Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounts Chapter-Wise Test 6 (Suggested Answers)
Uploaded by
Shweta BhadauriaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounts Chapter-Wise Test 6 (Suggested Answers)
Uploaded by
Shweta BhadauriaCopyright:
Available Formats
Q1A) (2 Marks)
i) False: Average due date results in.no loss to any party i.e. debtor or creditor.
ii) False: Average due date is mean date of several due. dates for payments.
iii) False: While calculating the average due date, any date may be taken as the base date.
iv) True: Red-ink interest is treated as negative interest.
v) False: There are three ways of preparing an Account Current: ( i) With help of interest table; (ii) By means of
products and (iii) By means of products of balances.
Q1B) In case the due date of a bill falls after the date of closing the account, then no interest is allowed for that.
However, interest from the date of closing to such due date is written in “Red-Ink” in the appropriate side of the
‘Account current’. This interest is called Red-Ink interest. This Red Ink interest is treated as negative interest. In
actual practice, however the product of such bill [value of bill X (due date-closing date) is written in ordinary ink in
the opposite side onwhich the bill is entered]. (5 Marks)
Q1C) If no specific date is mentioned as the date on which the payment is due, the date of the transaction itself is to
be presumed to be the due date. In calculating the number of days, either the date of the transaction or the due
date is excluded.
In case of opening balance, number of days are to be calculated including both opening and closing dates. For the
purchase return transaction, take the same due date of related purchase transaction. Similarly for the sale return
transaction, take the same due date of related sale transaction. (5 Marks)
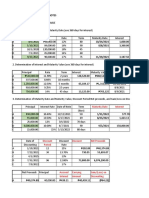
Q2A) CALCULATION OF AVERAGE DUE DATE [BASE DATE 1ST APRIL]
Due Date Amount No. of Days from Base Date to Due Date Products
Rs. Rs.
April 1 198,000 0 0
April 10 495,000 9 4455,000
May 16 990,000 45 44,550,000
June 9 297,000 69 20493,000
1980,000 69498,000
Average Due Date = Base Date + Days equal to Total of Products/Total
Amount days Average Due Date = 1st April + 69498,000/1980,000
= 1st April + 35.1 days= 6th May, 2022
Interest therefore has been calculated on Rs. 20,000 from 6th May, 2022 to 30th June, 2022 i.e.,
for 55 days @ 15% per annum.
Interest = 1980,000 × 15/100×55/365 = Rs. 44752.95 (10 Marks)
Q2B) MR. Amit IN ACCOUNT CURRENT WITH MR. Zakir
Dr. (INTEREST UPTO 15TH MARCH, 2022 @10% P.A.) Cr.
Date Particulars Rs. Days Product Date Particulars Rs. Days Product
2022 2022
Jan.01 To Balance b/d 176,000 75 88,00,000 Jan29 By 52800 46 2472800
PurchasesA/c
Jan15 To Sales A/c 981200 60 58872000 Feb10 By Cash A/c 44,000 34, 1496,000
Mar.13 To Red ink Mar13 By Bills
product Receivable A/c 44,000
(Rs.88,000 x 29) 2552,000 Mar15 By Balance of
Mar To Interest A/c 4840 product 17688,000
(Rs 17714400 x 10 x 1)
/
(100 × 366)
278960 21639200 278960 21639200
(10 Marks)
Sol 3 (10 Marks)
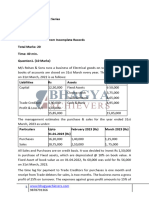
Taking 19.6.2022 as a Base date
Transaction Date Due Date Amount Amount
8.3.2018 11.7.2018 36,000 22 792,000
16.3.2018 19.6.2018 45,000 0 0
7.4.2018 10.9.2018 54,000 83 4482,000
17.5.2018 20.8.2018 45,000 62 2790,000
180,000 8064,000
Average Due Date= date Base+ Total of Product/ Total of Amount
= 19.6.2022 + ` 8064,000/`180,000
= 19.6.2022 + 44.8 days (or 45 days approximately)
= 3.8.2022
Mehnaaz wants to save interest of ` 1413 The yearly interest is ` 180,000 × 18% = ` 32400.
Assume that days corresponding to interest of ` 1413 are Y.
