Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hegel
Uploaded by
Oto Shubladze0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
hegel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageHegel
Uploaded by
Oto ShubladzeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770-1831) was a German philosopher who made
significant contributions to the field of metaphysics, epistemology, logic, and
political theory. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in
Western philosophy, particularly for his development of a comprehensive
philosophical system known as "Hegelianism" or "Hegelian philosophy."
Hegel's philosophy is often referred to as "dialectical idealism" or "absolute
idealism." It is characterized by his dialectical method, which he employed to
analyze and understand the nature of reality, history, and human consciousness.
Hegel believed that reality is fundamentally dynamic and evolving, and that
progress occurs through a process of conflict, contradiction, and resolution.
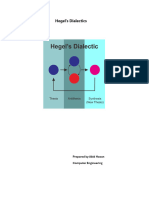
One of Hegel's central concepts is the dialectic, which involves the interplay of
opposing forces or ideas. According to Hegel, each stage of development (thesis)
contains within it the seeds of its own negation (antithesis), leading to a
synthesis that incorporates elements of both and represents a higher level of
truth. This process repeats itself continuously, driving the progression of
history, thought, and spirit towards an ultimate goal or end, which Hegel referred
to as the "Absolute."
Hegel applied his dialectical method to various aspects of human experience,
including nature, history, religion, art, and philosophy itself. He believed that
reality is fundamentally shaped by a rational principle or "world spirit" that
unfolds through historical development. Hegel's philosophy of history emphasizes
the importance of historical events and societal progress as manifestations of the
unfolding of the world spirit.
In Hegel's metaphysics, he posited the concept of "Geist" or "spirit," which refers
to the self-consciousness and collective consciousness of human beings. According
to Hegel, the development of Geist occurs through a historical progression of
social, cultural, and political institutions. He saw the state as the highest
expression of Geist, embodying the rational and ethical principles of society.
You might also like
- Georg Hegel: Literary Analysis: Philosophical compendiums, #6From EverandGeorg Hegel: Literary Analysis: Philosophical compendiums, #6No ratings yet
- Hegel's Absolute IdealismDocument21 pagesHegel's Absolute IdealismJimNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Philosophy of History and the Dialectic ProcessDocument11 pagesHegel's Philosophy of History and the Dialectic ProcessСілвестер НосенкоNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Historicism and Philosophy of HistoryDocument5 pagesHegel's Historicism and Philosophy of HistoryfitranaamaliahNo ratings yet
- HegelDocument20 pagesHegelAkash RajanNo ratings yet
- Hegel and HistoryDocument267 pagesHegel and HistoryShih-hong Chuang100% (1)
- Theory of ImperialismDocument266 pagesTheory of ImperialismSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Hegel 1770-1831 and His TheoryDocument36 pagesHegel 1770-1831 and His TheorySarma SigaraNo ratings yet
- J.D. Ponce on Georg W. F. Hegel: An Academic Analysis of Phenomenology of Spirit: Idealism Series, #1From EverandJ.D. Ponce on Georg W. F. Hegel: An Academic Analysis of Phenomenology of Spirit: Idealism Series, #1No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Art (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)From EverandThe Philosophy of Art (Barnes & Noble Digital Library)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Hegelian Dialectic & Democratization Process: Understanding the Two Philosophical ConceptsFrom EverandHegelian Dialectic & Democratization Process: Understanding the Two Philosophical ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel Thesis AntithesisDocument5 pagesGeorg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel Thesis Antithesisjessicacotterreno100% (2)
- George Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel - MylegalnotebookDocument10 pagesGeorge Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel - MylegalnotebookRaamit aroraNo ratings yet
- Assignment of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesAssignment of Philosophyraza_akram2009No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Art (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)From EverandThe Philosophy of Art (Barnes & Noble Library of Essential Reading)Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Andy Blunden Hegel and MediationDocument21 pagesAndy Blunden Hegel and MediationMatthewDelNevoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hegel's Philosophy and InfluenceDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Hegel's Philosophy and InfluenceMarkNo ratings yet
