Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RAINBOW
Uploaded by
Baha Udin Jazuli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageRainbows are meteorological phenomena caused by the reflection, refraction, and diffraction of light within water droplets, appearing as colorful circular arcs opposite the sun. They are formed by sunlight entering a raindrop, reflecting inside, and refracting upon exiting, with primary rainbows showing red on the outside and double rainbows having the color order reversed with red on the inside.
Original Description:
Description rainbow
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRainbows are meteorological phenomena caused by the reflection, refraction, and diffraction of light within water droplets, appearing as colorful circular arcs opposite the sun. They are formed by sunlight entering a raindrop, reflecting inside, and refracting upon exiting, with primary rainbows showing red on the outside and double rainbows having the color order reversed with red on the inside.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageRAINBOW
Uploaded by
Baha Udin JazuliRainbows are meteorological phenomena caused by the reflection, refraction, and diffraction of light within water droplets, appearing as colorful circular arcs opposite the sun. They are formed by sunlight entering a raindrop, reflecting inside, and refracting upon exiting, with primary rainbows showing red on the outside and double rainbows having the color order reversed with red on the inside.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
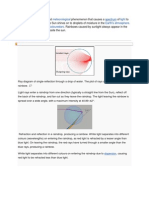
RAINBOW
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon caused by the reflection, refraction and diffraction
of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. Rainbows usually
form colourful circular arcs. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the part of the sky
directly opposite the sun.
Rainbows can be full circles. However, observers usually only see an arc formed by light
droplets on the ground,[1] and centred on a line from the sun to the observer's eye.
In a primary rainbow, the arc shows red on the outside and purple on the inside. This rainbow is
caused by light being refracted as it enters the water droplet. It is then reflected inwards at the
back of the droplet and refracted again as it exits.
In a double rainbow, the second arc is seen outside the primary arc and the colour order is
reversed, with red on the inner side of the arc. This is caused by light being reflected twice on
the inside of the droplet before leaving it.
You might also like
- WorksheetHandoutNo.12 MaryJoy v. ChiquilloDocument9 pagesWorksheetHandoutNo.12 MaryJoy v. ChiquilloDulce J. LuatonNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Sky BlueDocument7 pagesWhy Is The Sky BlueY D Amon GanzonNo ratings yet
- Meteorological Reflection Refraction Dispersion Spectrum ArcDocument1 pageMeteorological Reflection Refraction Dispersion Spectrum ArcyosephineikaaNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument1 pageRainbowMari Creon A. BaumgardnerNo ratings yet
- Meteorological Reflection Refraction Dispersion Spectrum ArcDocument3 pagesMeteorological Reflection Refraction Dispersion Spectrum ArcAzreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- How Are Rainbow FormedDocument11 pagesHow Are Rainbow Formedmohammad narmi100% (3)
- Why Are Rainbows in An Arc Shape?Document16 pagesWhy Are Rainbows in An Arc Shape?smnjawadNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument2 pagesRainbowMarsudi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Rainbow (Repaired)Document56 pagesRainbow (Repaired)Lileng LeeNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument25 pagesRainbowarvindkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text About RainbowDocument4 pagesExplanation Text About RainbowSelvia ErnindaNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasindhusmNo ratings yet
- To Bing 2018Document22 pagesTo Bing 2018Herwindo NathanaelNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument7 pagesRainbowEljona YzellariNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text About RainbowDocument4 pagesExplanation Text About RainbowNeyHafniiCyuwCyu25% (4)
- What Are Rainbows?: Home World Clock Time Zones Calendar Weather Sun & Moon Timers Calculators Apps & API Free FunDocument7 pagesWhat Are Rainbows?: Home World Clock Time Zones Calendar Weather Sun & Moon Timers Calculators Apps & API Free FunshettyNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument4 pagesReport TextDaffaandhika PutraNo ratings yet
