Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geography Lesson 3
Geography Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Debsruti Saha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
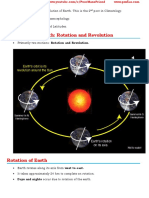
5 views2 pagesThe Earth has two types of motions: rotation and revolution. Rotation is the Earth's movement on its axis once every 24 hours, creating days and nights. Revolution is the Earth's elliptical movement around the sun once every 365.25 days, creating the seasons and changes in sunlight intensity towards the poles. There are two solstices - summer and winter - when the sun's rays are most direct over the Tropic of Cancer or Capricorn, respectively, creating the longest and shortest days. There are also two equinoxes in spring and autumn when the sun's rays are equally distant from the north and south poles, creating equal day and night lengths worldwide.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Earth has two types of motions: rotation and revolution. Rotation is the Earth's movement on its axis once every 24 hours, creating days and nights. Revolution is the Earth's elliptical movement around the sun once every 365.25 days, creating the seasons and changes in sunlight intensity towards the poles. There are two solstices - summer and winter - when the sun's rays are most direct over the Tropic of Cancer or Capricorn, respectively, creating the longest and shortest days. There are also two equinoxes in spring and autumn when the sun's rays are equally distant from the north and south poles, creating equal day and night lengths worldwide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesGeography Lesson 3
Geography Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Debsruti SahaThe Earth has two types of motions: rotation and revolution. Rotation is the Earth's movement on its axis once every 24 hours, creating days and nights. Revolution is the Earth's elliptical movement around the sun once every 365.25 days, creating the seasons and changes in sunlight intensity towards the poles. There are two solstices - summer and winter - when the sun's rays are most direct over the Tropic of Cancer or Capricorn, respectively, creating the longest and shortest days. There are also two equinoxes in spring and autumn when the sun's rays are equally distant from the north and south poles, creating equal day and night lengths worldwide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Lesson 3 MOTIONS of the EARTH
Two type of motions:
- Rotation:
a. Movement of the Earth on its axis
b. 24 hours one rotation ‘Earth day’
c. Days and night
d. West to east (anti-clockwise)
e. Inclination of Earth’s tilt 661/2 with orbital plane
- Axial tilt (obliquity) 231/2 with vertical line to the orbital plane
f. The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the Circle of
Illumination.
g. Unequal heating (vertical rays over the Equator and slant towards the poles)
h. Tilted axis is always pointed towards the Pole Star
- Revolution:
a. Movement of the Earth around the sun
b. In elliptical orbit
c. 3651/4 days (365 days 6 hours)
d. 365 days one year
e. ¼ day or 6 hours added to February month every 4 years 29 Days i.e,
Leap Year
f. Change of seasons : Summer, Winter, Spring, Autumn
g. Seasons in the northern hemisphere are reversed to that of southern
hemisphere
h. Because of changes in position of Earth while revolving around the sun
i. Intensity and duration of sunshine goes on changing towards the poles
Solstices
- That time of the year when the sun’s vertical rays fall over one of the two tropics.
