Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting Reviewer
Uploaded by
Krista Benedicto 12ABM2Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting Reviewer
Uploaded by
Krista Benedicto 12ABM2Copyright:
Available Formats
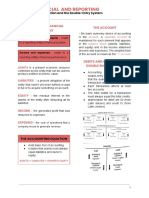
Fundamentals of accounting
LESSON 1
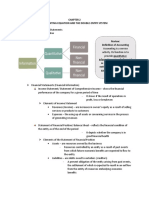
Statement of Financial Position - this statement
informs the users of the financial condition of
the business at a given date, usually at the end
of an accounting period.
Two Forms of Statement Financial Position:
Account Form - In the account form of
Statement of Financial Position, the assets are
listed on the left side of the report and the
liabilities and proprietorship on the right side.
Report Form - A Statement of Financial Position Statement Heading - This includes the name of
prepared in report form shows the assets on the the business. It tells what kind of statement it is,
top section of the statement and the liabilities and gives the date for which the report is
and owner’s equity on the bottom section. prepared.
Charlotte’s Designer and Tailoring Shop Assets, Liabilities, Proprietorship - Items are
Statement of Financial Position grouped and each group of items is identified by
special captions.
Captions - Classifications of each group of items
appear against the left margin of the statement
Account Titles - Individual account titles in each
classification are indented.
Current Assets - The individual current assets
are usually listed in order of their liquidity, with
the most liquid asset, cash appearing first.
Plant, Property, Equipment - The plant assets Assets - This includes anything owned or
are often listed in order of their expected useful possessed by the business which is capable of
life. Land, having the longest expected useful being expressed in terms of money or
life, appears first. possessing monetary values, and which,
consequently, is available for the payment of the
Note (#) - The separate computational schedule debt of the business.
attached to the report explaining in detail the
aggregated amount presented on the face of the Liabilities - These are economic obligations(i.e.
financial statement. debts) payable to an individual or an
organization outside the business.
Current Liabilities - The current liabilities are in
theory listed in order of due date, with the Owner’s Equity - This represents the claim of an
earliest due date appearing first. owner of a business over the assets of the
business after the claims of the creditors have
Captions Indicating Totals - Each group of items been satisfied.
(i.e, total current assets, total plant, property
and equipment, total current liabilities, etc) is LESSON 2
indented further. The SCI is a Statement that reports the results of
operations of the business for one accounting
Single Rule Line - The last figure in each group of period. The SCI is describe as a “for the period”
items is underlined. report.
Final Tools - The two final tools (i.e. , total assets
and total liabilities and owner’s equity) appear
as the last line in their respective sections and
are underlined twice (double ruled) to indicate a
final total.
Peso Sign - Peso signs are used (a) to the left of
the first amount of a group of amounts being
combined and (b) to the left of each final total.
Peso Amount - The peso amount for the Financial statements - is a set of interconnected
detailed items is shown in one column; the total reports.
of each classification is extended into the last
column on the right-hand side of the statement. Income - refers to a transaction that increases
assets and /or decreases liabilities leading to
Accounting Equation - This relationship exists increase in equity resulting from the operations
regardless of the size of the enterprise or the of the business and not from the owner’s
variety of its assets, liabilities, and ownership contribution.
interest. This identity is called the basic
accounting equation. Expenses - are transactions that decrease assets
Often it is stated as: and/or increase liabilities leading to decrease in
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity equity resulting from the operations of the
business and not because of distributions to
This equation connotes that the total resources owners.
(assets) equals to the total amount owed
(liabilities) plus proprietorship (owner’s equity). Two Kinds of Income:
Other times the equation appears as: Revenues - are income generated from the
Assets – Liabilities = Owner’s Equity primary operations of the business.
or Gains - on the other hands are income derived
Assets – Owner’s Equity = Liabilities from other activities of the business.
Two Kinds of Expenses:
Expenses - are related to the primary operations
of the business.
Losses - are from other activities of the business.
Elements of the Statement of Comprehensive that the inventory account is updated only at
Income: end of the year or end of the month.
REVENUE Cost of merchandise acquired is collected using
Service Income - The Service Income account is the Purchases account. We also introduce two
generally used to describe revenue derived from contra- Purchase accounts: Purchase Returns
rendering of services. and Allowances and Purchase Discount.
