Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Investment Appraisal
Uploaded by
HaddonesKimberly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesInvestment Appraisal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInvestment Appraisal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesInvestment Appraisal
Uploaded by
HaddonesKimberlyInvestment Appraisal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
INVESTMENT APPRAISAL
• Is a process of evaluating whether it is worthwhile to invest funds in a project.
• It is important to carry investment appraisal because large sums of money are involved.
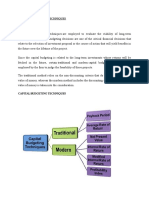
FOUR METHODS USED
SIMPLE METHODS/ NON (DCF) METHODS
1. Accounting Rate of Return
2. Payback Period
DISCOUNTED CASHFLOW METHODS
3. Net Present Value
4. Internal Rate of Return
NB. Accounting Rate of Return is based on profits where as Payback Period, NPV and IRR are based
on cashflows.
1. ACCOUNTING RATE OF RETURN
• This is the average profit (after depreciation) expressed as a percentage of average capital
invested.
ARR= Average profit/Average capital ×100
Average profit= Total profit/Number of years
Or Average Profit = (Total cashflows-Initial outlay)/number of years
Average capital=Initial outlay/2
Or Average capital=Initial Outlay /2 + working capital
A project with high ARR is the best
2. PAYBACK PERIOD
• It measures the time taken by an investment’s future cashflows to recover the initial outlay
• It is based on cashflows not profits.
• A project with a shorter payback is the best.
3. NET PRESENT VALUE
• Refers to the difference between the total discounted cashflows and the initial outlay.
• NPV considers the time value of money since a dollar received today worths more than a
dollar received tomorrow because of loss of investment and inflation.
• The discounting rate used is the cost of capital
• A project with a high NPV is the best
NB A project with a Negative NPV is rejected as the future discounted cashflows will not cover
the initial outlay.
4. INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN
• This the rate of return that gives a NPV of zero if discounted to cashflows.
• The IRR represents the maximum a firm is willing to pay for finance.
• The IRR is accepted if it is above the cost of capital and the project with high IRR is the best.
(𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑏𝑒𝑡𝑤𝑒𝑒𝑛 𝐷𝐹× 𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑁𝑃𝑉)
IRR (%) = 𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝐷𝐹 =
𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑁𝑃𝑉+𝑁𝑒𝑔𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑁𝑃𝑉
You might also like
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Capital Budgeting-Investment DecisionDocument31 pagesCapital Budgeting-Investment DecisionDRIP HARDLYNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Techniques Explained in DetailDocument26 pagesCapital Budgeting Techniques Explained in DetailTisha SosaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Methods ExplainedDocument35 pagesCapital Budgeting Methods ExplainedPRIYA RATHORENo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document9 pagesChapter 13Diana Mark AndrewNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument2 pagesCapital Budgetingmengjun0987654311No ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument17 pagesCapital BudgetingAnirudha GoraiNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting and Investment Analysis IIDocument19 pagesCapital Budgeting and Investment Analysis IIrahulborntobewildNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Capital BudgetingDocument20 pagesTechniques of Capital Budgetinggoogle BabaNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument36 pagesCapital BudgetingYusuf TakliwalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 SynopsisDocument7 pagesChapter 11 SynopsissajedulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document2 pagesChapter 14jhouvanNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Techniques for Long-Term Investment DecisionsDocument8 pagesCapital Budgeting Techniques for Long-Term Investment DecisionsDoreen AwuorNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: Cash FlowDocument12 pagesTopic 5: Cash FlowMZK0621 Seah Pei NiNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Processes & TechniquesDocument22 pagesCapital Budgeting Processes & TechniquesNilima Islam Mim 201-11-6426No ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Financial EvaluationDocument9 pagesChapter Five: Financial EvaluationKide Mar MarNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument8 pagesCapital Budgeting Techniqueswaqaar raoNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument6 pagesCapital BudgetingKhushbu PriyadarshniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Investment AppraisalDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Investment AppraisalMaleoaNo ratings yet
- Technic of Cap BudDocument6 pagesTechnic of Cap BudAmar NathNo ratings yet
- Topic 06 - Capital Budgeting - BM18275Document6 pagesTopic 06 - Capital Budgeting - BM18275ravindu 11111No ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument14 pagesCapital BudgetingD Y Patil Institute of MCA and MBANo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument18 pagesCapital Budgeting: Submitted To: Submitted byKhushboo GoyalNo ratings yet
- ProfitabilityDocument36 pagesProfitabilityShronik PatelNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting V3Document12 pagesCapital Budgeting V3BMRsnehaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting DemoDocument13 pagesCapital Budgeting DemoNeha UjjwalNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument22 pagesCapital BudgetingRajatNo ratings yet
- MAS Handout - Capital BudgetingDocument7 pagesMAS Handout - Capital BudgetingDivine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - Discounted and Undiscounted MethodDocument47 pagesCapital Budgeting - Discounted and Undiscounted MethodTacitus KilgoreNo ratings yet
