Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forces
Forces
Uploaded by
Ezaan Haque0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageForces
Forces
Uploaded by
Ezaan HaqueCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
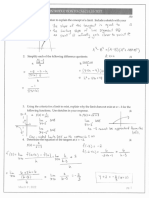
Bh
a
2223N
45kg
& = 4.9 mist
Statement: The acceleration when puling the crate
is 4.9 mist
Sample Problem 2: Overcoming Static Friction
‘crate is placed on an inclined board as shown in Figure 5.
(One end ofthe board is hinged so thatthe angle @is adjustable.
The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the board
[s 0.30, Determine the angle at which the crate just begins to sip
hinge
2s
Figure 5
Given: 1s ~ 0.30
Required: @
‘Analysis: The force of static friction on the crate can be as
large as F, = gh, Where Fy is the normal force. First draw
the FBD of the crate. Then calculate the normal force using
the y-components. Then calculate the angle @ using the
x-components and the fact that the abject isin equilibrium:
Solution:
‘Sample Problem
Figure 6 shows two blocks joined witha rope that runs over
pulley. The mass of m, Is 5.0 kg, and the incline is 35°.
The coefficient of static friction between m, and the incined
plane is 0.25, Determine the largest mass for m, such that both
blocks remain at rest
ni ae
88 Chapter 2+ Dynamics
(6) Statement: The worker should pull the erate because
pulling decreases the normal force on the crate.
Consequently, the force of friction is less, which
Produces a greater acceleration
3h, = +h + CF,c0s 0)
0= Fy F,cos
Fy = Fos
A= ashi
ssl F 0s )
Fe = nsFyc080
2A= +hsine —
0= Ashe —
Fsine =F
Resin = yaF;cos0
sino
wean
sind
te = tano
and = ns
@ = tans
= tar1(030)
air
‘Statement: The angle at which the crate just begins to slip
is 17
alculating Mass in Friction Problems
Given: m,
Required: m,
‘Analysis: Draw an FBD ofthe situation, As long as the blocks are
at rest, the tension in the rope Is equal tothe force of gravity on
My Fe = Fa = mo.
Now consider m, To remain at rest, the net force must also
be zero, First, use the y-components to determine the normal
force; then use the x-components to calculate m,
5.0 kg; 6 = 35%; ws = 0.25
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pe2e I2St - 242 4260 7 100 - : Polynomial Equations and Inequalities AssignmentDocument8 pagesPe2e I2St - 242 4260 7 100 - : Polynomial Equations and Inequalities AssignmentEzaan HaqueNo ratings yet
- U6Document4 pagesU6Ezaan HaqueNo ratings yet
- S (3) Tes (%) 3) (2) : Sin /8T 3r/ SM (2m - 7Document4 pagesS (3) Tes (%) 3) (2) : Sin /8T 3r/ SM (2m - 7Ezaan HaqueNo ratings yet
- Decimal Review 5-6Document9 pagesDecimal Review 5-6Ezaan HaqueNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument4 pagesQuizEzaan HaqueNo ratings yet