Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ob2 Sas 34
Uploaded by
????Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ob2 Sas 34
Uploaded by
????Copyright:
Available Formats
Care of Mother and Child At-Risk or with
Problems (Acute and Chronic)-Lecture
STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET BS NURSING / SECOND YEAR
Session # 34
LESSON TITLE: NURSING CARE OF A FAMILY WHEN A
CHILD HAS A NEUROLOGICAL ALTERATIONS
LEARNING OUTCOMES: Materials:
At the end of the lesson, the student nurse can: Book, pen and notebook, index card/class list,
speaker and LCD projector
1. Define the common types of disorders in the gastrointestinal
system and nervous system that occur in children. Reference:
2. Integrate the knowledge of the common types of disorders in Pilliteri, Adele and Silbert-Flagg, JoAnne (2018)
the gastrointestinal system and nervous system that occur in Maternal and Child Health Nursing, 8th Edition.
children and describe these disorders that occur in these USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins
classifications of children in formulating nursing care plan in
giving quality maternal and child health nursing care
LESSON REVIEW/PREVIEW (5 minutes)
MAIN LESSON (50 minutes)
Please refer to Chapter 52: Nursing Care of A Family When a Child Has an Unintentional Injury -Poisoning p. 1478 and
Chapter 49: Nursing Care of A Family When a Child Has a Neurological Disorder-Increased Intracranial Pressure p. 1383
POISONING
The substances most frequently ingested in children 5 years and younger include cosmetics/personal care
products, household cleaning products, analgesics, foreign bodies such as toys, and topical preparations.
Children younger than 6 years of age are at high risk for ingesting pharmaceutical agents.
Nearly 9,500 children will be hospitalized yearly for unsupervised ingestion of prescription medications.
The most commonly ingested medications include opioids and benzodiazepines, acetaminophen, cough and
cold remedies, ibuprofen, and diphenhydramine.
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF POISONING AT HOME
The parent should be prepared to provide the following information to the poison control center:
What was swallowed; if the name of a medicine is not known, what it was prescribed for and a description of it
(color, size, shape of pills)
The child’s weight and age and how long ago the poisoning occurred
The route of poisoning (oral, inhaled, sprayed on skin)
An estimation of how much of the poison the child took (a bottle of cleaner or medicine should say how many
pills or how much liquid it originally contained)
The child’s present condition (sleepy, hyperactive, comatose)
If the poison was in pill form, parents should check whether there are pills scattered under a chair before they
assume they were swallowed.
If one child in a family has swallowed a poison, parents should investigate whether other children have also
poisoned themselves because a preschooler often shares “candy” with a younger sibling.
If the poison control center advises parents to make the child vomit, the best way to do this is to place a finger at
the back of the child’s throat.
Old remedies such as giving mustard or salty water are not that effective and waste time that could be spent
telephoning an emergency service (911) for help or transporting the child to the hospital.
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 1 of 6
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF POISONING AT THE HEALTH CARE FACILITY
In the emergency department, the best method to deactivate a swallowed poison is the administration of
activated charcoal either orally or by way of an NG tube to halt the action of the poison.
Activated charcoal is supplied as a fine black powder that is mixed with water for administration.
Adding a sweet syrup to the mixture can make it more palatable.
Caution parents that, as the charcoal is excreted through the bowel over the next 3 days, stools will appear black
so they do not mistake the color for blood
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Increased ICP occurs because of an increase in the CSF volume, blood entering the CSF, cerebral edema, head
trauma or infection, space-occupying lesions such as brain tumors, or the development of hydrocephalus or
Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Sign and Symptoms of Increased Intracranial Pressure is on table 43.1
Sign or Symptom Indication of Increased Intracranial Pressure
Increased head An increase >2 cm per month in first 3 months of life, >1
circumference cm per month in the second 3 months, and >0.5 cm per
month for the next 6 months
Fontanelle changes Anterior fontanelle tense and bulging; closing late
Vomiting Occurring in the absence of nausea, on awakening in
morning or after nap; possibly projectile
Eye changes Diplopia (double vision) from pressure on abducens
nerves; white of sclera evident over pupil (setting sun
sign); limited visual fields, papilledema
Vital sign changes Elevated temperature and blood pressure; decreased
pulse and respiration rates
Pain Headache, often present on awakening and standing;
increasing with straining at stool (Valsalva maneuver)
or holding breath
Mentation Irritability, altered consciousness such as sleepiness
Table 43.1
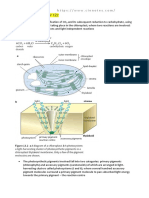
ASSESSMENT INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE MONITORING
the initial signs children may show are headache, Intraventricular catheters are threaded into the
irritability, or restlessness. lateral ventricle, filled with normal saline, and then
Growing pressure on the brainstem, which controls connected to an external pressure monitor.
