Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MicroEcono MicroEconomicAnalysisII
Uploaded by
Mirza Muneeb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesMicro
Original Title
MicroEcono_MicroEconomicAnalysisII
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesMicroEcono MicroEconomicAnalysisII
Uploaded by
Mirza MuneebMicro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Cluster University Srinagar
Department of Economics
Syllabus for 5-Year Integrated Programme
Course Title: Micro Economic Analysis - II Semester :8th
Course Code: IEC-C2181 (Core) Credits: 04
Course Description
This course aims to acquaint students with fundamental theory of oligopoly. Theory of games is
also included to introduce students to the complicacies of oligopolistic markets. Further General
equilibrium theory and Welfare Economics are also covered in this course to acquaint students
with the weaknesses of partial equilibrium analysis.
Unit I: Oligopolistic markets and Game theory
Non-collusive oligopoly– Cournot, Bertrand, Chamberlin, Kinked demand curve and Stackelberg
models; Simultaneous games and sequential games; Zero-sum and Non-zero sum games;
Prisoner’s Dilemma; Dominant strategy equilibrium; Nash Equilibrium; Game in extensive and
normal form, Repeated games; Collusive oligopoly– cartels and price leadership.
Critical evaluation of marginal analysis; Average cost pricing; Bain’s limit pricing theory,
Managerial theories of firm-Baumol’s static and dynamic models of sales revenue maximization.
Unit II: Input markets
Marginal productivity theory; Factor pricing in perfectly competitive markets; Factor pricing in
imperfect product and factor markets; Work-Leisure trade-off; Backward bending supply curve of
labour; Elasticity of technical substitution and factor shares; Technical progress and income
distribution; Pricing of fixed factors of Production- rent and quasi-rent; Euler’s product exhaustion
theorem.
Unit III: General equilibrium
Partial equilibrium Vs General equilibrium; Walrasian system, Existence, Uniqueness and
Stability of an equilibrium, Static properties of general equilibrium- Efficiency in exchange and
production, Production possibility frontier; Simultaneous equilibrium of production and
consumption; Equilibrium and Walras law; Competitive market equilibrium and Pareto efficiency;
Fundamental theorems of welfare economics.
Unit IV: Welfare Economics
Criteria of welfare maximization – Bentham’s criteria, Pareto optimality criterion, Kaldor- Hicks
compensation criteria; Maximisation of social welfare– Grand utility possibility frontier;
Determination of welfare maximizing configuration; Social choice and Arrow’s impossibility
theorem; Social welfare functions- Rawlsian and Benthamite.
References:
1. Henderson, J.M & R.E. Quandt. (1980).Micro Economic Theory: A Mathematical Approach,
McGraw Hall, New Delhi.
2. Varian, H. R. (2009).Intermediate Microeconomics (8thed.).W.W Norton & Company.
3. Nicholson, W. (1992).Microeconomic Theory: Basic Principals and Extensions. The Dryden
Press, USA.
4. Varian, H. R (1992).Microeconomic Analysis (3rd ed.). W.W Norton Company.
5. Perloff, J. M. (2001).Microeconomics, Addison Wisely Longman, India.
6. Koutsoyiannis, A. (1979).Modern Microeconomics, Macmillan Press, London.
7. Layard, P. R. G. and Walters, A.W. (1978).Microeconomic Theory, McGraw Hill, New York.
8. Sen, A. K. (1999).Microeconomics - Theory and Applications, Oxford University Press.
9. Pindyck, R. S. and Rubinfeld, D. L. (1999).Microeconomics, Prentice Hall of India.
10. Hall, R.E. and Lieberman M. (2010).Microeconomics-Principles and applications
(5thed.).Cengage Learning.