Sales - The Sales Revenue account is generally Returns of defective goods are reported under
used to describe revenue derived from selling of Purchase Returns and Allowances.
goods. Discounts taken are reported under Purchase
Discount.
Accounts Payable - we mentioned that suppliers
give discounts to their customers to encourage Net purchases is equivalent to Purchases plus
early payments. We delivered the goods to the Freight-In less Purchase Returns and Purchase
buyer and appropriately recorded Sales Discount (Net Purchases = Purchases + Freight-
Revenue based on full selling price. In – Purchase Returns – Purchase Discount).
We use another Contra-Sales account called
Sales Discount.
Net Sales - refer to Gross Sales less Sales Return
and Allowances and Sales Discount. Beginning and ending inventory are determined
(Net Sales = Gross Sales – Sales Return – Sales based on the physical count of the merchandise
Discount) owned by the company. The ending inventory of
the prior-period is also the beginning inventory
of the current period. The “periodic” adjustment
updates the inventory account to bring it to the
balance based on year-end physical count.
Operating Expenses - It refers to all other
expenses related to the operation of the
business, other than cost of sales. These include
salaries of employees, supplies, utilities
EXPENSES (electricity, telephone and water bills), gasoline
Cost of Goods Sold (Cost of Sales) expense, representation, bad debts expense,
This is an account used by companies that sells depreciation and amortization.
goods instead of services. For trading
operations, Cost of Sales collects the cost of the Bad debt expense - is an operating expense
merchandise sold. This includes the purchase related to accounts receivable. It is an estimated
price of inventory, brokerage and shipment cost expense.
to bring the goods the premises of the company.
This shipment cost is called Freight-in. Presentation of Statement of Comprehensive
Income:
Cost of sales - is part of inventory accounting. There are two formats for the SCI,
Accountants have two ways of keeping records Single-step - is closely related to the nature of
of inventory – perpetual and periodic inventory expense format.
system. Multi-step - approach is also associated with the
function of expense.
Perpetual - means that the Inventory and Cost
of Goods Sold accounts are “perpetually”
updated.
The other method is called periodic inventory
system. The Inventory account is only
“periodically” updated. “Periodically” means
You might also like
- FABM2Document50 pagesFABM2Anne LayuganNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting and Business Management 2: Statement of Financial Position Account FormDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Accounting and Business Management 2: Statement of Financial Position Account Formmarcjann dialinoNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument30 pagesFinancial StatementsMarcel VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Accounting EquationDocument5 pagesThe Accounting EquationHuskyNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesFABM 2 Lecture NotesLucky MimNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms For FA2 and MA2 AmendedDocument12 pagesGlossary of Terms For FA2 and MA2 AmendedS RaihanNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument35 pagesAccountingJohn Eric Caparros AzoresNo ratings yet
- Accounting HWDocument2 pagesAccounting HWFayeNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesFabm 2 Reviewerlun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - Accounting For Non AccountantsDocument129 pagesDocuments - Pub - Accounting For Non Accountantsakhmad hidayat100% (1)
- Fabm Research ProjectDocument41 pagesFabm Research ProjectMon Kiego MagnoNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting With Corporate Accounting The Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemDocument11 pagesBasic Accounting With Corporate Accounting The Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemJulyzza PisueñaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 2 Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemGabrielle Joshebed AbaricoNo ratings yet
- Acc1 Lesson Week7Document28 pagesAcc1 Lesson Week7KeiNo ratings yet
- Poa ReviewerDocument4 pagesPoa Reviewerdevora aveNo ratings yet