- Rainbow FormationDocument25 pagesRainbow FormationGanesh SingaramNo ratings yet
- What Causes A Rainbow GP 2021Document4 pagesWhat Causes A Rainbow GP 2021Cesar LazaroNo ratings yet
- Rainbow: Some Fascinating Facts PhysicsDocument5 pagesRainbow: Some Fascinating Facts PhysicsRishi AmritNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument3 pagesRainbowDesy WindyanaNo ratings yet
- Explanation TextDocument1 pageExplanation TextrisaNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument5 pagesRainbowsevenNo ratings yet
- RainbowsDocument1 pageRainbowsSamartha RVNo ratings yet
- Rainbow Facts For KidsDocument2 pagesRainbow Facts For KidsSharanu HolalNo ratings yet
- 5Th Group: Melsi Triana Erica Rachma Putri Triska Ladini Meilika Dwi PutriDocument7 pages5Th Group: Melsi Triana Erica Rachma Putri Triska Ladini Meilika Dwi PutriMelsi TrianaNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary RainbowDocument11 pagesPrimary and Secondary Rainbowrichard rhamilNo ratings yet
- Rainbows: An Example of Natural Dispersion of LightDocument1 pageRainbows: An Example of Natural Dispersion of LightReeja MathewNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument14 pagesRainbowabcdefghNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Light Visible Light Is Composed of A Spectrum of WavelengthsDocument1 pageDispersion of Light Visible Light Is Composed of A Spectrum of WavelengthsIrtifa TazkiaNo ratings yet
- How Are Rainbows FormedDocument9 pagesHow Are Rainbows FormedAliza SikanderNo ratings yet
- The Rainbow Fran PérezDocument5 pagesThe Rainbow Fran PérezcarlosvyNo ratings yet
- X-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument27 pagesX-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldBilal kaziNo ratings yet
- Atm RFN SctrngPOONAMDocument4 pagesAtm RFN SctrngPOONAMpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- Rainbow TEXTDocument1 pageRainbow TEXTYusufNo ratings yet
- Rainbow FormationDocument6 pagesRainbow FormationMystical ProductionsNo ratings yet
- RainbowDocument1 pageRainbowNabil Hamzah ANo ratings yet
- Rainbow Formation: The Path of Light Through A DropletDocument2 pagesRainbow Formation: The Path of Light Through A DropletNisha Lauren VishvanathNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument3 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful WorldVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- RainbowsDocument3 pagesRainbowsRyss FloresNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 5-8Document17 pagesPhysical Science 5-8Dainavi Lizarte Bayucan PalitayanNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourfulworld rs1Document4 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourfulworld rs1Anushka TripathiNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument28 pagesRefraction of LightLance Louis Bersamin DacaraNo ratings yet
- Physical PhenomenonDocument5 pagesPhysical PhenomenonDiana MLNo ratings yet
- LightDocument183 pagesLightSai Vishnu GainiNo ratings yet
- 10 PhysicsDocument4 pages10 PhysicsNicka Asereht MinaNo ratings yet
- How Does A Rainbow FormDocument6 pagesHow Does A Rainbow FormJaylord lamdagNo ratings yet
- Sharjah Indian School Br. Juwaiza Grade: X Physics-L - 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument4 pagesSharjah Indian School Br. Juwaiza Grade: X Physics-L - 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDennNo ratings yet
- What Is A Rainbow?Document12 pagesWhat Is A Rainbow?Angelina PondeteNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument3 pagesPhysics AssignmentAllen Dan Joyce LopezNo ratings yet
- Dispersion & ColorsDocument23 pagesDispersion & ColorsJhon Rey SardidoNo ratings yet
- Class10 ScienceDocument4 pagesClass10 ScienceDr.Jyotika ChopraNo ratings yet
- How Do Rainbows Form?Document2 pagesHow Do Rainbows Form?Pratiwi SaputriNo ratings yet
- What Is A RainbowDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Rainbowthe punisher 1No ratings yet
- Human Eye & Colourful WorldDocument25 pagesHuman Eye & Colourful WorldUlhas VairagkarNo ratings yet
- Human Eye & Colourful WorldDocument25 pagesHuman Eye & Colourful WorldUlhas VairagkarNo ratings yet
- Why Do Rainbows Appear? What Are The Differences Between PrimaryDocument2 pagesWhy Do Rainbows Appear? What Are The Differences Between Primarythe punisher 1No ratings yet
- How A Rainbow Works - Elocution Speech by HarshiDocument1 pageHow A Rainbow Works - Elocution Speech by HarshisbNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Light NotesDocument2 pagesDispersion of Light NotesMahesh GawadeNo ratings yet