You might also like
- Forecasting Volatility in the Financial MarketsFrom EverandForecasting Volatility in the Financial MarketsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Syllabus FOR B.A. (Honours) Economics Under Choice Based Credit SystemDocument24 pagesSyllabus FOR B.A. (Honours) Economics Under Choice Based Credit SystemJaga SwainNo ratings yet
- First Sem SyllabusDocument8 pagesFirst Sem SyllabusPunte GiriNo ratings yet
- UG SyllabusJuly2016Document40 pagesUG SyllabusJuly2016AathiNarayananCNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - Econ - 101 PDFDocument164 pagesMicroeconomics - Econ - 101 PDFSatis ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ma Economics PDFDocument59 pagesMa Economics PDFHarish ItkarNo ratings yet
- 9 EconomicsDocument25 pages9 EconomicsMalsawmkima Maski-aNo ratings yet
- Annexure-172. B.com. Programme Ge CoursesDocument4 pagesAnnexure-172. B.com. Programme Ge CoursesANANT AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- FT I Manag EcoDocument3 pagesFT I Manag EcoKavyaNo ratings yet
- 1 1 2Document149 pages1 1 2nahid mushtaqNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University - Ma Applied Economics SyllabusDocument27 pagesPondicherry University - Ma Applied Economics SyllabusNevin TomNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For B.A. (Pass Course) : Page - 1Document19 pagesSyllabus For B.A. (Pass Course) : Page - 1TapaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Actuarial Economics: Indira Gandhi National Open University, New DelhiDocument8 pagesM.Sc. Actuarial Economics: Indira Gandhi National Open University, New Delhiallan2inNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Econ 101Document164 pagesMicroeconomics Econ 101Alphá Kídd100% (1)
- P8MBA4Document1 pageP8MBA4Ramalingam SivaramanNo ratings yet
- FC103 Managerial Economics 61011102Document3 pagesFC103 Managerial Economics 61011102Abhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Bpam 112 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesBpam 112 Course Outlinemansaraymusa788No ratings yet
- Centre For Development StudiesDocument113 pagesCentre For Development StudiesIndraneel Ps100% (1)
- Economics For Business Decisions Book 2 For M.com Sem 1 2019Document161 pagesEconomics For Business Decisions Book 2 For M.com Sem 1 2019Gaurav PatilNo ratings yet
- HSS4161: Applied Economics: Course Context and Overview: This Course Has Been Designed To Be An Advanced Level CourseDocument3 pagesHSS4161: Applied Economics: Course Context and Overview: This Course Has Been Designed To Be An Advanced Level Courseraghav dhamaniNo ratings yet
- VFHKJHDocument56 pagesVFHKJHuihgfhjjhghNo ratings yet
- Acce CourseDocument14 pagesAcce CourseShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument7 pagesNew SyllabusApong LkrNo ratings yet
- PG Syllabus Cbcs-Final 2018-21Document38 pagesPG Syllabus Cbcs-Final 2018-21Ravi SDNo ratings yet
- M.A. Part I Semester I: Four Courses in Each of The Two Semesters For M.A in EconomicsDocument11 pagesM.A. Part I Semester I: Four Courses in Each of The Two Semesters For M.A in EconomicsHolly JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument2 pagesMicroIshman SinghNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics LOLP For PGDM 2013-15 by Pankaj KumarDocument4 pagesManagerial Economics LOLP For PGDM 2013-15 by Pankaj KumarRaja ßalaNo ratings yet
- National University: SyllabusDocument14 pagesNational University: Syllabusঅবাকঅমিয়No ratings yet
- Block-2 Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument72 pagesBlock-2 Theory of Consumer BehaviourCqf 107No ratings yet
- Economics - I: Course Code: ILB 302 Credit Units: 04 Course ObjectiveDocument1 pageEconomics - I: Course Code: ILB 302 Credit Units: 04 Course ObjectivewasisiNo ratings yet
- BA Micro Eco SyllabusDocument1 pageBA Micro Eco SyllabusBhavina Joshi IPSANo ratings yet
- Ma-Economics SyllabusDocument47 pagesMa-Economics SyllabusAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Annexure-172. B.COM. PROGRAMME GE COURSESDocument5 pagesAnnexure-172. B.COM. PROGRAMME GE COURSES8717878740No ratings yet
- Economics SyllabusDocument4 pagesEconomics SyllabusarushiNo ratings yet
- Economics ElectiveDocument8 pagesEconomics ElectiveVINAY YADAVNo ratings yet
- StudySchemeEconomics BZUDocument26 pagesStudySchemeEconomics BZUTipu SultanNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics - Undergraduate-Curriculum-Framework-2022 PDFDocument2 pagesMicro Economics - Undergraduate-Curriculum-Framework-2022 PDFMUDASIRNo ratings yet
- UGC Model Syllabus (Eco Gen)Document14 pagesUGC Model Syllabus (Eco Gen)Debanjana DeyNo ratings yet
- Honours 1st Year EconomicsDocument13 pagesHonours 1st Year Economicsjahidulislamsakib621No ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS 3 KkhsouDocument188 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS 3 KkhsouptgoNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)Document7 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)haroonsaeed12No ratings yet
- BA in EconomicsDocument18 pagesBA in EconomicsSumit KawadeNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument1 pageEconomicsNaren Kavi100% (3)
- Module 1 (30 Marks) Consumer BehaviourDocument34 pagesModule 1 (30 Marks) Consumer BehaviourSukanya BaralNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS - Managerial EconomicsDocument2 pagesSYLLABUS - Managerial EconomicsJohn Mwakima100% (1)