- FARreviewerDocument5 pagesFARreviewerKimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Accounting in ActionDocument3 pagesChapter 1. Accounting in ActionÁlvaro Vacas González de EchávarriNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Reviewer 1Document7 pagesFabm 2 Reviewer 1lun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Apuntes AccountingDocument35 pagesApuntes AccountingPatricia Barquin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Cheat SheetHiếuNo ratings yet
- Actg 1 Module 3Document5 pagesActg 1 Module 3Mae BertilloNo ratings yet
- T 32fd6f43 3cd3 4d19 b62d 111e849211bfincome StatementDocument45 pagesT 32fd6f43 3cd3 4d19 b62d 111e849211bfincome StatementthukrishivNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Double Entry Bookkeeping System and The Accounting EquationDocument9 pagesModule 2 - Double Entry Bookkeeping System and The Accounting EquationPrincess Joy CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument24 pagesChapter OneffahddmmNo ratings yet
- Basic Financial Accounting and Reporting (Bfar) : Philippine Based (Summary and Class Notes)Document22 pagesBasic Financial Accounting and Reporting (Bfar) : Philippine Based (Summary and Class Notes)LiaNo ratings yet
- Act6153b - Accounting Terms - MilliosDocument3 pagesAct6153b - Accounting Terms - MilliosJerald MilliosNo ratings yet
- Updated Lecture Partnership and CorporationDocument10 pagesUpdated Lecture Partnership and CorporationAppleNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING1Document12 pagesACCOUNTING1Trixie GabatinoNo ratings yet
- CH2 Fabm2Document27 pagesCH2 Fabm2Crisson FermalinoNo ratings yet
- Accounting - PonesDocument4 pagesAccounting - PonesLuisa PonesNo ratings yet
- Accounting Term Alternatives DescriptionDocument1 pageAccounting Term Alternatives DescriptionstefpanNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow + Income Statement NotesDocument5 pagesCash Flow + Income Statement NotesElla AikenNo ratings yet
- 3 The Accounting EquationDocument26 pages3 The Accounting EquationJohn Alfred CastinoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 2-Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDan GalvezNo ratings yet
- Notes For Week 1Document7 pagesNotes For Week 1algokar999No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument36 pagesChapter 1 NotesSina RahimiNo ratings yet
- THE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Document10 pagesTHE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Che AllejeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemalonNo ratings yet
- Travel Expense Account or Purchase AccountDocument17 pagesTravel Expense Account or Purchase AccountCRAFNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in FABM 3rd QuarterlyDocument4 pagesReviewer in FABM 3rd Quarterlydeivejenrych95No ratings yet
- 01 Lecture - MT - ch01 - 0607-082023 - Acctg Concepts 01Document22 pages01 Lecture - MT - ch01 - 0607-082023 - Acctg Concepts 01JIM KYRONE GENOBISANo ratings yet
- Unit I - Accounting EquationDocument6 pagesUnit I - Accounting EquationAnime LoverNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemDocument24 pagesThe Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemJohn Mark MaligaligNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting (Notes)Document6 pagesPrinciples of Accounting (Notes)hjpa2023-7388-23616No ratings yet
- New AccountsDocument2 pagesNew AccountsManjunathreddy SeshadriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Accounting EquationDocument3 pagesLesson 3: Accounting EquationDante SausaNo ratings yet
- The Original Attachment: BasicsDocument32 pagesThe Original Attachment: BasicsvijayNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - TestDocument9 pagesFinancial Accounting - TestAdriana MassaadNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DiscussionDocument10 pages1st Quarter DiscussionCHARVIE KYLE RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Accounting ProcessDocument4 pages2 - The Accounting ProcessWea AmorNo ratings yet
- Acctg 121N Chapters 5 11Document3 pagesAcctg 121N Chapters 5 11Jhon Mark CruzNo ratings yet
- Acctg 121N Chapters 5 11Document3 pagesAcctg 121N Chapters 5 11Hazraphine LinsoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Focus NoteDocument24 pagesAccounting Focus NoteLorelyn Ebrano AltizoNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial Position: Group 1Document11 pagesStatement of Financial Position: Group 1Jazzlyn BorlonganNo ratings yet
