Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cases of Pronouns Lecture
Cases of Pronouns Lecture
Uploaded by
majoy140 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pagePronouns are used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. There are three types of personal pronouns: first person refers to the speaker, second person refers to the person being spoken to, and third person refers to the person being spoken about. Pronouns have different cases depending on their function in a sentence - nominative, objective, and possessive. Nominative pronouns are subjects and subjective complements. Objective pronouns are direct and indirect objects and objects of prepositions. Possessive pronouns show ownership.
Original Description:
compilation of information about cases of pronouns
Original Title
CASES OF PRONOUNS LECTURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPronouns are used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. There are three types of personal pronouns: first person refers to the speaker, second person refers to the person being spoken to, and third person refers to the person being spoken about. Pronouns have different cases depending on their function in a sentence - nominative, objective, and possessive. Nominative pronouns are subjects and subjective complements. Objective pronouns are direct and indirect objects and objects of prepositions. Possessive pronouns show ownership.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCases of Pronouns Lecture
Cases of Pronouns Lecture
Uploaded by
majoy14Pronouns are used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. There are three types of personal pronouns: first person refers to the speaker, second person refers to the person being spoken to, and third person refers to the person being spoken about. Pronouns have different cases depending on their function in a sentence - nominative, objective, and possessive. Nominative pronouns are subjects and subjective complements. Objective pronouns are direct and indirect objects and objects of prepositions. Possessive pronouns show ownership.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
A
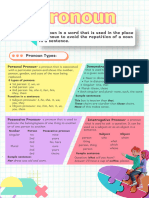
pronoun is a word that replaces a noun in a sentence. Pronouns are used to avoid repeating the same nouns over
and over again.
Personal Pronouns- take the place of specific nouns that name people, places and things. Personal pronouns are used
instead of a name to avoid repetition and to help ease the flow of sentences.
First person is the person speaking (or writing).
Second person is the person (or possibly persons) being spoken to or written to.
Third person is the person (or persons) being spoken or written about.
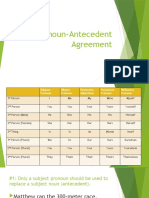
A. Nominative Case/Subjective Case
Functions:
1. subjects -The one being talk about, the doer of the action.
He is my friend.
You have some ice cream.
2. subjective complements. (A subjective complement is a noun or pronoun which follows a linking
verb (am, is, was, are, were, be, seem, appear, has, have, had) and is the same as the subject.)
It was she on the phone.
The superhero was he.
B. Objective C
C. ase –
Functions:
1. direct objects- a thing or a person who received the action of the verb.
John kicked him.
Mr. Smith fired them after what happened.
2. indirect objects- ask “to whom/what?” or “for whom/what” the direct object is intended. The indirect
object will chronologically exist before the direct object in a sentence.
Mom gave me money.
Tristan sent her flowers and chocolates.
3. objects of prepositions- the pronoun that comes after the preposition is called the object of
the preposition.
Sue sold the house (to them).
For us, the final examination was difficult.
C. Possessive Case – used to show ownership.
Examples: Karen had her hair cut yesterday.
Those books are theirs.
Roger will mail my letter for me.
The cat caught its paw in the fence.
You might also like
- English Grammar - Part 1Document36 pagesEnglish Grammar - Part 1Ibsadin MustefaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - PronounsDocument25 pagesGrammar - PronounsSvetlana StefogloNo ratings yet
- Personal PronounsDocument13 pagesPersonal PronounsMaryurys SalasNo ratings yet
- What Are Pronouns?Document16 pagesWhat Are Pronouns?Sheilah Mae PadallaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAccu Xii BhianNo ratings yet
- Uses and Properties of NounsDocument4 pagesUses and Properties of NounsJovielene Mae Sobusa100% (1)
- ENHANCEMENT COURSE Uses and Properties of NounsDocument4 pagesENHANCEMENT COURSE Uses and Properties of NounsJovielene Mae SobusaNo ratings yet
- LECTURESDocument7 pagesLECTURESNimrod CabreraNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument7 pagesLecturesNimrod CabreraNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns and Verb "To Be"Document13 pagesPersonal Pronouns and Verb "To Be"Maryurys SalasNo ratings yet
- ENGL 102 - Nouns and PronounsDocument9 pagesENGL 102 - Nouns and Pronounsjoy05.alexa.01No ratings yet