- HSS 101 - Economics HandbookDocument4 pagesHSS 101 - Economics HandbookAditya PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document44 pagesUnit 1Nitesh BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- M.A. (Economics) Curtailed Syllabus 2020-21Document37 pagesM.A. (Economics) Curtailed Syllabus 2020-21aditya.hata1113No ratings yet
- Aa PDFDocument195 pagesAa PDFsujatha ramkiNo ratings yet
- I. Economics Four Year Course StructureDocument25 pagesI. Economics Four Year Course StructureRokhod ProductionNo ratings yet
- LAW1301 - MANAGERIAL-ECONOMICS - TH - 1.1 - 0 - LAW 1301 - Managerial EconomicsDocument2 pagesLAW1301 - MANAGERIAL-ECONOMICS - TH - 1.1 - 0 - LAW 1301 - Managerial EconomicssNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 ECONOMICSDocument61 pagesUnit-1 ECONOMICSMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-06 at 3.04.08 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-06 at 3.04.08 PMshibilayasirNo ratings yet
- BA Economics (Pass) 1st & 2nd Sem - 16!11!17Document4 pagesBA Economics (Pass) 1st & 2nd Sem - 16!11!17Rishu RajNo ratings yet
- Tlaw189l Managerial-Economics TH 1.0 0 Tlaw189lDocument2 pagesTlaw189l Managerial-Economics TH 1.0 0 Tlaw189lShreyaah TSNo ratings yet
- 29 EconomicsDocument10 pages29 Economicsarjuntatikonda69No ratings yet
- Chiang Fundamental Mathematical Economics SolutionDocument3 pagesChiang Fundamental Mathematical Economics SolutionAshim KumarNo ratings yet
- Contact Hours: 48 Credit Hours: 3.0Document3 pagesContact Hours: 48 Credit Hours: 3.0Ibrahim shamatiNo ratings yet
- BS ECON Course Outlines Punjab UniversityDocument61 pagesBS ECON Course Outlines Punjab UniversityvaniNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics-Course OutlineDocument6 pagesMicroeconomics-Course OutlineSimran MittalNo ratings yet
- Econ2103 T3Document2 pagesEcon2103 T3AdreshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Market EquilibriumDocument14 pagesLesson 4 - Market EquilibriumCharles Corporal ReyesNo ratings yet
- Quiz MicroDocument5 pagesQuiz Microchittran313No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document42 pagesTutorial 5kikNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Test Bank 1Document27 pagesMicroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Test Bank 1kristen100% (37)
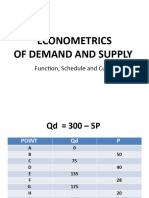
- Econometrics of Demand and SupplyDocument15 pagesEconometrics of Demand and SupplySer MyrNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics I Session 18-24 Consumer BehaviourDocument57 pagesMicroeconomics I Session 18-24 Consumer BehaviourMahi YadavNo ratings yet
- ECO2201 - Slides - 2.2 - Consumer Choice and Utility MaximizationDocument51 pagesECO2201 - Slides - 2.2 - Consumer Choice and Utility Maximizationjokerightwegmail.com joke1233No ratings yet
- Economics Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesDocument6 pagesEconomics Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesAndres Krauss100% (1)
- Law of DemandDocument38 pagesLaw of DemandAnandRajNo ratings yet
- Econ CH 6 Section 2 SGDocument2 pagesEcon CH 6 Section 2 SGAbi CalderaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Elasticity and Its ApplicationValcorza Karen100% (1)
- Ordinal Utility TheoryDocument20 pagesOrdinal Utility TheoryJagdish BhattNo ratings yet
- Theory of Income DeterminationDocument4 pagesTheory of Income DeterminationAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Rules For Maximizing UtilityDocument7 pagesRules For Maximizing UtilityCarla Mae F. DaduralNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 ELASTICITYDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 ELASTICITYCHZE CHZI CHUAHNo ratings yet
- Fred Baker Moseley: EducationDocument15 pagesFred Baker Moseley: EducationSebastian Marquez DiazNo ratings yet
- The Law of Comparative AdvantageDocument49 pagesThe Law of Comparative AdvantageHoly BunkersNo ratings yet
- Asharab Aamir SheikhDocument7 pagesAsharab Aamir Sheikhhumair chauhdaryNo ratings yet
- 1 Master of Business Administration All Courses 2 BBA in Retailing With The Modular ApproachDocument4 pages1 Master of Business Administration All Courses 2 BBA in Retailing With The Modular ApproachassignmentbazaarNo ratings yet
- 06 UtilityDocument8 pages06 UtilityThục ÁiNo ratings yet
- 3Document4 pages3Rahmatullah Mardanvi100% (3)
- Answer To P and A Chapter 8Document8 pagesAnswer To P and A Chapter 8dilasesiyaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics (Chapter 10 Bis) Game TheoryDocument17 pagesManagerial Economics (Chapter 10 Bis) Game Theoryapi-3703724100% (1)
- Diamond ChemicalsDocument3 pagesDiamond ChemicalsJohn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Behavioral FinanceDocument61 pagesBehavioral FinanceRohan GuravNo ratings yet
- NPTEL Assign 1 Jan23 Behavioral and Personal FinanceDocument5 pagesNPTEL Assign 1 Jan23 Behavioral and Personal FinanceNitin Mehta - 18-BEC-030No ratings yet
- Ped Worksheet 2 AnswersDocument3 pagesPed Worksheet 2 Answersapi-505089065No ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument10 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandClaNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument23 pagesDemand and Supply Analysisdipu jaiswalNo ratings yet