Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 7
Uploaded by
Kishan SinghCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 7
Uploaded by
Kishan SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
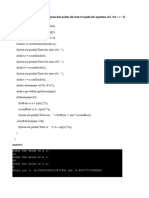
Lab 7: Write a program using TCP/IP socket between client and server and perform two-way
communication
Client :
BufferedReader br
import java.io.*; = new BufferedReader(
import java.net.*; new InputStreamReader(
s.getInputStream()));
class Client2 { BufferedReader kb
= new BufferedReader(
public static void main(String args[]) new InputStreamReader(System.in));
throws Exception while (true) {
{
Socket s = new Socket("localhost", 888); String str, str1;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
DataOutputStream dos System.out.println(str);
= new DataOutputStream( str1 = kb.readLine();
s.getOutputStream()); ps.println(str1);
}
BufferedReader br ps.close();
= new BufferedReader( br.close();
new InputStreamReader( kb.close();
s.getInputStream())); ss.close();
s.close();
BufferedReader kb System.exit(0);
= new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in)); } // end of while
String str, str1; }
}
while (!(str = kb.readLine()).equals("exit")) {
dos.writeBytes(str + "\n"); Output:
str1 = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str1);
}
// close connection.
dos.close();
br.close();
kb.close();
s.close();
}
}
Figure 1 Server
Server :
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class Server2 {
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(888);
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("Connection established");
// to send data to the client
PrintStream ps Figure 2 client
= new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
Lab 8: Write a program to illustrate JDBC connectivity and perform CRUD operation on a table
student/employee (at least 5 attributes)
import java.sql.*; stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
public class StudentDatabase { sql = "DELETE FROM student WHERE id = 1";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
static final String JDBC_DRIVER =
"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; sql = "SELECT * FROM student";
static final String DB_URL = ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/student";
while (rs.next()) {
static final String USER = "root"; int id = rs.getInt("id");
static final String PASS = "password"; String name = rs.getString("name");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
public static void main(String[] args) { String gender = rs.getString("gender");
String grade = rs.getString("grade");
Connection conn = null; System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " +
Statement stmt = null; name + ", Age: " + age + ", Gender: " + gender + ", Grade:
" + grade);
try { }
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
rs.close();
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, stmt.close();
USER, PASS); conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
stmt = conn.createStatement(); se.printStackTrace();
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS } catch (Exception e) {
student " + e.printStackTrace();
"(id INTEGER not NULL } finally {
AUTO_INCREMENT, " + try {
" name VARCHAR(255), " + if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
" age INTEGER, " + } catch (SQLException se2) {
" gender VARCHAR(10), " + }
" grade VARCHAR(10), " + try {
" PRIMARY KEY ( id ))"; if (conn != null) conn.close();
stmt.executeUpdate(sql); } catch (SQLException se) {
sql = "INSERT INTO student (name, age, gender, se.printStackTrace();
grade) " + }
"VALUES ('Kishan Singh', 20, 'Male', 'A')"; }
stmt.executeUpdate(sql); }
}
sql = "UPDATE student SET grade = 'B' WHERE
id = 1";
Lab 9: Write a program to illustrate Batch Transaction with prepared statement
import java.sql.*;
public class BatchTransactionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase";
String username = "myuser";