- Calculating Profitability IndexDocument16 pagesCalculating Profitability Indexpam nandaNo ratings yet
- EAM Unit3 PDFDocument68 pagesEAM Unit3 PDFYogesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Ch14 Capital BudgetingDocument20 pagesCh14 Capital BudgetingPatrick GoNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Methods SummaryDocument3 pagesCapital Budgeting Methods Summarykyra inarsolinNo ratings yet
- Subject: Internal Rate of ReturnDocument7 pagesSubject: Internal Rate of ReturnDeepak Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting-Theory and NumericalsDocument47 pagesCapital Budgeting-Theory and Numericalssaadsaaid50% (2)
- Capital BudgetingDocument39 pagesCapital BudgetingDhara KanungoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDLfhxtIOwMb77mrPSB6zPbwJ nCGMj4u3t nqJm5cxUZU HylVBI0B54-mcxc-rNjgLkEXuSk9WcTCRA-Q5RJl9LL1h4L O7yYO6Yn Gu4bo-k0Dj1aRelUsY PDFDocument23 pagesACFrOgDLfhxtIOwMb77mrPSB6zPbwJ nCGMj4u3t nqJm5cxUZU HylVBI0B54-mcxc-rNjgLkEXuSk9WcTCRA-Q5RJl9LL1h4L O7yYO6Yn Gu4bo-k0Dj1aRelUsY PDFPrashant TodkarNo ratings yet
- Non Discounted Techniques LectureDocument3 pagesNon Discounted Techniques Lectureamormi2702No ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument26 pagesCapital Budgeting TechniquesMahima GirdharNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, IndoreDocument14 pagesDr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, Indorechaterji_aNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, IndoreDocument14 pagesDr. Sandeep Malu Associate Professor SVIM, Indorechaterji_aNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Techniques and MethodsDocument7 pagesCapital Budgeting Techniques and Methodsbhagat103No ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument31 pagesCapital BudgetingJanu JinniNo ratings yet
- Topic VII Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument16 pagesTopic VII Capital Budgeting TechniquesSeph AgetroNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument13 pagesCapital BudgetingTanya SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Discounting or Modern Methods of Capital BudgetingDocument18 pagesDiscounting or Modern Methods of Capital BudgetingRiyas Parakkattil100% (1)
- Capital Budgeting Methods and TechniquesDocument20 pagesCapital Budgeting Methods and TechniquesZaira PangesfanNo ratings yet
- Time Adjusted Capital Budgeting MethodsDocument15 pagesTime Adjusted Capital Budgeting MethodsDarth VaderNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument8 pagesCapital Budgeting TechniquesNagarajan CheyurNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument35 pagesCapital BudgetingShivam Goel100% (1)
- Capital Budgeting Decisions: DR R.S. Aurora, Faculty in FinanceDocument31 pagesCapital Budgeting Decisions: DR R.S. Aurora, Faculty in FinanceAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch20 InvestmentAppraisalDocument32 pagesCh20 InvestmentAppraisalsohail merchantNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Investment Decision: Lecturer: Hibak A. NouhDocument21 pagesBusiness Finance Investment Decision: Lecturer: Hibak A. NouhHibaaq AxmedNo ratings yet
- Financial management paper investment decisionsDocument28 pagesFinancial management paper investment decisions2154 taibakhatunNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Manoranjan PandaDocument15 pagesPresented By: Manoranjan Pandamikunpanda30No ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting MethodsDocument32 pagesCapital Budgeting MethodsDarth VaderNo ratings yet
- 6 Capital Budgeting TechniquesDocument49 pages6 Capital Budgeting TechniquesAkwasi BoatengNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Investment AnalysisDocument32 pagesTechniques of Investment AnalysisPranjal Verma0% (1)
- MS-44L (Capital Budgeting With Risks & Returns)Document18 pagesMS-44L (Capital Budgeting With Risks & Returns)juleslovefenNo ratings yet
- 0580 P4 Revision WorksheetDocument40 pages0580 P4 Revision WorksheetHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- 8.missionaries in ZimbabweQ&ADocument13 pages8.missionaries in ZimbabweQ&AHaddonesKimberly100% (1)
- Stem and Leaf..box and WhiskerDocument3 pagesStem and Leaf..box and WhiskerHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- 10.COLONISATION OF SOUTHERN AFRICA EditedDocument14 pages10.COLONISATION OF SOUTHERN AFRICA EditedJeketera ShadreckNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Test 3Document4 pagesForm 1 Test 3HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Upper Sixth Term One 2022 Pure Mathematics 1Document1 pageUpper Sixth Term One 2022 Pure Mathematics 1HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Permutations and Combinations.Document4 pagesPermutations and Combinations.HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Maths End of Term 1 2023Document12 pagesForm 5 Maths End of Term 1 2023HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry WorksheetDocument16 pagesCoordinate Geometry WorksheetHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Test 3Document4 pagesForm 1 Test 3HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Data Security NotesDocument3 pagesData Security NotesHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Find The Roots of Given Polynomials, Which May Be Real or ComplexDocument1 pageFind The Roots of Given Polynomials, Which May Be Real or ComplexHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Laws of Indices ExerciseDocument5 pagesLaws of Indices ExerciseHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- User Defined Data Type: Syllabus ContentDocument10 pagesUser Defined Data Type: Syllabus ContentMasrur SakibNo ratings yet
- MTE 101 Test 3Document2 pagesMTE 101 Test 3HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Form 1 CSC Mid Year Exam2019Document4 pagesForm 1 CSC Mid Year Exam2019HaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Vectors E - QuestionsDocument2 pagesVectors E - QuestionsHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet