Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presotto AGC, Bhering CLB, Mesquita MF, Barão VAR. Marginal Fit and Photoelastic Stress Analysis of CAD-CAM and Overcast 3-Unit Implant-Supported
Uploaded by
Catalina GuiñezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presotto AGC, Bhering CLB, Mesquita MF, Barão VAR. Marginal Fit and Photoelastic Stress Analysis of CAD-CAM and Overcast 3-Unit Implant-Supported
Uploaded by
Catalina GuiñezCopyright:
Available Formats
TIPS FROM OUR READERS
Improved digital impressions of edentulous areas
Ju-Hyoung Lee, DDSa
Intraoral scanners (IOSs) are widely used in the fabri- PROCEDURE
cation of fixed dental prostheses, in that their accuracy
compares well with traditional impression making.1 1. Mix pressure-indicating paste (Pressure Indicator
Recently, IOSs have been successfully used in the fabri- Paste; Mizzy Inc) and interim zinc oxide-eugenol
cation of removable dental prostheses.2-5 Digital cement (Temp-Bond; Kerr Corp).9
impressions are useful for patients with a gag reflex and 2. While retracting the vestibules (Fig. 1), dry the
sensitivity to impression materials.2-4 Moreover, IOSs edentulous area and draw irregular shapes on the
can register excessively movable tissue in a passive state residual ridges with the mixture and the dental
to achieve a mucostatic impression.2,3,6,7 However, microapplicator (Microbrush; Microbrush Intl).
scanning edentulous area with IOSs may be difficult and Connect the shapes with lines toward the center of
time-consuming, because edentulous sites are smooth the palate (Fig. 2).
and devoid of features.8 The stitching process may be 3. Scan the edentulous area with the IOS (TRIOS
faulty, especially in the palatal area.8 This article Color Pod; 3Shape Inc) (Fig. 3). If incorrect stitching
introduces a time-saving technique that easily captures is noted, rescan from the drawn area to the inac-
tissues, prevents incorrect data processing, and uses curately stitched area. After the scan procedure,
common and inexpensive materials. soak a piece of gauze in the removal liquid (PIP
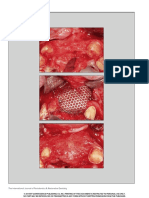
Figure 1. Occlusal view of maxillary arch with anterior movable tissue. Figure 2. Irregular shapes and lines drawn with mixture of pressure-
indicating paste and zinc oxide-eugenol cement.
a
Assistant Professor, Department of Dentistry, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea; and Graduate student, Department of
Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
448 THE JOURNAL OF PROSTHETIC DENTISTRY
March 2017 449
2. Kattadiyil MT, Mursic Z, AlRumaih H, Goodacre CJ. Intraoral scanning of hard
and soft tissues for partial removable dental prosthesis fabrication. J Prosthet
Dent 2014;112:444-8.
3. Lin WS, Chou JC, Metz MJ, Harris BT, Morton D. Use of intraoral digital
scanning for a CAD/CAM-fabricated milled bar and superstructure framework
for an implant-supported, removable complete dental prosthesis. J Prosthet
Dent 2015;113:509-15.
4. Londono J, Abreu A, Baker PS, Furness AR. Fabrication of a definitive obtu-
rator from a 3D cast with a chairside digital scanner for a patient with severe
gag reflex: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent 2015;114:735-8.
5. Mansour M, Sanchez E, Machado C. The use of digital impressions to fabricate
tooth-supported partial removable dental prostheses: a clinical report.
J Prosthodont 2016;25:495-7.
6. Page HL. Mucostatics. Ticonium Contacts 1946;4:7.
7. Bindhoo YA, Thirumurthy VR, Kurien A. Complete mucostatic impression: a
new attempt. J Prosthodont 2012;21:209-14.
8. Patzelt SB, Vonau S, Stampf S, Att W. Assessing the feasibility and accuracy of
digitizing edentulous jaws. J Am Dent Assoc 2013;114:914-20.
