Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Ken_nerve0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views58 pagesIntroduction to Data Analytics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntroduction to Data Analytics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views58 pagesLesson 1
Uploaded by
Ken_nerveIntroduction to Data Analytics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 58
Introduction to Data Analytics
Rola)
Sie eel sii
Copyright ©2020, Smartademy Pt, Lid Al ights reserved,
Raise hands if you are.
a. Currently working, have not
done any data analytics
b. Currently studying, have not
done any data analytics
¢. Have done some data
analytics in the past
2. Share with the class your name,
what you do, and a brand/ company
that you think kicks ass in data
analytics
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
‘Smarteademy
at
How to get the most rete)
1. Practical > theoretical. Get involved!
2. Be data-driven. Not just a buzzword, time to get your hands dirty.
3. Intellectual curiosity. Don't hesitate to ask any questions.
a. Zoom Q&A, Chat
b. Telegram
4. Apply learnings in context. It’s all about what business you are working on.
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. eel
Lesson 1: Learning Objectives
What is data analytics?
2. Why is data analytics important?
3. Course Roadmap
4. Howdo we define our problem statement and identity key metrics for our
business objective
5. Which are the key method we should consider for our data analytics
problem statement
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. eel
VE mee Pelee atotoed
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
What my parents think I do What society thinks | do
What my boss thinks | do PTE Aiea MUL @ (oF
it does a data analytics analyst do?
Va Re-Ceitc WVae [oy
El ae WAU Wt ered
Data analytics involves 9
examining massive amounts _?
of data to uncover hidden ©
patterns, correlations and
other insights to drive decision ~
making in companies of all sizes.
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
Analytics 1.0 Analytics 2.0
The era of “business
intelligence”.
The basic conditions of the Analytics
For the first time, data about 1.0 period predominated for half a
production processes, sales, century, until the mid-2000s, when
‘customer interactions, and internet-based and social network
more were recorded, firms primarily in Silicon
aggregated, and analysed. Valley—Google, eBay, and so
on—began to amass and analyze
new kinds of information,
The era of big data
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. All sights reseed
Analytics 3.0
The era of data-enriched
offerings
ci
Analytics 3.0 marks the point
when other large organizations
started to follow suit.
Today it's not just information
firms and online companies
that can create products and
services from analyses of data.
It's every firm in every industry.
Why is Data Analytics important?
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
Case Study 1: Predicting and understanding attrition rates
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved.
“Why do people
leave companies?”
Is a complicated question.
But according to OCBC
Bank's head of group
human resources, the
answer lies in the data.
Case Study 2: Insurance Analytics in Tableau
INSURANCE FRAUD OVERVIEW ti
2,270 90M $33,721
ee
tie ty
:
Ta a
= SAU cies ance
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved. Source: Hitachi-solutions
How to do Data Analytics?
Define the question or goal behind the Collect the right data to Perform data cleaning to improve data quality
analysis: what are you trying to discover? and prepare it for analysis and
help answer this question. interpretation-getting data into the right format,
getting rid of unnecessary data, correcting
spelling mistakes, etc.
Manipulate data. This may include Analyze and interpret the data Present this data in meaningful ways: graphs,
plotting the data out, creating pivot using statistical tools (Le visualizations, charts, tables, etc.
tables, and so on. finding correlations, trends,
outliers, etc.) Data analysts may report their findings to project
‘managers, department heads, and senior-level
business executives to help them make decisions
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved. ‘and spot patterns and trends.
Course Roadmap
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
Python is @ programming language for statistical computing
‘and graphics,
itis widely used among statisticians, data miners, data
analysts, business analysts, and data scientists for
developing statistical software, data analysis, machine
learning and 9.0n,
‘SQL (Structured Query Language) isa language used to
interact with databases that store data, allowing us to
retrieve dota quickly and easily.
Data visualization helps key decision-makers in a business
(usually non-tech senior execs) see analytics presented
visually in graphs, charts, etc. so they can identify trends
cond pattems and understand complex information
Copyright © 2020, Smarteademy Pte. Ltd. All rghts reserved.
“Python gives aspiring analysts and data scientists,
the ability to represent complex sets of data in an
impressive way" Python has been adopted by many
high-profile companies ike Google and Facebook as.
the language of choice to analyze dato.
‘SQL cllows you to perform operations on milions of
rows of data. I's the 2nd most in-demand skil for data
anaiysis jobs (only after data analysis tse
It you are creative, this may be the perfect skil to
learn. Learning data visualization can give you an
edge over other job applicants since employers are
looking for people who understand both the science
‘and art behind dota analysis.
What to Expect from this Course
Ue ea gm atts Detar ansl ies
TSE | irivriitpeteweny) © Data Analytics objectives and case studies in finance industry
Data Analytics landscape
EM |) Sainte Daa Types
bata Stuctures
+ Fundamenas of Statist
ped Basic statistics using python
{Exploratory Data Anas
‘Introduction to Data Visualisation
ory ‘¢ Identifying the right chart to use
‘¢ Introduction to web crawlers
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
Smartcademy
What to Expect from this Course
esr
ae ee outelna, a Dashboard Creation & Formatting
A Aad * Storytelling skills
Mock Presentations [PME Iareiad
en Porc) © Course Review
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
Smartcademy
In order to pass this
course, students need to:
1. Pass a minimum of 3
MCQ tests
AND
2. Pass their Capstone
Project
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd Allrghts reserve.
MCQ Quiz (25 Before Lesson2 | 13
Questions)
MO Quiz (25 Before Lesson3 [13
Questions)
MO Quiz (25 Before Lesson [13
Questions)
MO Quiz (25 Before Lesson5 | 13
Questions)
MO Quiz (25 Before Lessoné | 13
Questions)
MO Quiz (25 Before Lesson? [13
Questions)
Capstone Project, Referto instructor | Referto
Dashboard
Rubrics
Copyright © 2020, smartcademy Pte Ltd. All rights reserves
For your fnal capstone project you should
‘© Prepare a 10 page slide deck in response to one ofthe three case studies, and
‘showhow you address them through your data analytics techniques.
‘© Your slide deck should cover the following:
1
2.
Define your business objective or problem statement and identify relevant
metrics
Identity lealy the sources of data and steps taken extract the data from the
Collect, consolidate and organise the data
Exploratory data analysis to ensure the data integrity and data quality is
‘suticient to conduct analysis
Working Tableau Dashboard wth a minimum of different chart types that
hhelp address the problem statement
‘Showproper data analysis to approach the chosen case study
Using the dashboard, demonstrate how you can derive data driven
decisions
‘© Design a dashboard that can visualize your data. The dashboard should showat
least two diferent charts (ine charts, maps, bar charts, etc.) and idertity 2
recommendations or 2 insights based on your detned problem statement. Focus on
‘the organization ofthe dashboard, the use of colors, the labeling ofthe axes, to
‘ensue i looks professional
‘Smarteademy
Data Analytics
Pa)
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
alytical concepts
> Descriptive analytics
@ utilizes data to understand past and present
> Predictive analytics
@ analyzes past performance to predict the future
> Prescriptive analytics
@ uses optimization techniques to recommend the best solution
Copyright 2020, Smartcademy Pt. Ltd. Al rights reserve. a
Analytical concepts
> Data aggregation » Snapshot ofthe past > When you want fo
EEE (eee > Data mining » Limited abilty o ‘summarize results for
apy ete clan ‘Quide decisions allpart of your
business
» Statistical models » Guess at the future > When you want to
ile > Simulation Helps inform fow ‘make an educated
roy oa complexity decisions guess at likely results
Optimization models» Most effective where * When you have
(ore > Heuristics you have more Jimportant. complex or
control over whet ie ‘time-sensitive
Oe
being mode decisions to make
nalytical concepts ta Science
lOptimization “What's the best that can happen?"
Prescriptive Analytics
Randomized Testing “What if we try this?”
Predictive Modeling/
“What will happen next?”
Forecastin, ee Predictive Analytics
[Statistical Modeling “whys this happening?”
lAlerts “what actions are needed"
lQuery/Drill Down “What exactly is the problem?"
Descriptive Analytics
|Ad hoc reports/ “How many, how often, where?”
|Scorecards
|standard Reports “What happened?” cnrpree Andy testy Oevenprt
2
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved.
Quick introduction to Data
An Overview
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
EEN
amor
4Vs of Big Data
OLUME
ARIETY
ELOCITY
ERACITY
DATA: BY THE NUMBERS
Initial approa
e@ UNDERSTAND the data
o Where is it from?
o What does it represent?
o When was it collected?
o Does it potentially contain errors?
e Qualitatively analyze each variables
first
o Are they important?
o Are they related to other variables?