- Principles of Accounting: Republic Act No. 9298Document9 pagesPrinciples of Accounting: Republic Act No. 9298Nicole CapundanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument9 pagesChapter 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsJean EliaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)From EverandUnderstanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Financial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersFrom EverandFinancial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersNo ratings yet
- Freddie Mac: Structured Pass-Through Certificates (SPCS) Series K-016Document419 pagesFreddie Mac: Structured Pass-Through Certificates (SPCS) Series K-016DinSFLANo ratings yet
- Case Study - Bordeos, Kristine - Sec 5Document6 pagesCase Study - Bordeos, Kristine - Sec 5Kristine Lirose BordeosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Solution Manual Kieso IFRSDocument74 pagesChapter 10 Solution Manual Kieso IFRSIvan JavierNo ratings yet
- Format For Course Curriculum: Course Title: Advanced Financial Accounting Course Code: ACCT 603 Credit Units: 3 Level: PGDocument4 pagesFormat For Course Curriculum: Course Title: Advanced Financial Accounting Course Code: ACCT 603 Credit Units: 3 Level: PGUbaid DarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Consolidation ofDocument64 pagesChapter 04 Consolidation ofBetty Santiago100% (1)
- Corporate-Accounting-bk GoelDocument3 pagesCorporate-Accounting-bk Goeltanisha kochharNo ratings yet
- Ey Ppa Study 2023Document10 pagesEy Ppa Study 2023tukonradNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fs AnalysisDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Fs AnalysisYlver John YepesNo ratings yet
- Bcom Paper Code: BCOM 314 Principles of InsuranceDocument37 pagesBcom Paper Code: BCOM 314 Principles of InsuranceShajana ShahulNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Services (F) (5 Sem) : Unit-2 Primary and Secondary Market: Primary MarketDocument11 pagesFinancial Markets and Services (F) (5 Sem) : Unit-2 Primary and Secondary Market: Primary Marketdominic wurdaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accounting For Junior High School: Airotciv Ivy Blaise P. Mangawang, Mba InstructorDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Accounting For Junior High School: Airotciv Ivy Blaise P. Mangawang, Mba InstructorKristienne SalesNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Perlakuan Aset Tetap Sesuai Sak Etap No. 15 (Studi Kasus Pada PT. Suryakabel Cemerlang) 351Document10 pagesTinjauan Perlakuan Aset Tetap Sesuai Sak Etap No. 15 (Studi Kasus Pada PT. Suryakabel Cemerlang) 351Parini WaeNo ratings yet
- TWO FACES: DEMYSTIFYING THE MORTGAGE ELECTRONIC REGISTRATION SYSTEM'S LAND TITLE THEORY (MERS) SSRN-id1684729Document39 pagesTWO FACES: DEMYSTIFYING THE MORTGAGE ELECTRONIC REGISTRATION SYSTEM'S LAND TITLE THEORY (MERS) SSRN-id1684729CarrieonicNo ratings yet
- EAadhaar 729903033801 11062018192543 831288Document5 pagesEAadhaar 729903033801 11062018192543 831288Pritam GanjaveNo ratings yet
- Estadistica Eje 2Document13 pagesEstadistica Eje 2valentina serna ramirezNo ratings yet
- Atw263 Principle of FinanceDocument19 pagesAtw263 Principle of FinanceeshakaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Intermediate Accounting Volume 1Document11 pagesChapter 5 - Intermediate Accounting Volume 1Buenaventura, Elijah B.No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Death of A PartnerDocument23 pagesUnit 5: Death of A PartnerKARTIK CHADHANo ratings yet
- #Pvofguaranteedpaymentof10,000In5Years: PV PVDocument7 pages#Pvofguaranteedpaymentof10,000In5Years: PV PVL.E.O.ZNo ratings yet
- Credit CardsDocument22 pagesCredit CardsEti Prince BajajNo ratings yet
- Popularity of Credit Cards Issued by Different BanksDocument25 pagesPopularity of Credit Cards Issued by Different BanksNaveed Karim Baksh75% (8)
- Electronic Contribution Collection List SummaryDocument12 pagesElectronic Contribution Collection List SummaryPbs Aurora PrinceNo ratings yet
- MR - MD Samiullah: Page 1 of 1 M-2263937Document1 pageMR - MD Samiullah: Page 1 of 1 M-2263937Notty AmreshNo ratings yet
- Latsol AklDocument10 pagesLatsol AklAlya Sufi IkrimaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Insurance IndustryDocument19 pagesProject Report On Insurance IndustryNilima Thakur KhareNo ratings yet
- AOM 2023-004 Understated Due To NGADocument4 pagesAOM 2023-004 Understated Due To NGAKean Fernand BocaboNo ratings yet
- Sol Vamshi Final 30nov19Document10 pagesSol Vamshi Final 30nov19Balaji MahiNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument14 pagesDepreciationKris Hazel RentonNo ratings yet
- Module 8. FARDocument9 pagesModule 8. FARAntonNo ratings yet
- DBT 112 2021 - 22Document1 pageDBT 112 2021 - 22omkar daveNo ratings yet