- Sun appears to stand still at its highest point in each hemispheres
- Tropics of Cancer & Tropic of Capricorn
- Two solstices:
a. Summer solstice (21st June)
- Northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun
- Sun rays: directly on Tropic of Cancer (more heat)
- Areas near the poles: less heat (slanting rays)
- Summer in the northern hemisphere
- Areas beyond Arctic Circle ( continuous daylight for about 6 months)
- Longest day; shortest night (21st Jan)
- Reverse in southern hemisphere :
o Winter
o Longer nights
o Shorter days
b. Winter solstice (22nd December)
- Southern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun
- Sun rays: directly on Tropic of Capricorn (more heat, more light)
- Summer: longer days; shorter nights
- Reverse in Northern hemisphere
- 22nd December : shortest days; longest night in Northern Hemisphere
Equinoxes
- The sun’s ray directly fall on the Equator
- North Pole and South Pole equal distance from the sun
- None of them are inclined or away from the sun
- Equal day and night throughout the world
- 2 Equinoxes:
a. Spring Equinox (21st March)
- Northern hemisphere: Spring
- Southern hemisphere: Autumn
b. Autumn Equinox (23rd September)
- Northern hemisphere: Autumn
- Southern hemisphere: Spring
You might also like
- UNIT 1.2 - Solar System, Earths MovementsDocument11 pagesUNIT 1.2 - Solar System, Earths MovementsAitana GADANo ratings yet
- Motion of The EarthDocument21 pagesMotion of The EarthNargis ShamimNo ratings yet
- Earth and SpaceDocument15 pagesEarth and SpaceAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Dignities and Debilities Consideration by M. ImranDocument2 pagesDignities and Debilities Consideration by M. Imranm-imran100% (1)
- Geography NotesDocument185 pagesGeography NotesShubham SinhaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Motions of The Earth PDFDocument8 pagesCH 3 Motions of The Earth PDFKaruna SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Rotation and Revolution NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Rotation and Revolution NotesMERLIN ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- Earth TiltDocument39 pagesEarth TilteurizirueNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Unit 1 3 - Earth-Sun RelationshipDocument34 pagesAstronomy Unit 1 3 - Earth-Sun Relationshipapi-278569039No ratings yet
- Earth Moon Sun Mind MapDocument1 pageEarth Moon Sun Mind Mapravichandran100% (3)
- Chapter 1 Astronomy The Cycles of The SkyDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Astronomy The Cycles of The SkyMa. Lucille AbarracosoNo ratings yet
- Class VI Motions of The Earth NotesDocument3 pagesClass VI Motions of The Earth Notesaam aadmiNo ratings yet
- 9 - Geo - Rotation & RevolutionDocument6 pages9 - Geo - Rotation & RevolutionMahesh k KNo ratings yet
- Class Notes On The Motions of The EarthDocument4 pagesClass Notes On The Motions of The EarthAdnan EonnNo ratings yet
- Seasons in The Sun : QuestionsDocument11 pagesSeasons in The Sun : QuestionsfostbarrNo ratings yet
- Discovering The Essential UniverseDocument24 pagesDiscovering The Essential UniverseShanelle OwensNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q4 Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The EarthDocument33 pagesG7 Science Q4 Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The EarthAnaly AndamonNo ratings yet
- Seasons ActivitiesDocument14 pagesSeasons ActivitiesShumaila BaigNo ratings yet
- 9-1 The Earth-Moon System WebDocument9 pages9-1 The Earth-Moon System WebKelli McDaniel MarchbanksNo ratings yet
- CHP 01 - Rotation and RevolutionDocument5 pagesCHP 01 - Rotation and RevolutionKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- Motions of The Earth: Rotation and RevolutionDocument10 pagesMotions of The Earth: Rotation and RevolutionVikram DasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Motions of The EarthDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Motions of The EarthAmazing DayNo ratings yet
- Motions of The EarthDocument3 pagesMotions of The EarthmanibalanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On EarthDocument35 pagesTutorial On EartherbrijeshNo ratings yet
- G-6 Motions of The Earth-NotesDocument2 pagesG-6 Motions of The Earth-NotespinkyNo ratings yet