- Modern Idealism Hegel (Part 2)Document8 pagesModern Idealism Hegel (Part 2)MarkNo ratings yet
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich HegelDocument17 pagesGeorg Wilhelm Friedrich HegelSahil Jaybhay100% (1)
- Olave AJM Hispanization 602Document21 pagesOlave AJM Hispanization 602roanneiolaveNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Continental Philosophy and Triadic MethodDocument3 pagesHegel's Continental Philosophy and Triadic Methodj i l l i a nNo ratings yet
- Hegel's DialecticsDocument5 pagesHegel's Dialecticsabidhasan8426No ratings yet
- Hegel - Introduction To The Philosophy of HistoryDocument2 pagesHegel - Introduction To The Philosophy of HistoryittykayNo ratings yet
- Hegel On History Issue 129 Philosophy NowDocument7 pagesHegel On History Issue 129 Philosophy Nowcpshgr8pxzNo ratings yet
- The Specter of NihilismDocument8 pagesThe Specter of NihilismAndres AnzaldiNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Dialectical Method and the Divine StateDocument10 pagesHegel's Dialectical Method and the Divine StateRahul JensenNo ratings yet
- Hoffheimer 85Document15 pagesHoffheimer 85JackNo ratings yet
- Hegel and IdealismDocument12 pagesHegel and IdealismFe CanoyNo ratings yet
- HistoricismDocument10 pagesHistoricismHilary Lewis MoritzNo ratings yet
- Hegel On HistoryDocument8 pagesHegel On HistoryDrazen MilicNo ratings yet
- Hegel: A Guide For The PerplexedDocument166 pagesHegel: A Guide For The PerplexedMavaddat Javid100% (3)
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (Document4 pagesGeorg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (RoyalNo ratings yet
- Hegal Synopsis PolDocument3 pagesHegal Synopsis PolMehvashNo ratings yet
- The Philosophy of HistoryFrom EverandThe Philosophy of HistoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (58)
- Hegel's Early Development and The Gnostic TraditionDocument18 pagesHegel's Early Development and The Gnostic TraditionAZERNo ratings yet
- Hegel 4Document19 pagesHegel 4jpaolo89No ratings yet
- History of Philosophy. G.W.F. Hegel. His Life, Works and Thought.From EverandHistory of Philosophy. G.W.F. Hegel. His Life, Works and Thought.No ratings yet
- Crisafi 1Document37 pagesCrisafi 1samadrita dasNo ratings yet
- HegelDocument2 pagesHegelARSHIYA ANJUM HU21POLS0100006No ratings yet
- 19th Century Philosophy TrendsDocument71 pages19th Century Philosophy TrendsBeverlyn JamisonNo ratings yet
- Gunn and Wilding ExtractDocument19 pagesGunn and Wilding Extractdavidtapia13No ratings yet
- Hegel Dialect Theory: Art of Investigating or Discussing The TruthDocument11 pagesHegel Dialect Theory: Art of Investigating or Discussing The Truthshreya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Jean Faurot PhenomenologyDocument6 pagesJean Faurot PhenomenologyP.E. RanghbdsyhkNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Philosophy of Dialectic ProcessDocument10 pagesHegel's Philosophy of Dialectic ProcessAlwin RamosNo ratings yet
- Hegel and HistoryDocument267 pagesHegel and HistorySunny WangNo ratings yet
- Deleuze Contra Hegel The Rupture of The PDFDocument20 pagesDeleuze Contra Hegel The Rupture of The PDFcaptainnemo18No ratings yet
- German Idealism 2Document11 pagesGerman Idealism 2aruna copyingNo ratings yet
- 8 LectureDocument14 pages8 LectureAkbibi YazgeldiyevaNo ratings yet
- Hegel EschatologyDocument17 pagesHegel EschatologyCalebNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Phenomenology of Spirit Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770-1831) Is Probably The Greatest German IdealistDocument22 pagesHegel's Phenomenology of Spirit Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770-1831) Is Probably The Greatest German IdealistBobby BlackNo ratings yet
- Karl Marx-Dialectical MaterialismDocument3 pagesKarl Marx-Dialectical MaterialismRebati Patili100% (2)
- 1the PlaceDocument2 pages1the PlaceDax PaxNo ratings yet
- Hegel TheoryDocument15 pagesHegel Theoryajwa fareedNo ratings yet
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich HegelDocument41 pagesGeorg Wilhelm Friedrich HegelAnders SamuelssonNo ratings yet
- Stirner's Egoism and The Ghost of Hegel by Gary Browning Oxford Brookes UniversityDocument10 pagesStirner's Egoism and The Ghost of Hegel by Gary Browning Oxford Brookes UniversityLibrairie IneffableNo ratings yet
- Hegel and HistoryDocument267 pagesHegel and HistoryFernanda MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Hegel's Philosophy of Synthesis and DialecticDocument14 pagesHegel's Philosophy of Synthesis and DialecticFe CanoyNo ratings yet