respiration and cardiac activity, soon causes pulse As pressure in the ventricle fluctuates, it registers
and respiration rates to slow. through the filled catheter onto an oscilloscope
Compression of cranial vessels leads to a screen plus a written printout.
compensatory increase in blood pressure (or pulse ICP in children normally ranges from 1 to 10
pressure, the gap between the systolic and mmHg; a level greater than 15 mmHg needs
diastolic blood pressures). Pressure on the further assessment.
hypothalamus, the temperature-regulating center As blood pressure rises and falls with the influx of
of the body, causes an increase in body blood through vessels, so does ICP.
temperature. On a monitor, this appears as A waves (plateau
diplopia (double vision). waves), B waves (short-duration waves), or C
On funduscopic examination, papilledema may be waves (small, rhythmic bursts).
detected. If brain ischemia is present, wave patterns change
Compare a new assessment against all recordings even before there is a deviation in blood pressure
taken in the last 24 hours so a progressive change or pulse rate
can be detected. insertion of intraventricular catheters or
decorticate posturing: the child’s arms are screws.it enables early detection should problems
adducted and flexed on the chest with wrists arise but also because it helps to reduce the risk of
flexed, hands fisted; the lower extremities are further injury or complications.
extended and internally rotated; the feet are
plantar flexed
Decerebrate posturing, which occurs when the
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 2 of 6
midbrain is not functional, is characterized by rigid
extension and adduction of the arms and pronation
of the wrists with the fingers flexed; the legs are
held extended with the feet plantar flexed.
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
Actions such as coughing, vomiting, and sneezing and rapid administration of intravenous (IV) fluid increase
ICP. When a parent is burping an infant after a feeding, caution them to be careful not to put pressure on the
jugular veins because this is another action that increases ICP.
Placing a child in a semi-Fowler’s position (use an infant seat for babies) or administering a corticosteroid such
as dexamethasone (Decadron) can effectively reduce cerebral edema and its accompanying pressure.
An osmotic diuretic, such as mannitol, given IV, causes a shift of fluid from extravascular compartments into the
vascular stream (from brain tissue into blood vessels), so it also reduces pressure.
Children usually have an indwelling urinary catheter inserted before beginning an osmotic diuretic to ensure that
the child’s kidneys are able to successfully excrete the intravessel fluid and prevent back pressure on the heart.
If the ICP is caused by excessive fluid accumulating in the brain’s ventricles, a ventricular tap may be necessary
for immediate reduction of pressure.
Because increased ICP is a sign of an underlying disorder, after the pressure is reduced, the underlying cause
must then be identified and rectified or the pressure will rise again from the original disorder.
CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING (30 minutes)
You will answer and rationalize this by pair. This will be recorded as your quiz. One (1) point will be given to correct
answer and another one (1) point for the correct ratio. Superimpositions or erasures in you answer/ratio is not allowed.
Multiple Choice
1. Nurses should begin screening for lead poisoning when a child reaches which age?
A. 12 months
B. 6 months
C. 18 months
D. 24 months
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
2. Which therapeutic agent is called the universal antidote?
A. Glucose
B. Activated Charcoal
C. Protamine Sulfate
D. Pysostigmine
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
3. The drug Deferoxamine is administered in which drug overdose?
A. Iron
B. Beta blockers
C. Calcium gluconate
D. Digoxin
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 3 of 6
4. Which drug is used in acetaminophen overdose?
A. Acetylcysteine
B. Physostigmine
C. Flumazenil
D. Acetylsalicylic Acid
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:__________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