9. Kaku T, Ogino Y, Matsushita Y, Koyano K. Technique for identifying kerati-
nized gingival tissue and soft tissue morphology on 3-dimensional implant-
planning software images. J Prosthet Dent 2016;116:21-4.
Figure 3. Software view of mucostatic impression of maxillary arch.
Corresponding author:
Remover; Mizzy Inc) and clean the edentulous area Dr Ju-Hyoung Lee
with it. Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine
Daegu
REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Email: jus2u@cu.ac.kr
REFERENCES
Acknowledgments
1. Chochlidakis KM, Papaspyridakos P, Geminiani A, Chen CJ, Feng IJ, Ercoli C. The author thanks Hye-Jung Yun for technical assistance.
Digital versus conventional impressions for fixed prosthodontics: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent 2016;116:184-90. Copyright © 2016 by the Editorial Council for The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.
Lee THE JOURNAL OF PROSTHETIC DENTISTRY
You might also like
- Zygomatic Implants: Optimization and InnovationFrom EverandZygomatic Implants: Optimization and InnovationJames ChowNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Prosdent 2019 11 009Document2 pages10 1016@j Prosdent 2019 11 009James LinNo ratings yet
- A 3D Printing Replication Technique For Fabricating Digital DenturesDocument6 pagesA 3D Printing Replication Technique For Fabricating Digital DenturesAlex BurdeNo ratings yet
- Implant Planning and Placement Using Optical Scanning and Cone Beam CT TechnologyDocument6 pagesImplant Planning and Placement Using Optical Scanning and Cone Beam CT TechnologyPraveen Raj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Obturator 2023Document7 pagesObturator 2023Dina AbdelmoezNo ratings yet
- Protocol For Indirect Restoration Intraoral Scanning Under Dental Dam Isolation A Dental TechniqueDocument5 pagesProtocol For Indirect Restoration Intraoral Scanning Under Dental Dam Isolation A Dental Techniquefloressam2000No ratings yet
- Full-Arch Implant Surgical and Restorative Considerations: ImplantsDocument4 pagesFull-Arch Implant Surgical and Restorative Considerations: ImplantsTín ĐăngNo ratings yet
- Simplified Approach for Implant Placement Using Diagnostic and Surgical StentDocument7 pagesSimplified Approach for Implant Placement Using Diagnostic and Surgical Stentwaf51No ratings yet
- 10.1016@j.prosdent.2016.01.004.PdfAdaptation of An Interim Partial Removable Dental Prosthesis As A Radiographic Template For Implant PlacementDocument2 pages10.1016@j.prosdent.2016.01.004.PdfAdaptation of An Interim Partial Removable Dental Prosthesis As A Radiographic Template For Implant PlacementdentureNo ratings yet
- Role of Computed Tomography Imaging in Dental Implantology: An OverviewDocument5 pagesRole of Computed Tomography Imaging in Dental Implantology: An OverviewGiulian SabinNo ratings yet
- Functionally Suitable Digital Removable Complete Dentures: A Dental TechniqueDocument5 pagesFunctionally Suitable Digital Removable Complete Dentures: A Dental TechniqueDani Montero PerezNo ratings yet
- A Technique For Digital Impression and Bite Registration For A Single Edentulous ArchDocument5 pagesA Technique For Digital Impression and Bite Registration For A Single Edentulous ArchsaniaNo ratings yet
- PIIS002239132030593XDocument5 pagesPIIS002239132030593XJuliana ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- TARLOWimplantstentarticleDocument3 pagesTARLOWimplantstentarticlewaf51No ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Endodontic Guide For Adhesive Fiber Post Removal: A Dental TechniqueDocument4 pagesThree-Dimensional Endodontic Guide For Adhesive Fiber Post Removal: A Dental TechniqueLuisAlpalaNo ratings yet
- Using Intraoral Scanning To Fabricate Complete Dentures: First ExperiencesDocument5 pagesUsing Intraoral Scanning To Fabricate Complete Dentures: First ExperiencesgermanpuigNo ratings yet