= Ill
ca
e Exploring actual data
o Data types
o Common values/ outliers
o Errors
o Summarizing each columns (variables)
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd. Allrghts reserved. “
Words Numbers
Unstructured Structured
Can be observed, hard to measure Can be measured
Quality is important Quantity is important
Types of Data
Discrete
e Can be counted as opposed to being measured
e Fixed Values within a Fixed Range
e Eg. Time in hours, Days in a wee!
¢ Continuous
e Can_take on an infinite range of values
e E.g. Temperature, Weight
36
ypes of Da
Categorical
© Nominal Data
¢ No quantitative relationships between each other
e Example: Students’ race — ['Chinese’, ‘Malay’, ‘Indian’, ‘Others’]
© Ordinal Data
© Quantitative relationships present, can be ordered
fuents’ weight category— [‘Underweight’, ‘Normal’,
37
ypes of Data - Quantitative
¢ Interval Data
¢ Similar to ordinal data, but with constant differences
e Example: Students’ score — [10, 20,30, 40]
* No meaning in ratio: Student who scored 40 does not means they are
4times smarter than students scoring 10
Ratio Data
¢ Ratios are meaningful
e Example: Students’ actual weight in kg— [40, 60, 80, 90]
38
ns to ask about the data
Nature of the data
* If data is ordinal/interval/ratio, will it make sense of it is sorted?
+ Is there a range for possible values?
* What are the mathematical operations we can perform on the values?
39
If | would like to find out whether number of bedrooms or reviews affect
overall satisfaction, will all of the data be relevant?
roams siey sd __onki6 Tom.Npe enuney —_ohy_bogh ralgbntaed vis over tcton sosommodaiNs betas
© oreo amo cristo SHO tan Shame MN MA 8 as 10
+ syysmoo rano ssemeeno SMO? nan Shon MN TIT 180 so wo 1
2 sossro amo srosseno SMO nan Seon MN MRD oo wo 10
3 ome rane eeatmao SMO? naw Shop NN MAD 00 eo wo 1
4 tomo rao cota SMO nam Seon MM 18 oo 1
© suze raano sterseso SMO? naw Shot MN MAG eo 2
© soresico ramo storocso SMO nan Seon MN TST 1 oo wo
40
umm ng Datase
+Astatistic is a a fact or piece of data obtained from a study of a
large quantity of numerical data. Let's start with basics:
* Mean: Average of a numerical quantity
*eg.:[1, 2,7, 10,15] +7
: “The middle item” (requires an ordering)
1,2, 7,10, 15] >7
2, 7,8, 10, 15] > 7 to 8 (Some would say (7+8)/2 = 7.5)
‘shortest; ‘short’ , ‘average; ‘tall, ‘tallest’] > ‘average
‘shortest, ‘short’ , ‘tall, ‘tallest’] > ‘short’ or ‘tall (cannot divide by 2)
lost frequently occurring item
*e.g.:[1.2,2,7,10] +2
a
The 5 Number Summ
1. Minimum: Smallest value
2. First/Lower Quartile: 25% of the collection is less than or equal this
3. Median / 2nd Quartile: 50% of the collection is less than or equal this;
50% of the collection is greater than or equal to this
4. Third/Upper Quartile: 75% of the collection is less than or equal this
5. Maximum: Largest value
Lonmerquariie Median —_Upperquartle
(singapore oata science scadery 2
arson’s Correlatio'
Correlation (the Pearson correlation coefficient) measures the strength and direction of
the linear relationship between two variables and can take on any value between -1 and +1.
e Values close to -1 or +1 indicate a strong and linear relationship between the two variables.
e Values close to 0 indicate a weak and/or nonlinear relationship between the two variables.
e Values above 0 indicate a positive relationship between the two variables.
e Values below 0 indicate a negative relationship between the two variables.
Correlatio
= ‘Cunviinear |
rong negative relationship
Data Quality Standards
Pa)
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
ai
Completeness / Comprehensiveness
Consistency
Accuracy
Format
Timeframe
Validity / Integrity
1.
