0% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views18 pagesBIOLOGY SS 1 WEEK 5 .PPTX E
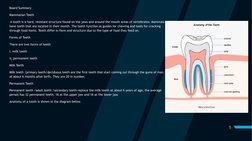
The document outlines a biology lesson plan on mammalian teeth and digestive enzymes, with the objectives of defining teeth, listing the forms of human teeth and types of teeth, and explaining how teeth adapt based on an animal's diet. The 40-minute lesson involves students identifying teeth, learning about their anatomy and function, comparing teeth between species, and assessing their understanding through questions and an assignment to draw and label teeth.
Uploaded by
Official PageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views18 pagesBIOLOGY SS 1 WEEK 5 .PPTX E
The document outlines a biology lesson plan on mammalian teeth and digestive enzymes, with the objectives of defining teeth, listing the forms of human teeth and types of teeth, and explaining how teeth adapt based on an animal's diet. The 40-minute lesson involves students identifying teeth, learning about their anatomy and function, comparing teeth between species, and assessing their understanding through questions and an assignment to draw and label teeth.
Uploaded by
Official PageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Period 1: Mammalian Teeth and Digestive Enzymes: Introduces mammalian teeth, their types, functions, teaching methods, and related activities.
- Introduction to Biology Lesson: Provides an introduction to the Biology lesson series including structure and educational objectives.
- Period 2: Dental Formula and Adaptation to Mode of Nutrition: Covers dental formulas and how they relate to dietary adaptations in different species.
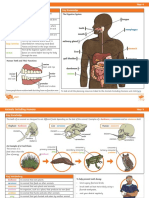
- Period 3: Digestive Enzymes: Explains the role and types of digestive enzymes in human and animal nutrition, including practical activities.
- Practice and Summary: Encourages practical experiments for understanding enzyme activity and wraps up the lesson series.