5. In which poisoning the Digibind is used as an effective antidote?
A. Cholinergics
B. Benzodiazepine
C. Digoxin
D. Atropine
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
6. Which of the following is a part of the main structures that play a role with altering intracranial pressure:
A. Neurons
B. Cerebrospinal fluid
C. Periosteum
D. Dura mater
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
7. A nurse is collecting data about a child who has been admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of
seizures. The nurse checks for causes of the seizure activity by:
A. Testing the child's urine for specific gravity
B. Asking the child what happens during a seizure
C. Obtaining a family history of psychiatric illness
D. Obtaining a history regarding factors that may occur before the seizure activity
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:__________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
8. A nurse is assisting with data collection from an infant who has been diagnosed with hydrocephalus. If
the infant's level of consciousness diminishes, a priority intervention is:
A. Taking the apical pulse
B. Taking the blood pressure
C. Testing the urine for protein
D. Palpating the anterior fontanel
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 4 of 6
9. A mother arrives at the emergency department with her 4-year-old child and states that the child fell off a
bunk bed. A head injury is suspected, and a nurse is monitoring the child continuously for signs of
increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which of the following is a late sign of increased ICP in this child?
A. Nausea
B. Bradycardia
C. Bulging fontanel
D. Dilated scalp veins
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________ ____
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
10. Which of the following is contraindicated in a patient with increased ICP?
A. Lumbar puncture
B. Midline position of the head
C. Hyperosmotic diuretics
D. Barbiturates medications
ANSWER: ________
RATIO:___________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
RATIONALIZATION ACTIVITY (THIS WILL BE DONE DURING THE FACE TO FACE INTERACTION)
The instructor will now rationalize the answers to the students. You can now ask questions and debate among yourselves.
Write the correct answer and correct/additional ratio in the space provided.
1. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
4. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
5. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
7. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
8. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________ _______________
_____________________________________________________________________
9. ANSWER: ________
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 5 of 6
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
10. ANSWER: ________
RATIO:_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
LESSON WRAP-UP (5 minutes)
You will now mark (encircle) the session you have finished today in the tracker below. This is simply a visual to help you
track how much work you have accomplished and how much work there is left to do.
You are done with the session! Let’s track your progress.
PERIOD 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
PERIOD 2
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
PERIOD 3
32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46
AL STRATEGY: CAT 3-2-1
3-2-1
Three things you learned:
1. __________________________________________________
2. __________________________________________________
3. __________________________________________________
Two things that you’d like to learn more about:
1. __________________________________________________
2. __________________________________________________
One question you still have:
1. __________________________________________________
(For next session, review Chapter 49: Nursing Care of a Family When a Child Has a Neurological Disorder-
Neurocutaneous Syndromes p. 1386, Cerebral Palsy p. 1388 and Infection P.1391)
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 6 of 6
You might also like
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pediatrics Nclex Review PointersDocument14 pagesPediatrics Nclex Review PointersCathryn Dominique Tan100% (1)
- Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and ManagementFrom EverandCongenital Hyperinsulinism: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and ManagementDiva D. De León-CrutchlowNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Presentation On Meningitis PatientDocument20 pagesCare Plan Presentation On Meningitis PatientDuop Jock LiemNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics RemarksDocument62 pagesPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- Pediatric EmergencyDocument98 pagesPediatric Emergencyian ismail100% (5)