- CH3b - Wk7-8. Solar Angle and Solar RadiationDocument55 pagesCH3b - Wk7-8. Solar Angle and Solar RadiationAhmed AbdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q4 - Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The Earth-1Document33 pagesG7 Science Q4 - Week 5 Evidence of Rotation of The Earth-1laurenmartinez0913No ratings yet
- Earth's Revolution: Seasons and Retrograde Motion of PlanetsDocument18 pagesEarth's Revolution: Seasons and Retrograde Motion of PlanetsSameer WaliaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Today : The Tilting of The Earth: Shaping Our Seasons and ClimatesDocument13 pagesEcology Today : The Tilting of The Earth: Shaping Our Seasons and ClimatesTrung LeNo ratings yet
- Sun and The Design ProcessDocument28 pagesSun and The Design ProcessJireh Grace100% (5)
- World GeographyDocument36 pagesWorld GeographyRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Earth/Sun Relations and SeasonsDocument10 pagesTutorial On Earth/Sun Relations and SeasonsJennifer HenryNo ratings yet
- Earth-Sun Relationship: (Use With Notes and Homework Quiz Handout)Document27 pagesEarth-Sun Relationship: (Use With Notes and Homework Quiz Handout)sheil.cogayNo ratings yet
- SeasonalityDocument16 pagesSeasonalityScienceGramNo ratings yet
- Motions of The EarthDocument8 pagesMotions of The EarthnidhiNo ratings yet
- Earth Part 1Document49 pagesEarth Part 1Vartika RaghwaniNo ratings yet
- Rotation and Revolution NotesDocument3 pagesRotation and Revolution NotesManan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Geography Means Description of EarthDocument23 pagesGeography Means Description of EarthKarthikeyan ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-Sslc-Social Science 2 - All - Chapters-EmDocument48 pagesSheniblog-Sslc-Social Science 2 - All - Chapters-Emgm1650045No ratings yet
- Stuvia 848773 Atpl G Nav ResumeDocument9 pagesStuvia 848773 Atpl G Nav ResumeAnuar SNo ratings yet
- Motion of The EarthDocument1 pageMotion of The EarthBasco Martin Jr100% (1)
- Meaning and Effects of Revolution of The EarthDocument3 pagesMeaning and Effects of Revolution of The EarthtosinadebayoabikNo ratings yet
- Ak ch3Document2 pagesAk ch3durgaNo ratings yet
- Motions NotesDocument6 pagesMotions NotesAyesha SyedNo ratings yet
- Motions of The Earth NotesDocument1 pageMotions of The Earth NotesKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Geography. Class-6 Lesson-3 Topic-Motions of The Earth. Homework-1Document3 pagesGeography. Class-6 Lesson-3 Topic-Motions of The Earth. Homework-1RamakantaSahooNo ratings yet
- Earth and Sun Relationships PDFDocument9 pagesEarth and Sun Relationships PDFAparajita MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Rotation Revolution Equinoxes Solstices Aphelion Perihelion Sun Angles Direct/Indirect Sun Migration of Direct Sun Latitudinal ZonesDocument13 pagesAstronomy Rotation Revolution Equinoxes Solstices Aphelion Perihelion Sun Angles Direct/Indirect Sun Migration of Direct Sun Latitudinal ZonesJorge Vega RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Motions of The Earth (Ncert)Document3 pagesMotions of The Earth (Ncert)Nirali MehtaNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Black Book PDFDocument18 pagesIndian Geography Black Book PDFαиgєl ѕєlєиαNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument185 pagesGeography Noteshome123No ratings yet
- AS 101 Module 1 Quiz ReviewDocument11 pagesAS 101 Module 1 Quiz ReviewahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Huda MadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Rotation and RevolutionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Rotation and RevolutionShilpy UmapatiNo ratings yet
- NDA Complete World Geography English (New)Document58 pagesNDA Complete World Geography English (New)Nigam Chaudhary100% (1)
- World Geography: Strictly Based On Nda/Na Examination CurriculumDocument58 pagesWorld Geography: Strictly Based On Nda/Na Examination CurriculumTera YarrNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Movements PDFDocument37 pagesThe Earth's Movements PDFEnola PearlNo ratings yet
- Earth and Solar System: Equinoxes 20 Mar. 23 Sep. Summer WinterDocument12 pagesEarth and Solar System: Equinoxes 20 Mar. 23 Sep. Summer WinterHamza OmranNo ratings yet