String password = "mypassword";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, username, password)) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false); // disable auto-commit
String insertQuery = "INSERT INTO customers (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(insertQuery);
ps.setString(1, "Prateek Verma");
ps.setString(2, "paaartik@verma.com");
ps.addBatch();
ps.setString(1, "Ajay Sngh");
ps.setString(2, "ajay@singh.com");
ps.addBatch();
ps.setString(1, "Kishan Singh");
ps.setString(2, "kishan@singh.com");
ps.addBatch();
‘
int[] updateCounts = ps.executeBatch();
for (int i : updateCounts) {
if (i == Statement.EXECUTE_FAILED) {
throw new SQLException("Batch update failed");
}
}
conn.commit();
System.out.println("Batch transaction completed successfully");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
You might also like
- AJP Programs (16.... )Document6 pagesAJP Programs (16.... )ɪᴛs࿐ᴀᴀʏᴀɴNo ratings yet
- Andres, Monica Bscs - 4ADocument4 pagesAndres, Monica Bscs - 4AMonica AndresNo ratings yet
- NetworkprogDocument47 pagesNetworkprogparul_pandeyNo ratings yet
- JDBC ProgramDocument1 pageJDBC ProgramPooja PatilNo ratings yet
- Networking ProgramsDocument8 pagesNetworking ProgramsrajNo ratings yet
- Java Client - ServeurDocument5 pagesJava Client - Serveurflav legrand mongouoNo ratings yet
- JDBC Programs P-1: Package Import Public Class Public Static Void Throws Null Null TryDocument17 pagesJDBC Programs P-1: Package Import Public Class Public Static Void Throws Null Null Trynivya inventateqNo ratings yet
- T1.start T2.start T3.startDocument7 pagesT1.start T2.start T3.startManahil RanaNo ratings yet
- Tybca 15 MarksDocument30 pagesTybca 15 Marksapi-446272000No ratings yet
- CN Exp 5Document8 pagesCN Exp 5anoNo ratings yet
- Print Java Prac7 10Document9 pagesPrint Java Prac7 10Khushali JivaniNo ratings yet
- GajaDocument17 pagesGajaMurnali MeghaNo ratings yet
- DA3 AnsDocument11 pagesDA3 AnsPARTH SUNIL CHAVAN 20BCI0055No ratings yet
- Final CN PracticalsDocument60 pagesFinal CN PracticalsAnurati KNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: PROGRAM (Socket Programming Using TCP)Document4 pagesExperiment 1: PROGRAM (Socket Programming Using TCP)Om Chavan 3119050No ratings yet
- OnDocument6 pagesOnlê duy linhNo ratings yet
- TCP Socket For AdditionDocument9 pagesTCP Socket For AdditionindrajeetNo ratings yet
- Java Ex10 ShelvaDocument5 pagesJava Ex10 Shelvasumathi palaniswamiNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument35 pagesCloud ComputingGayatri Dilip JuwatkarNo ratings yet
- First Question:: Assignment: 4 Teacher Name: 谢成 XcDocument6 pagesFirst Question:: Assignment: 4 Teacher Name: 谢成 XcMD Saidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AIM:-Create A Program That Will Communicate With The Server. (Echo Server/One Way Communication) TheoryDocument9 pagesAIM:-Create A Program That Will Communicate With The Server. (Echo Server/One Way Communication) Theoryvijay singhNo ratings yet
- JDBC CodeDocument3 pagesJDBC Codes14utkarsh2111019No ratings yet
- Ajp Practical 19Document6 pagesAjp Practical 19nstrnsdtnNo ratings yet
- CSL-210-Lab11 - Database ConnectivityDocument7 pagesCSL-210-Lab11 - Database ConnectivityrizwanNo ratings yet
- Cs 6411 Netwoks Manual For Cse 2013 RegulationDocument64 pagesCs 6411 Netwoks Manual For Cse 2013 Regulationtiruman0% (1)
- First Question:: Assignment: 4 Teacher Name: 谢诚Document6 pagesFirst Question:: Assignment: 4 Teacher Name: 谢诚MD Saidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Steps To Run JDBCDocument5 pagesSteps To Run JDBCTakumi MisakaNo ratings yet
- Network ProgramsDocument18 pagesNetwork ProgramsGanesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- DS Prax CodeDocument52 pagesDS Prax CodePravina PanchalNo ratings yet
- CCManualDocument68 pagesCCManualrutikNo ratings yet
- RohithaPamidalaSQLHandsOn4 18oct23Document3 pagesRohithaPamidalaSQLHandsOn4 18oct23suraj.nithya.pugazhNo ratings yet
- Bca Java LabDocument18 pagesBca Java LabAnuradha PatnalaNo ratings yet