- Parts of Speech (April)Document131 pagesParts of Speech (April)April M Bagon-FaeldanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Structure of EnglishDocument17 pagesLesson 1-Structure of EnglishMay Rhea Siapno LopezNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Bhs InggrisDocument45 pagesPronoun Bhs InggrisCut Raudahtul FitriNo ratings yet
- Nish-Handouts 2 (Long 2 Copies)Document4 pagesNish-Handouts 2 (Long 2 Copies)Souma MagarangNo ratings yet
- Pronoun-Antecedent AgreementDocument29 pagesPronoun-Antecedent AgreementJoshua Tala-ocNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01Document41 pagesPronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01John Harvey Magos0% (1)
- ProunounDocument12 pagesProunounRowell BosquillosNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns: All You Need To Know!Document11 pagesPersonal Pronouns: All You Need To Know!Oper SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- PronoundsDocument10 pagesPronoundsAbigail GoloNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument3 pagesPronounsredouanestudiesNo ratings yet
- Case of PronounDocument13 pagesCase of PronounLykaNo ratings yet
- Personal PronounsDocument6 pagesPersonal PronounsIma MariyamaNo ratings yet
- The Simple SentenceDocument5 pagesThe Simple SentencePetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun: Thresia Trivict Semiun, S.PD., M.PDDocument21 pagesPersonal Pronoun: Thresia Trivict Semiun, S.PD., M.PDThresia Trivict SemiunNo ratings yet
- A01 Act#1 IBALEDocument6 pagesA01 Act#1 IBALELester IbaleNo ratings yet
- Basic EnglishDocument45 pagesBasic EnglishPacatang EvelynNo ratings yet
- CS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFDocument25 pagesCS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFMark Anthony CasupangNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument43 pagesPronounsanneNo ratings yet
- Hybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Document10 pagesHybrid English 4 Q2 M3 W3Jedasai PasambaNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Usage of PronounsDocument60 pagesGrammatical Usage of PronounsMuffin DyNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Reference SheetDocument2 pagesPronouns Reference SheetdevorehumanitiesNo ratings yet
- Materi Tutor Structure 1Document10 pagesMateri Tutor Structure 1Rosa LindaNo ratings yet
- Final ModulemoduleeeeDocument10 pagesFinal ModulemoduleeeeReshnee TabañagNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument11 pagesPronounsSohelfariza UlfaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech-1Document7 pagesParts of Speech-1Chithra ShreeNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument26 pagesPronounsSteven DaviesNo ratings yet
- What Is The Objective Case?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Objective Case?Ikra MalikNo ratings yet
- Anglais ST2 AdouiDocument7 pagesAnglais ST2 AdouiŘãýãńë BëłNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns: Uses, Charts, and ExamplesDocument4 pagesPersonal Pronouns: Uses, Charts, and ExamplesSam YanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke-3 - PronounsDocument4 pagesPertemuan Ke-3 - PronounsNurul FitriaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun BingDocument4 pagesPronoun BingInnaufa QonitaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun CasesDocument9 pagesPronoun CasesGerald TuganoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 1Document2 pagesPronouns 1SMbunnyleeNo ratings yet
- The Linguistic Structure of Modern English Sentence SemanticsDocument30 pagesThe Linguistic Structure of Modern English Sentence SemanticsGeorgiana Argentina DinuNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review Packet 8 Pronouns Answer Key 1Document13 pagesGrammar Review Packet 8 Pronouns Answer Key 1Frances FangNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument35 pagesTypes of PronounsmakgeolliNo ratings yet
- Pronoun N Subject and Object of SentenceDocument1 pagePronoun N Subject and Object of SentencePaul Sanjay SurisettyNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review Packet 8 PronounsDocument13 pagesGrammar Review Packet 8 PronounsSarah TallimaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Document5 pagesPronoun Cases and Types English Composition 1Helen ZakiNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument4 pagesPronounsMecislavs GrigorcuksNo ratings yet
- Nouns AdvancedDocument3 pagesNouns AdvancedReema SinghNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsAbdelkarim BouhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 PronounsDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Pronounstalanikola.insiangNo ratings yet
- Engpro4 Reviewer MidtermDocument27 pagesEngpro4 Reviewer MidtermAlyanna ManaloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Communication SkillsDocument13 pagesReviewer in Communication SkillsElline Andreana Reyes100% (2)
- Personal Pronouns Presentation in Blue Green Bold StyleDocument19 pagesPersonal Pronouns Presentation in Blue Green Bold StyleErica Jane PrinoNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument10 pagesPronounsKat RosillonNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Module 3 Unit 2 HW Resources For FamiliesDocument15 pagesGrade 3 Module 3 Unit 2 HW Resources For Familiesapi-248799070No ratings yet