- Neonatal Danger SignsDocument6 pagesNeonatal Danger Signsmarkus_danusantosoNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Pedia Nervous, Hema,,Renal, SkeletalDocument178 pagesNCM 102 Pedia Nervous, Hema,,Renal, SkeletalMika SamsonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of at Risk/ High Risk/ Sick ClientDocument256 pagesNursing Care of at Risk/ High Risk/ Sick ClientAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus: Charmaine Lainne R. Aspan G4BDocument28 pagesHydrocephalus: Charmaine Lainne R. Aspan G4Bchang02No ratings yet
- Pediatric Assessment Triangle EditDocument31 pagesPediatric Assessment Triangle EditAlbert Gunawan100% (1)
- Hydrocephalus PresentationDocument49 pagesHydrocephalus PresentationSourina BeraNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 17Document9 pagesOb2 Sas 17Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument38 pagesBirth AsphyxiaÅbübâkêř Äbd-ëřhēēm BãřřîNo ratings yet
- EncephalitisDocument46 pagesEncephalitismeenoNo ratings yet
- HIGH RISK INFANT (1 Month - 12 Months) : 1. Failure To ThriveDocument14 pagesHIGH RISK INFANT (1 Month - 12 Months) : 1. Failure To ThriveRosaree Mae PantojaNo ratings yet
- 322 Convulsions and Status EpilepticusDocument7 pages322 Convulsions and Status EpilepticusMohammad Irfan khanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Triage PatDocument52 pagesPediatric Triage Patdrsapnataneja100% (1)
- Elective - Neurologic Reporting 1Document23 pagesElective - Neurologic Reporting 1GenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Escherichia Coli Streptococcus Group B Haemophilus Influenzae Streptococcus Pneumoniae Neisseria Meningitides Staphylococcus AureusDocument4 pagesEscherichia Coli Streptococcus Group B Haemophilus Influenzae Streptococcus Pneumoniae Neisseria Meningitides Staphylococcus AureusBrent NicholsNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders in The Pediatric Patient: Presented by Marlene Meador RN, MSN, CNEDocument57 pagesNeurological Disorders in The Pediatric Patient: Presented by Marlene Meador RN, MSN, CNEsharepoint88No ratings yet
- MaceeDocument40 pagesMaceeKaryl Anne LantingNo ratings yet
- Flowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiated NewbornDocument3 pagesFlowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiated Newborndessy pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Flowchart 1 Immediate Management of An AsphyxiatednewbornDocument3 pagesFlowchart 1 Immediate Management of An Asphyxiatednewborndessy pratiwiNo ratings yet
- E. Common Acquired and Congenital AnomaliesDocument6 pagesE. Common Acquired and Congenital AnomaliesKarmela ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Precise Neurological ExamDocument30 pagesThe Precise Neurological ExamZīshān FārūqNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Newborn and Infant-NewDocument11 pagesAssessing The Newborn and Infant-NewJan Jamison ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Seizures 2014Document17 pagesNeonatal Seizures 2014akankshaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology: Jocelyn C. BanataoDocument12 pagesPediatric Cardiology: Jocelyn C. BanataoCms CSUNo ratings yet
- 2020 Immediate Care of The Newborn 3Document56 pages2020 Immediate Care of The Newborn 3Ellah PerenioNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia in NewbornDocument30 pagesAsphyxia in NewbornKowsalya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Author: Section Editor: Deputy EditorDocument26 pagesAuthor: Section Editor: Deputy EditorBùi Công MinhNo ratings yet
- Congenital Neurologic DisordersDocument114 pagesCongenital Neurologic DisordersKirk08No ratings yet
- Infant Apnea: Continuing Education ActivityDocument5 pagesInfant Apnea: Continuing Education ActivitymemoaranedaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Breath Holding Spells in ChildrenDocument4 pagesReview Article: Breath Holding Spells in ChildrenMuh Ridho AkbarNo ratings yet
- Simple Febrile SeizureDocument63 pagesSimple Febrile SeizureMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- NP2 PDFDocument11 pagesNP2 PDFUmm AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia Ik 2Document74 pagesAsphyxia Ik 2Ste VenNo ratings yet
- NSG124 - 16 Alteration in Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNSG124 - 16 Alteration in Nervous Systemlaurie.charlynjaneNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia of The Newborn. Birth TraumaDocument68 pagesAsphyxia of The Newborn. Birth TraumaNinaNo ratings yet
- Neonatology Lec1 2023Document17 pagesNeonatology Lec1 2023khaleelNo ratings yet
- Physical ExamDocument4 pagesPhysical ExamSam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Rationale: Guthrie Capillary TestDocument5 pagesRationale: Guthrie Capillary TestMarivy GalonNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Sick ChildDocument29 pagesPresentation1 Sick Childsyed askariNo ratings yet
- Birth Asphyxia: by Anne E. Odaro MCM/2017/69852Document26 pagesBirth Asphyxia: by Anne E. Odaro MCM/2017/69852ElvisNo ratings yet
- ANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningDocument9 pagesANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningMaryAnn Tiburcio CuevasNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesAlterations in Nervous SystemVIVIEN CONSIGNANo ratings yet