- PR 18 ExerciseDocument4 pagesPR 18 ExerciseAbcNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument25 pagesJavaLynnNo ratings yet
- JDBC ProgramDocument6 pagesJDBC ProgramShobha KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.create Chat Application Using Either TCP or UDP Protocol.: Server CodeDocument10 pages1.create Chat Application Using Either TCP or UDP Protocol.: Server CodeKevin VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- Java Da-3Document10 pagesJava Da-3Annapoorna A Nair 21MIS0130No ratings yet
- Practical 18 A JPDocument6 pagesPractical 18 A JPAkankshaNo ratings yet
- CC ManualDocument66 pagesCC ManualHarshita WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2 FragmantationDocument6 pagesExperiment No.2 Fragmantationpavan nirmalNo ratings yet
- Name:-Rami Dirgh Roll No: - 3210 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Document28 pagesName:-Rami Dirgh Roll No: - 3210 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Harsh vaghelaNo ratings yet
- Java InternalDocument4 pagesJava InternalNaman jainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Write A Program To Implement A Server Calculator Containing ADD, MUL, SUB, DIVDocument6 pagesAssignment 2: Write A Program To Implement A Server Calculator Containing ADD, MUL, SUB, DIVMeera NairNo ratings yet
- Index Advance Java Lab FileDocument36 pagesIndex Advance Java Lab FileMOHIT VERMANo ratings yet
- Name:-Prajapati Movan Roll No: - 3204 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Document28 pagesName:-Prajapati Movan Roll No: - 3204 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Harsh vaghelaNo ratings yet
- Name:-Parmar Smit Roll No: - 3191 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Document28 pagesName:-Parmar Smit Roll No: - 3191 Div: - B DCN (P) Ass4Harsh vaghelaNo ratings yet
- CN-2013 Program Only ModifiedDocument44 pagesCN-2013 Program Only ModifiedJONo ratings yet
- JavaslipsDocument93 pagesJavaslipsSaadNo ratings yet
- Name:-Vaghela Harsh S Roll No: - 3227 Div: - B Data Communication and Networking (P) Ass 4Document31 pagesName:-Vaghela Harsh S Roll No: - 3227 Div: - B Data Communication and Networking (P) Ass 4Harsh vaghelaNo ratings yet
- Java AssignmentDocument7 pagesJava AssignmentprogrammerNo ratings yet
- 20MSIT002 Assignment-1 JDBCDocument5 pages20MSIT002 Assignment-1 JDBCyash gamingNo ratings yet
- Implement The Following in Java: (PART - B) 7. Write A Program For Error Detecting Code Using CRC-CCITT (16-Bits)Document7 pagesImplement The Following in Java: (PART - B) 7. Write A Program For Error Detecting Code Using CRC-CCITT (16-Bits)BinduNo ratings yet
- C++ ProgramsDocument30 pagesC++ Programsankush laybarNo ratings yet
- Advance Networking Lab FileDocument15 pagesAdvance Networking Lab FileDiya DuttaNo ratings yet
- InsertDocument1 pageInserttusharyadav796270No ratings yet
- Practical-3.3: Program To Insert Values in A Table at Run Time Using JDBCDocument3 pagesPractical-3.3: Program To Insert Values in A Table at Run Time Using JDBCSaket NisanNo ratings yet
- ProbDocument1 pageProbghizlane ghizlaneNo ratings yet
- Java TCP UdpDocument11 pagesJava TCP UdpKevin PatelNo ratings yet
- KNC 501 (Unit 2)Document33 pagesKNC 501 (Unit 2)Kishan SinghNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages: 02 Sub Code: NCS 601Document2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages: 02 Sub Code: NCS 601Kishan SinghNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Interview Questions by Ammar HaiderDocument12 pagesObject Oriented Programming Interview Questions by Ammar HaiderDestiny OgahNo ratings yet
- Cheistry Com.Document19 pagesCheistry Com.Kishan SinghNo ratings yet
- COMPLETEDocument19 pagesCOMPLETEKishan SinghNo ratings yet
- DemoDocument3 pagesDemoNeeraj JalotaNo ratings yet
- Dummy PDFDocument1 pageDummy PDFKishan SinghNo ratings yet
- 2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFDocument10 pages2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFVKNo ratings yet
- 2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFDocument10 pages2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFVKNo ratings yet
