Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Furosemide Medication Card
Uploaded by
Anja de VriesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Furosemide Medication Card
Uploaded by
Anja de VriesCopyright:
Available Formats
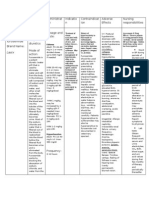
Generic Name: Furosemide Trade name: Lasix
Pharmacologic Class: Loop Diuretic Usual dose: 20 to 40 mg IV (slowly over 1 to 2 minutes), I
0-80 mg orally once (Max: 600 mg/day)
Action (What does it do? How long does it take to work?): Uses for this medication: edema associated with congestiv
Mobilizes excess fluid and decreases BP. Acts by inhibiting the failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and renal disease (including n
luminal Na-K-Cl cotransporter in the thick ascending loop of syndrome) and high BP (hypertension)
Henle, thus causing more Na, Cl, & K to be excreted in the urine.
Onset: PO 1hr, IV 5 mins Duration: PO 4-6hrs, IV 2hrs
Common side effects: dizziness, headache, hypotension, electrolyte imbalance, diarrhea, constipation, loss of appetite, blurred v
Adverse effects: hypokalemia, hyponatremia, dehydration, hypotension
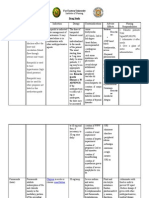
Clinical Judgment
Pre-administration assessment: What should the nurse assess before administering the medication?
- Vital signs – BP & HR
- Daily weights, I/O
- Respiratory assessment –pulmonary edema?
- Kidney function – Cr, BUN (high = kidney impairment)
- Electrolytes (especially serum *K level – if too low, HOLD)
- Other labes - blood glucose, serum uric acid levels
How will the nurse know if it is appropriate to administer?
- Within safe dose range, no allergy to medication, no hypokalemia, no severe kidney impairment, BP and HR within tar
for order
Post- administration assessment: What should the nurse assess after administering the medication? How will you know if the m
is effective?
Goal: decreased BP, increases urine output, decreased edema
- Daily weights, I/O
- Respiratory assessment
- Monitor for S&S kidney problems - swelling, urinating less, feeling tired or SOB
- Monitor for S&S of liver/pancreas problems - loss of appetite, upper stomach pain (may spread to your back), N/V, dar
urine, jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Electrolytes - S&S of imbalance: increased thirst/urination, constipation, muscle weakness, leg cramps, numbness or ti
feeling jittery, fluttering in chest
Nursing considerations:
- Older clients = Falls risk (orthostatic HPTN) change positions gradually
- Consider pre-existing kidney function and impact on kidneys *Lasix is hard on kidneys!
- Using more than recommended dose will not make this medicine more effective. High doses of furosemide may cause
irreversible hearing loss
- Tell your doctor if you have an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or any type of scan using a radioactive dye that is in
into a vein - contrast dyes and furosemide can harm your kidneys
- Instruct client to consult health care professional regarding dietary potassium guidelines
- Instruct client to monitor weight weekly and report significant changes
- Caution patient to use sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent photosensitivity reactions
- Advise diabetic patients to monitor blood glucose closely; may cause increased blood glucose levels.
You might also like
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesEmergency Drugspraiseiswhatido9440No ratings yet
- Medsurg and Pharm HESI ReviewDocument8 pagesMedsurg and Pharm HESI ReviewSarah Vance100% (4)
- LOSARTANDocument3 pagesLOSARTANReinell GoNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEa_lavina02No ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Care Plan September 25 Med-SurgDocument19 pagesCare Plan September 25 Med-Surgapi-251516913No ratings yet
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument21 pagesAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanNo ratings yet
- Levodopa Card#4Document2 pagesLevodopa Card#4USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Classification: Recommended Dosage, Route, and FrequencyDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Classification: Recommended Dosage, Route, and FrequencyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazideKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument5 pagesAtropine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (1)
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinSheri490100% (2)
- Methadone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesMethadone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drus Study AaaaaaDocument6 pagesDrus Study AaaaaamarkharoldNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsAdhaNo ratings yet
- Diltiazem CD Med CardDocument2 pagesDiltiazem CD Med CardAnja de VriesNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesMagnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- CardizemDocument1 pageCardizemSheri490100% (1)
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- CARDIO Intensive CareDocument6 pagesCARDIO Intensive CareDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Drug LisinoprilDocument1 pageDrug LisinoprilSrkocherNo ratings yet
- cadwithlvfailure-200409082733Document32 pagescadwithlvfailure-200409082733Gerome ManantanNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Online AudioDocument4 pagesFurosemide: Online AudioDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument4 pagesFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesPropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassie100% (1)
- Labor and Delivery MedsDocument12 pagesLabor and Delivery MedsSam DanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesKhim CaronanNo ratings yet
