGEDRevathi KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- ACCA F9 Financial Management Solved Past PapersDocument304 pagesACCA F9 Financial Management Solved Past PapersSalmancertNo ratings yet
- Business Finance 2011Document2 pagesBusiness Finance 2011Sita ChapaiNo ratings yet
- Instructions For CandidatesDocument3 pagesInstructions For Candidatesshubham jagtapNo ratings yet
- DIVIDEND INVESTING: Maximizing Returns while Minimizing Risk through Selective Stock Selection and Diversification (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDIVIDEND INVESTING: Maximizing Returns while Minimizing Risk through Selective Stock Selection and Diversification (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Fiscal Decentralization Reform in Cambodia: Progress over the Past Decade and OpportunitiesFrom EverandFiscal Decentralization Reform in Cambodia: Progress over the Past Decade and OpportunitiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Risk Assesment - Internal ControlDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Risk Assesment - Internal ControlVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- GST Ca Interg9 QuestionDocument6 pagesGST Ca Interg9 QuestionVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- Audit Ca Inter QuestionDocument5 pagesAudit Ca Inter QuestionVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- Patliputra University, Patna: College Code & Name: 205 - COLLEGE OF COMMERCE, ARTS AND Science, PatnaDocument1 pagePatliputra University, Patna: College Code & Name: 205 - COLLEGE OF COMMERCE, ARTS AND Science, PatnaVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- 4 Process CostingDocument12 pages4 Process CostingVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- CA Inter Cost & Management Accounting Marginal Costing ProblemsDocument10 pagesCA Inter Cost & Management Accounting Marginal Costing ProblemsVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet
- PATLIPUTRA UNIVERSITY B.COM PART 1 RESULTDocument1 pagePATLIPUTRA UNIVERSITY B.COM PART 1 RESULTVishal Kumar 5504No ratings yet