- 2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFDocument10 pages2020 12 SP Phy Edu PDFVKNo ratings yet
- COVERDocument1 pageCOVERKishan SinghNo ratings yet
- EnglishCore SQP PDFDocument5 pagesEnglishCore SQP PDFMaya DeepakNo ratings yet
- COMPLETEDocument19 pagesCOMPLETEKishan SinghNo ratings yet
- COMPLETEDocument19 pagesCOMPLETEKishan SinghNo ratings yet
- Soda ConstructorDocument4 pagesSoda ConstructorMikeyXkidNo ratings yet
- Ifca MSC BHDDocument20 pagesIfca MSC BHDMelvin FoongNo ratings yet
- 2tradeasia Customer Application Information Form - UPDATEDocument10 pages2tradeasia Customer Application Information Form - UPDATEAnna Liza M. GasparNo ratings yet
- CUG - Directory 11-11-2020Document51 pagesCUG - Directory 11-11-2020vasanthaprasanth97No ratings yet
- Name: Salim Tadvi Reg No: 201070042: Computer NetworksDocument5 pagesName: Salim Tadvi Reg No: 201070042: Computer NetworksSALIM TADVINo ratings yet
- KST RemoteService 12 KR C4 enDocument29 pagesKST RemoteService 12 KR C4 enShiya PatelNo ratings yet
- Most Students Don't Know When News Is Fake, Stanford Study FindsDocument3 pagesMost Students Don't Know When News Is Fake, Stanford Study FindsCharlesNo ratings yet
- How To Auto Embed Videos From YouTube & Facebook To WordPress - BlackHatWorldDocument5 pagesHow To Auto Embed Videos From YouTube & Facebook To WordPress - BlackHatWorldJim TimNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Research MethodologyDocument19 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Research MethodologySrinivasan Subramanian75% (4)
- Search Engine OptimizationDocument27 pagesSearch Engine OptimizationAmith50% (2)
- Remote Access To Simatic Hmi Comfort Panels: General InformationDocument11 pagesRemote Access To Simatic Hmi Comfort Panels: General InformationIvan Navarro FerreteNo ratings yet
- Service Manual, Rev. C: Kodak Dryview 8100 Laser ImagerDocument375 pagesService Manual, Rev. C: Kodak Dryview 8100 Laser Imageredgar Bilbao RochaNo ratings yet
- Hotel Booking: A Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofDocument12 pagesHotel Booking: A Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of The Degree ofRanjan JhaNo ratings yet
- SQL Server DataBase MirroringDocument18 pagesSQL Server DataBase MirroringSarithaNo ratings yet
- UBL Business Banking Portal - Customer Form 2022Document16 pagesUBL Business Banking Portal - Customer Form 2022Markus EngNo ratings yet
- Week3 ModifiedDocument48 pagesWeek3 ModifiedAbdullah ShalanNo ratings yet
- I Purposive CommunicationDocument30 pagesI Purposive CommunicationMikylla Paula BelarminoNo ratings yet
- AWS Course ContentsDocument4 pagesAWS Course Contentstekula akhilNo ratings yet
- A Study On Spam Classification Using Machine Learning TechniquesDocument14 pagesA Study On Spam Classification Using Machine Learning TechniquesRamanpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Marketplace Work Flow Online Documentation - CedCommerceDocument15 pagesMarketplace Work Flow Online Documentation - CedCommerceKinge BilNo ratings yet
- SupportDocument8 pagesSupportFqckezNo ratings yet
- Manual Tankmaster Winsetup Inventory Management Software For Tank Gauging Systems en 80868Document122 pagesManual Tankmaster Winsetup Inventory Management Software For Tank Gauging Systems en 80868wdcjr1214No ratings yet
- Cisco Call Manager CUCM RTMTDocument338 pagesCisco Call Manager CUCM RTMTBinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Advisory FormDocument1 pageAdvisory Formshawn86% (7)
- 1.2.2 Lab - Linux ReviewDocument31 pages1.2.2 Lab - Linux ReviewMARY MAE MAGDALENE GREGORENo ratings yet
- Open Gapps LogDocument2 pagesOpen Gapps LogHayhay HayhayNo ratings yet
- Recovery PDFDocument1 pageRecovery PDFjony rabuansyah100% (1)
- Oracle BI Publisher E0 Training ManualDocument37 pagesOracle BI Publisher E0 Training Manualpro_shadNo ratings yet
- Ewk 1 - SyllabusDocument16 pagesEwk 1 - Syllabusmarpel100% (1)
- FirewallDocument6 pagesFirewallPepi ToNo ratings yet