Then, 32400 × Y/365 = ` 1413
or Y = 1413 × 365/3,600 = 15.9 days or 16 days (Approx.)
Hence, if Mehnaaz wants to save ` 1413 by way of interest, she should prepone the payment of amount involved by 16 days from
the Average Due Date. Hence, she should make the payment on 18.7.2022 (3.8.2022 – 16 days).
You might also like
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionFrom EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific: Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Computerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionFrom EverandComputerised Accounting Practice Set Using MYOB AccountRight - Advanced Level: Australian EditionNo ratings yet
- C4 W1 Final AssessmentDocument14 pagesC4 W1 Final Assessmentdiktat86No ratings yet
- M6 Promissory NotesDocument14 pagesM6 Promissory NotesAldous RenielNo ratings yet
- Sari2 Store Cust1Document413 pagesSari2 Store Cust1Tax JPowertek Engineering ServicesNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - BalderosaDocument3 pagesCase Analysis - BalderosajenNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationSumanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Ira Shalini M. YbañezDocument5 pagesIra Shalini M. YbañezIra YbanezNo ratings yet
- MS Set2 SP AccDocument14 pagesMS Set2 SP AccJohn JoshyNo ratings yet
- FYJC Book Keeping and Accuntancy Topic Final AccountDocument4 pagesFYJC Book Keeping and Accuntancy Topic Final AccountRavichandraNo ratings yet
- Accounts - Full Test 1Document6 pagesAccounts - Full Test 1Shushaanth SanthoshNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Answers and Solutions - Assignment On Materials and LaborDocument8 pages4.2 Answers and Solutions - Assignment On Materials and LaborRoselyn LumbaoNo ratings yet
- Problem On Cash Budget: 8 (The End of The Prior Quarter), The Company's Balance Were As FollowsDocument4 pagesProblem On Cash Budget: 8 (The End of The Prior Quarter), The Company's Balance Were As Followsshreya chapagainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting: Suggested Answers Certificate in Accounting and Finance - Autumn 2018Document6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting: Suggested Answers Certificate in Accounting and Finance - Autumn 2018Asad ShahNo ratings yet
- Depreciation WorksheetDocument17 pagesDepreciation WorksheetMayank VermaNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING I 2019 MinDocument6 pagesFINANCIAL ACCOUNTING I 2019 MinKedarNo ratings yet
- Chartered Accountancy Professional Ii (CAP-II) : Education Division The Institute of Chartered Accountants of NepalDocument81 pagesChartered Accountancy Professional Ii (CAP-II) : Education Division The Institute of Chartered Accountants of NepalPrashant Sagar GautamNo ratings yet
- RTP Dec 2020 QnsDocument13 pagesRTP Dec 2020 QnsbinuNo ratings yet
- FinAct ARDocument15 pagesFinAct ARnanaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term ExamDocument6 pagesShort-Term Examymkuzangwe16No ratings yet
- Activity 3Document5 pagesActivity 3Keith Joshua GabiasonNo ratings yet
- Sec A&G - Corp Fin - Tut2 - AnswersDocument12 pagesSec A&G - Corp Fin - Tut2 - AnswersChinmay GokhaleNo ratings yet
- FinAct ARDocument12 pagesFinAct ARNMCartNo ratings yet
- Notes On Average Due Date PDFDocument15 pagesNotes On Average Due Date PDFManjunath Manju100% (1)
- Pilaps & VilsDocument15 pagesPilaps & VilsGwendolyn PansoyNo ratings yet
- Ugmbcc04 - Business AccountingDocument4 pagesUgmbcc04 - Business AccountingShreya MitraNo ratings yet
- Interest During ConstructionDocument90 pagesInterest During ConstructionAzzata HijabNo ratings yet
- Exercises 7A1 and 7B1: Book: Administrative AccountingDocument9 pagesExercises 7A1 and 7B1: Book: Administrative AccountingScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Acc q2 SANSDocument11 pagesAcc q2 SANSTanvir AnjumNo ratings yet