‘ta Quality Standards
Completeness / Comprehensiveness: Ask what essential fields have to be
filled in for a dataset to be considered complete. For example, Name and
address may be crucial to the completeness of the data, while a customer’s
gender is less essential.
Possible Questions you can ask:
1. Are there any optional fields in the data collected?
2. Isall the necessary information available?
3. Do any data values have missing elements? Or are they unusable?
‘a Quality St
rds
2. Consistency: All iterations of a piece of data should be the same. Take a given
month's web traffic for example - in every report, platform, or spreadsheet, is the
number of website visits in that month the same? Or, are there inconsistencies
across these data? A lack of consistency in these points could lead to confusion
down the road.
Possible questions you can ask:
1. Are data values the same across the data sets?
2. Are there any distinct occurrences of the same data instances that
provide conflicting information?
ita Quality Standards
3. Accuracy: While consistency is about having the same value across all
channels, accuracy is about ensuring those consistent values are correct and
closely reflecting the reality of the results.
Possible questions you can ask:
1. Do data objects accurately represent the “real world” values they are
expected to model?
2. Are there incorrect spellings of product or person names, addresses,
and even untimely or not current data?
ita Quality Standards
4. Format: To avoid inaccuracy or confusion, make sure data entry formats are
consistent. For example, you do not want the year to be entered in some
locations as ’19 and in other locations at 2019.
Possible questions you can ask:
1. Do data values comply with the specified formats?
2. Ifso, do all the data values comply with those formats? Maintaining
conformance to specific formats is important.
‘ta Quality Standards
5. Timeframe: Timeliness of data refers to whether decisions marketers have
data insights at the optimal time, and ho current the data is. Do you have the
data when you need it, and are you referencing the most up to date version of
the dataset?
Timeliness depends on:
‘Companies that are required to publish their quarterly results within a given frame of time
‘Customer service providing up-to date information to the customers
Credit system checking in real-time on the credit card account activity
The timeliness depends on user expectation. Online availability of data could be required for room
allocation system in hospitality, but nightly data could be perfectly acceptable for a billing system.
‘ey Data Quality St
rds
6. Validity / Integrity: This criteria looks as whether a dataset follows the rules
and standards set. Are there any values missing that can harm the efficacy of the
data or keep analysts from discerning important relationships or patterns?
Possible questions you can ask:
1. Is there are any data missing important relationship linkages?
OTL Meee eda
PM emer Cerone
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
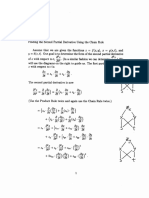
RS Sica Cy
100 x (1 + .08) = 108
Monthly Rate = (1+ >)
= Pyne
A=Px(1+7)
Hands-on!
Recap of Lesson 1
What is Data Analytics
Data Analytics Use Cases in Finance Industry
Types and Sources of Data
Data Quality Standards
RWNP
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. agp Smortondemy
Case Studies
* MCQs
© Case Study 1:
https://Awww.pwe.com/id/en/publications/Actuarial/d
ata-analytics-financial-services.pdf
Case Study 2:
https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Busin
ess%20Functions/Marketing%20and%20Sales/Our%2
Olnsights/EBook%20Biq%20data%20analytics%20and
%20the%20future%200f%20marketing%20sales/Big-D
ata-eBookashx
Case Study 3:
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/glo
bal/Documents/Financial-Services/qx-be-aers-fsi-credi
t-scoringpdf
Copyright © 2020, smarteademy Pte. Ltd Allrghts reserve.
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
THANK YOU
Copyright ® 2020. Smartcademy Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. a
You might also like
- Lesson 5Document47 pagesLesson 5Ken_nerveNo ratings yet
- Sequence & ProofsDocument13 pagesSequence & ProofsKen_nerveNo ratings yet
- 36 DebroglieDocument2 pages36 DebroglieBrandon GurrellNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Interference and Diffraction PDFDocument21 pagesCH 19 Interference and Diffraction PDFKen_nerveNo ratings yet
- 21 Electrical Potential PDFDocument27 pages21 Electrical Potential PDFKen_nerveNo ratings yet
- SecondPartial PDFDocument1 pageSecondPartial PDFKen_nerveNo ratings yet
- ACJC GP Prelims 2011 Paper 1Document2 pagesACJC GP Prelims 2011 Paper 1Shubhasheesh PrakashNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)