- HOI Medications List Provides Overview of Common DrugsDocument7 pagesHOI Medications List Provides Overview of Common DrugsjackyNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide ThiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazide ThiazideE100% (1)
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Lovenox Anticoagulant Prevent Thrombus Formation: VTE Prophylaxis Following Abdominal Surgery - 40Document8 pagesLovenox Anticoagulant Prevent Thrombus Formation: VTE Prophylaxis Following Abdominal Surgery - 40Joanie BNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument18 pagesDRUG StudyMargaux Moir0% (1)
- IbuprofenDocument3 pagesIbuprofenapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyDocument57 pagesDrug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyMichelle Davis-JacksonNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesCebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesdnllsgrraNo ratings yet
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDocument3 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaNo ratings yet
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Document7 pagesHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationDocument4 pagesPrescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument4 pagesLithiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- VerapamilDocument2 pagesVerapamilMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- PLASIL antiemetics classificationDocument5 pagesPLASIL antiemetics classificationAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocument31 pagesOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420No ratings yet
- Ondansetron Medication CardDocument2 pagesOndansetron Medication CardAnja de VriesNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSFrom EverandCLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms: Literatura/litteratura (Derived Itself From Littera: Letter or Handwriting)Document2 pagesLiterary Terms: Literatura/litteratura (Derived Itself From Littera: Letter or Handwriting)Berr WalidNo ratings yet
- MisOr Division Template in Action ResearchDocument14 pagesMisOr Division Template in Action ResearchAmorEmbone100% (2)
- The Irrefutable Laws of Leadership SummaryDocument6 pagesThe Irrefutable Laws of Leadership Summarycoachersland100% (3)
- Kotler Mm15e Inppt 12Document26 pagesKotler Mm15e Inppt 12aldi_unantoNo ratings yet
- Sr. Business Analyst RoleDocument6 pagesSr. Business Analyst RoleDrafting YTNo ratings yet
- LVL 1 The Slaying StoneDocument34 pagesLVL 1 The Slaying StoneArturo Partida95% (19)
- Transformations Women Gender and Psychology 3rd Edition Crawford Test BankDocument17 pagesTransformations Women Gender and Psychology 3rd Edition Crawford Test BankFrankDiazagsyr100% (12)
- Analisis Debussy PDFDocument2 pagesAnalisis Debussy PDFMiguel SeoaneNo ratings yet
- Connectors of Addition and ContrastDocument2 pagesConnectors of Addition and Contrastmmaarr100% (2)
- Theories of LearningDocument19 pagesTheories of LearningIndu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review ResearchDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Researchapi-534301945No ratings yet
- PalosliosDocument12 pagesPalosliossuwijak76797679No ratings yet
- Partner With Rittal: It's Easy To Become A Rittal PartnerDocument10 pagesPartner With Rittal: It's Easy To Become A Rittal PartnerBhanu Uday SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study EntDocument22 pagesCase Study Entnurul syafiqah yahyaNo ratings yet
- Snelgrove Language and Language Development Fianl ProjectDocument4 pagesSnelgrove Language and Language Development Fianl Projectapi-341640365No ratings yet
- 4 Strategies To Unlock Performance Management Constraints HFMDocument6 pages4 Strategies To Unlock Performance Management Constraints HFMajay kumarNo ratings yet
- Jose Noel Meza-Perez, A029 269 568 (BIA Feb. 28, 2011)Document3 pagesJose Noel Meza-Perez, A029 269 568 (BIA Feb. 28, 2011)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCNo ratings yet
- The Beginners Bible Coloring Book by JPR504Document37 pagesThe Beginners Bible Coloring Book by JPR504Ernesto Carmona Parra100% (1)
- Aerodynamic Validation of Emerging Projectile and Missile ConfigurationsDocument109 pagesAerodynamic Validation of Emerging Projectile and Missile Configurationssux2beedNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary 3Document3 pagesVocabulary 3borahae 3000No ratings yet
- A Bibliometric Analysis of Creativity in The Field of Business EconomicsDocument9 pagesA Bibliometric Analysis of Creativity in The Field of Business EconomicsDanielaNo ratings yet
- Temple Entry Movement and Nationalist Agitation in KeralaDocument25 pagesTemple Entry Movement and Nationalist Agitation in Keralahodhistory100% (4)
- Galatians Part 5Document3 pagesGalatians Part 5nullvoice84No ratings yet
- Vacuum Brake ReportDocument65 pagesVacuum Brake ReportsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Sourcing Rules in PurchasingDocument21 pagesSourcing Rules in Purchasingpradhan.neeladriNo ratings yet
- Qustion Bank LAB.docxDocument3 pagesQustion Bank LAB.docxshubhampoddar11.11No ratings yet
- Book of AbstractsDocument156 pagesBook of Abstractsdragance106No ratings yet
- Present Perfect: Grammar WorksheetDocument1 pagePresent Perfect: Grammar WorksheetkiaraNo ratings yet
- Dawn Ullmann - ReferenceDocument1 pageDawn Ullmann - Referenceapi-418750957No ratings yet
- Success Factors For Augmented Reality Business ModelsDocument36 pagesSuccess Factors For Augmented Reality Business ModelsAsutosh GuptaNo ratings yet