- Acc Comprehensive Project XiDocument11 pagesAcc Comprehensive Project Ximrnaman.0328No ratings yet
- Most Important Accounts Theory DiscussionDocument31 pagesMost Important Accounts Theory Discussionabdulganik240No ratings yet
- Sri Skanda Enterprises: Sathish Chellan Sir StatementDocument2 pagesSri Skanda Enterprises: Sathish Chellan Sir Statementdevi.gokhale8265No ratings yet
- VII. Instructions: Startup Expenses & CapitalizationDocument8 pagesVII. Instructions: Startup Expenses & CapitalizationPriyanshi Agrawal 1820149No ratings yet
- Accounting For Business DecisionsDocument7 pagesAccounting For Business DecisionsFaizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- CA Foundation Accounts Module I Average Due Date Without AnswersDocument19 pagesCA Foundation Accounts Module I Average Due Date Without AnswersVivek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- BTRN V3 Progress Check 1 Tutor Marked - Question Paper July19Document17 pagesBTRN V3 Progress Check 1 Tutor Marked - Question Paper July19Zach SullivanNo ratings yet
- A) Date Description Debit $ Credit $Document5 pagesA) Date Description Debit $ Credit $simranNo ratings yet
- Act1104 Quiz No. 3 Problem 1Document6 pagesAct1104 Quiz No. 3 Problem 1DyenNo ratings yet
- Business Pp2 MsDocument6 pagesBusiness Pp2 MsmartinNo ratings yet
- Deso 04Document5 pagesDeso 04Nguyễn Quốc TuấnNo ratings yet
- BBBBBDocument8 pagesBBBBBAlvira FajriNo ratings yet
- Latihan Susun LK & Arus Kas (Rommy Haris Winanda)Document9 pagesLatihan Susun LK & Arus Kas (Rommy Haris Winanda)rommyNo ratings yet
- Connect QuizzesDocument24 pagesConnect QuizzesAlyannaNo ratings yet
- ADFM Cash BudgetDocument5 pagesADFM Cash BudgetNidheena K SNo ratings yet
- Accounting GR 11 Acc T3 Week 6 Budgets - 2 ENGDocument5 pagesAccounting GR 11 Acc T3 Week 6 Budgets - 2 ENGsihlemooi3No ratings yet
- (266927) MOHD ALIFF ASMAWI BIN MAHYUDIN - Mid Term ExamDocument4 pages(266927) MOHD ALIFF ASMAWI BIN MAHYUDIN - Mid Term ExamAliph AsmawiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting: Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting: Page 1 of 6Hareem AbbasiNo ratings yet
- PQ3 BondsDocument2 pagesPQ3 BondsElla Mae MagbatoNo ratings yet
- SS Q1 Test Tax317 Dec 2021Document1 pageSS Q1 Test Tax317 Dec 2021Nik Syarizal Nik MahadhirNo ratings yet
- MTP May21 ADocument11 pagesMTP May21 Aomkar sawantNo ratings yet
- Sol Installment SalesDocument16 pagesSol Installment SalesMaria Beatrice100% (1)
- Promissory NotesDocument10 pagesPromissory Notespretty lyreNo ratings yet
- Bcom 3 Sem Corporate Accounting 1 19102078 Oct 2019Document5 pagesBcom 3 Sem Corporate Accounting 1 19102078 Oct 2019xyxx1221No ratings yet
- Treasury Management Vs Cash Management Answer To Warm Up ExercisesDocument8 pagesTreasury Management Vs Cash Management Answer To Warm Up Exercisesephraim0% (1)
- 15-Mca-Nr-Accounting and Financial ManagementDocument4 pages15-Mca-Nr-Accounting and Financial ManagementSRINIVASA RAO GANTA0% (2)
- Incomplete Records BTSDocument6 pagesIncomplete Records BTSdipakpunjabi18No ratings yet
- Final Exam - ACCT 5001P - Fall 2022Document23 pagesFinal Exam - ACCT 5001P - Fall 2022shuvorajbhattaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBR3zmYIfST M04WW9MOxJsCDOY8ij K10c8jFzoDesUe4hmgtwitQThRfZx9zgdfBbbfAPg9fYbdGwDnuwcmqyJhSe8wLpgC1wkMIV6jGps45E YC2ro8e WakacYQ6ARdjCeTf76iCHtdDocument6 pagesACFrOgBR3zmYIfST M04WW9MOxJsCDOY8ij K10c8jFzoDesUe4hmgtwitQThRfZx9zgdfBbbfAPg9fYbdGwDnuwcmqyJhSe8wLpgC1wkMIV6jGps45E YC2ro8e WakacYQ6ARdjCeTf76iCHtdMario FiskaNo ratings yet
- Ia ReportDocument7 pagesIa ReportnenzzmariaNo ratings yet