- Postnatal CareDocument19 pagesPostnatal Carejomarie gamiao0% (1)
- Discussion: 2.1 Tutorial DataDocument39 pagesDiscussion: 2.1 Tutorial DataTania Alsyabilla RuswandiNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument2 pagesHydrocephalusMCS LYRICSNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Asphyxia FinalDocument20 pagesNeonatal Asphyxia FinalAtawna AtefNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoDocument39 pagesPre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoLei Santillan0% (1)
- 1.8837 Hypoxic Ischaemic Encaphalopathy (HIE)Document2 pages1.8837 Hypoxic Ischaemic Encaphalopathy (HIE)Bia BarridoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric AssessmentDocument54 pagesPediatric AssessmentThetnaungsoeNo ratings yet
- Apgar ScoringDocument7 pagesApgar ScoringJessica Alvarado JermiasNo ratings yet
- Hesi Review For MaternityDocument29 pagesHesi Review For MaternitySteam Lc86% (21)
- Pedia Nursing Resource Unit - FinalDocument69 pagesPedia Nursing Resource Unit - FinalDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Closed Head Injury EG: Falls, Motor Vehicle Crashes, Bicycle InjuriesDocument13 pagesHead Injury: Closed Head Injury EG: Falls, Motor Vehicle Crashes, Bicycle InjuriesJudy HandlyNo ratings yet
- 2.1A Newborn Care: Emilio Aguinaldo College - School of MedicineDocument6 pages2.1A Newborn Care: Emilio Aguinaldo College - School of MedicineBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Aerobics and Anaerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesAerobics and Anaerobic ExerciseKirin Ira VicenteNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts of Damage Control Resuscitation and Damage Control SurgeryDocument52 pagesCurrent Concepts of Damage Control Resuscitation and Damage Control SurgerydewiswahyuNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument5 pagesExcretionSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- q3 2nd Summative Test Science FINALDocument2 pagesq3 2nd Summative Test Science FINALEDNA CALIMLIMNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument54 pagesFirst AidMadhavi ModaNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in ManagementDocument31 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in Managementokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- CryotherapyDocument15 pagesCryotherapychaitrareddyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Cardiovascular Systemahsan gujjar100% (1)
- Sensation: by Dr. Mufeed Akram TahaDocument38 pagesSensation: by Dr. Mufeed Akram TahaAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Central and Peripheral Factors in FatigueDocument6 pagesCentral and Peripheral Factors in FatigueEduardo VieyraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration - Mechanism of Respiration, GaseousDocument39 pagesPhysiology of Respiration - Mechanism of Respiration, GaseousRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytestentenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy - Watchie, Joanne (SRG)Document439 pagesCardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical Therapy - Watchie, Joanne (SRG)Abdallah Maroun Najem86% (14)
- Chapter - 13 - Cardiovascular - Responses - Exercise Physiology For Health Fitness and PerformanceDocument32 pagesChapter - 13 - Cardiovascular - Responses - Exercise Physiology For Health Fitness and Performanceec16043No ratings yet
- Cardiac Inspection and Palpation CardiologyDocument25 pagesCardiac Inspection and Palpation CardiologyMohamed El SayedNo ratings yet
- CBT QuestionsDocument20 pagesCBT QuestionsOGU CourageNo ratings yet
- Slides AUTACOIDSDocument29 pagesSlides AUTACOIDSStrange eeNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac OutputYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Medical HypothesesDocument23 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Medical HypothesesFabiano LacerdaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Recovery: A Wound Healing Model: by Dave StaplinDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Recovery: A Wound Healing Model: by Dave StaplinluckydexxxNo ratings yet
- Ganong All MCQDocument55 pagesGanong All MCQSagor Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- FLG 332 Renal Physiology - 1 (2019)Document58 pagesFLG 332 Renal Physiology - 1 (2019)Huzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Ss Organ Systems WorksheetDocument2 pagesSs Organ Systems Worksheet땡뿍뿍No ratings yet
- Meditec M700 Series: Multi-Parameter Patient MonitorsDocument8 pagesMeditec M700 Series: Multi-Parameter Patient MonitorsXavier Med Pvt. LtdNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverNo ratings yet
- Lower Correct: Wheelchair Is On The Client's RIGHT Side and The Nurse's LEFT SideDocument12 pagesLower Correct: Wheelchair Is On The Client's RIGHT Side and The Nurse's LEFT SideJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- GFZ 038Document3 pagesGFZ 038adri20121989No ratings yet
- 2.0 Introduction To Exercise Physiology SPS135Document53 pages2.0 Introduction To Exercise Physiology SPS135MUHAMMAD ARIF BIN MOHAMAD NOOR AZMANNo ratings yet