- Science Week 6 - 093108Document3 pagesScience Week 6 - 093108Junelyn T. AbabaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Astronomical CyclesDocument37 pagesPart 1 Astronomical Cyclesashutosh1966No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Day and Night and SeasonsDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - Day and Night and Seasonscasumae.depositarioNo ratings yet
- Concept of PovertyDocument3 pagesConcept of PovertyDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- One Word SubstitutionDocument60 pagesOne Word SubstitutionDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- SchedulesDocument1 pageSchedulesDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- PartsDocument1 pagePartsDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- PreambleDocument3 pagesPreambleDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- Gandhian EraDocument1 pageGandhian EraDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document3 pagesLesson 7Debsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- History Lesson 6Document4 pagesHistory Lesson 6Debsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- .NETDocument22 pages.NETDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- ListDocument1 pageListDebsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- HTML 5Document3 pagesHTML 5Debsruti SahaNo ratings yet
- Online Notebook Green Variant - by SlidesgoDocument50 pagesOnline Notebook Green Variant - by SlidesgoAilen Wendy Lopez MoralesNo ratings yet
- Learn English in SevenDocument57 pagesLearn English in SevensaadNo ratings yet
- Martin Luther King Jr. Day by SlidesgoDocument54 pagesMartin Luther King Jr. Day by SlidesgojoninpNo ratings yet
- Grace Ann Wooten - Milankovitch Cycles-2Document1 pageGrace Ann Wooten - Milankovitch Cycles-2api-528744022No ratings yet
- 03.04 How Do I Maintain FocusDocument4 pages03.04 How Do I Maintain FocusJosalin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nitty Gritty Astrology-1 SyllabusDocument2 pagesNitty Gritty Astrology-1 SyllabusLucas JonesNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis InfographicsDocument33 pagesSWOT Analysis Infographicssanjay kafleNo ratings yet
- Prithvi Hamara Avas Class 6th GeographyDocument71 pagesPrithvi Hamara Avas Class 6th Geographymanish.cdmaNo ratings yet
- Amber Heard Tropical Astrology Chart Without Time of BirthDocument2 pagesAmber Heard Tropical Astrology Chart Without Time of Birthmgv1No ratings yet
- CometsDocument3 pagesCometsMariel GregoreNo ratings yet
- Kepler Laws of Planetary MotionDocument4 pagesKepler Laws of Planetary Motionclairesantosss12No ratings yet
- The Voice of Truth International, Volume 27Document116 pagesThe Voice of Truth International, Volume 27World EvangelismNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP SO SÁNH HƠN VÀ HƠN NHẤT LỚP 6Document4 pagesBÀI TẬP SO SÁNH HƠN VÀ HƠN NHẤT LỚP 6Ngọc TạNo ratings yet
- 7 Eng FAL GR 7 Term 2 Revision NotesDocument22 pages7 Eng FAL GR 7 Term 2 Revision NotesannieNo ratings yet
- All About EclipsesDocument5 pagesAll About EclipsesHonelie Tomagan DasiganNo ratings yet
- Planets Main IdeaDocument2 pagesPlanets Main IdeatpsoftxNo ratings yet
- Meat Industry Company Profile by SlidesgoDocument41 pagesMeat Industry Company Profile by SlidesgoEstefany Denisse Martínez VásquezNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lesson PlansDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Lesson Plansapi-206098535No ratings yet
- Natal Chart Report PDFDocument8 pagesNatal Chart Report PDFVictor HugoNo ratings yet
- Asthvarga Lessons - The Vedic HoroscopeDocument14 pagesAsthvarga Lessons - The Vedic HoroscopeAashishh PatilNo ratings yet
- Chinese Language Day by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesChinese Language Day by Slidesgogilang rikoNo ratings yet
- Space Physics Question Sheet (SOLVED)Document24 pagesSpace Physics Question Sheet (SOLVED)AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Your Horoscope by Susan MillerDocument6 pagesYour Horoscope by Susan MillerAliNo ratings yet
- GravityDocument3 pagesGravityDarioCastro100% (1)
- Activity Worksheet: Smartphone AstronomyDocument3 pagesActivity Worksheet: Smartphone AstronomyMohankumar BanupriyaNo ratings yet
- Astronomer Avi Loeb Says Aliens Have VisitedDocument1 pageAstronomer Avi Loeb Says Aliens Have VisitedDonald TrummpNo ratings yet
- Bac Sample 1Document2 pagesBac Sample 1Kouam AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Earth's MoonDocument2 pagesEarth's MoonJhuly-an Silva VillanuevaNo ratings yet