- Two The 20%. The: Vinze and of As TinDocument4 pagesTwo The 20%. The: Vinze and of As TinPRAYAGRAJ MITRA MANDAL GROUPNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer Summary The Law On Obligations and Contracts PDFDocument63 pagesOblicon Reviewer Summary The Law On Obligations and Contracts PDFCarmelou Gavril Garcia ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Obinna FMTDocument33 pagesObinna FMTocmainNo ratings yet
- Numerical AbilityDocument7 pagesNumerical AbilityNagaraja RaoNo ratings yet
- Kotak Assured Savings Plan Brochure1Document12 pagesKotak Assured Savings Plan Brochure1snakesmithsmithNo ratings yet
- Wealth Secrets of The One Percent How The Super-Rich Became SupDocument30 pagesWealth Secrets of The One Percent How The Super-Rich Became SupGforex ProfitmanNo ratings yet
- 14 Heirs of Franco v. Spouses GonzalesDocument10 pages14 Heirs of Franco v. Spouses GonzalesCharlou GalaNo ratings yet
- Chs 5 - 7Document20 pagesChs 5 - 7abigael kebedeNo ratings yet
- CHP. 1 - Indian Financial SystemDocument7 pagesCHP. 1 - Indian Financial SystemNandini JaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bond ValuationDocument24 pagesChapter 11 Bond Valuationfiq8809No ratings yet
- Micro-History of Sikhs in Singapore and Malaya 2011Document15 pagesMicro-History of Sikhs in Singapore and Malaya 2011sssanndraNo ratings yet
- Public Auction: Will Sell The Property Described Below byDocument10 pagesPublic Auction: Will Sell The Property Described Below byDS ChongNo ratings yet
- Chap 023Document20 pagesChap 023George WagihNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Case Digest Siga An and CA AgroDocument5 pagesWeek 3 Case Digest Siga An and CA AgrosophiaNo ratings yet
- Investment Accounts: Basic ConceptsDocument13 pagesInvestment Accounts: Basic ConceptsDebasis KarNo ratings yet
- ECN204 Mid 2013WDocument11 pagesECN204 Mid 2013WexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Inventories and Investment Theories v2Document10 pagesInventories and Investment Theories v2Joovs JoovhoNo ratings yet
- TOC - Indian Retail BankingDocument9 pagesTOC - Indian Retail Bankings_arora_7412No ratings yet
- AOSDocument49 pagesAOSKiran KesireddyNo ratings yet
- Ch4ProbsetTVM13ed - MasterDocument4 pagesCh4ProbsetTVM13ed - MasterRisaline CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- TFA - Chapter 36 - Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument9 pagesTFA - Chapter 36 - Property, Plant and EquipmentAsi Cas Jav0% (1)
- Effect of Capital Formation On Economic Growth inDocument17 pagesEffect of Capital Formation On Economic Growth inAyano DavidNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document31 pagesReport 2AravindNo ratings yet
- 8maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8 PDFDocument14 pages8maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8 PDFKaran Pratap100% (1)
- Finman Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesFinman Finals Reviewerg.canoneo.59990.dcNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument8 pagesConsumer BehaviourMani KrishNo ratings yet
- Project Report For Animal Feed PlantDocument6 pagesProject Report For Animal Feed Plantsamars05No ratings yet
- Demand For Loan Restructure - BTBDocument5 pagesDemand For Loan Restructure - BTBwrmarleyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: Cost Estimation Techniques Chapter 3 Money Time Relationships and Equivalence Chapter 4Document65 pagesEngineering Economy: Cost Estimation Techniques Chapter 3 Money Time Relationships and Equivalence Chapter 4ismailNo ratings yet
- NISM Series IV Interest Rate Derivatives Workbook Jan 2020Document97 pagesNISM Series IV Interest Rate Derivatives Workbook Jan 2020Manas MishraNo ratings yet
- PDF e Banking Project On Sbi CompressDocument26 pagesPDF e Banking Project On Sbi CompressPawanNo ratings yet