- PLANEACIÓN VIRTUAL EN CIRUGÍA ORTOGNÁTICADocument68 pagesPLANEACIÓN VIRTUAL EN CIRUGÍA ORTOGNÁTICAAURA MOJICANo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Versus Drills Implant Site Preparation: A Histologic Analysis in Bovine RibsDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Versus Drills Implant Site Preparation: A Histologic Analysis in Bovine RibsAnusha BorraNo ratings yet
- Combining Conventional Impressions and Intraoral Scans: A Technique For The Treatment of Complete Denture Patients With Flabby TissueDocument4 pagesCombining Conventional Impressions and Intraoral Scans: A Technique For The Treatment of Complete Denture Patients With Flabby TissueDwi Isti NadiarohNo ratings yet
- 3d Printing 3Document5 pages3d Printing 3CherifNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Evaluation of Root Resorption During Orthodontic TreatmentDocument8 pagesVolumetric Evaluation of Root Resorption During Orthodontic TreatmentDrAshish KalawatNo ratings yet
- Avrampou COIR 2013Document8 pagesAvrampou COIR 2013jose luis delgadilloNo ratings yet
- A Modified Open Tray Implant Impression TechniqueDocument2 pagesA Modified Open Tray Implant Impression TechniquemsoaresmirandaNo ratings yet
- Harvard Digital Full ArchDocument6 pagesHarvard Digital Full ArchAmit SadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Guided Surgery in Dental ImplantologyDocument5 pagesGuided Surgery in Dental Implantologynarendra singhNo ratings yet
- Transforming Pediatric Dentistry With Digital TechDocument4 pagesTransforming Pediatric Dentistry With Digital TechswayampradeepmohapatraNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of Vertical and Lateral Gingival Displacement Produced by MecDocument8 pagesComparative Evaluation of Vertical and Lateral Gingival Displacement Produced by MecInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ma 2018Document17 pagesMa 2018Bruna SelauNo ratings yet
- Han 2019Document9 pagesHan 2019shraddhaNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture Digital Work Ow: Combining Basic Principles With A CAD-CAM ApproachDocument6 pagesComplete Denture Digital Work Ow: Combining Basic Principles With A CAD-CAM ApproachSarthak Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Dental Implantology Update PDFDocument8 pagesDental Implantology Update PDFViet Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Finite Element Approach For Locating The Center of Resistance of Maxillary TeethDocument12 pagesA Finite Element Approach For Locating The Center of Resistance of Maxillary Teeth김재훈No ratings yet
- Bone Depth and Thickness of Different Infrazygomatic Crest Miniscrew Insertion Paths Between The First and Second Maxillary Molars For Distal Tooth Movement: A 3-Dimensional AssessmenDocument11 pagesBone Depth and Thickness of Different Infrazygomatic Crest Miniscrew Insertion Paths Between The First and Second Maxillary Molars For Distal Tooth Movement: A 3-Dimensional AssessmenCynthia Alfaro100% (1)
- Complete Digital Workflow in Prosthesis Prototype FabricationDocument4 pagesComplete Digital Workflow in Prosthesis Prototype FabricationFrancisco Antonio Vargas GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of An Edentulous Patient With Microstomia Using Both Digital and Conventional Techniques: A Clinical ReportDocument5 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of An Edentulous Patient With Microstomia Using Both Digital and Conventional Techniques: A Clinical ReportDwi Isti NadiarohNo ratings yet
- Customized CAD-CAM Healing Abutment For Delayed Loaded ImplantsDocument4 pagesCustomized CAD-CAM Healing Abutment For Delayed Loaded Implantsbeautopia reviewsNo ratings yet
- dabreo1990Document3 pagesdabreo1990SaptarshiMondalNo ratings yet
- Setup 3DDocument8 pagesSetup 3DAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Insertion Torque and Periotest Values Are Important Factors Predicting Outcome After Orthodontic Miniscrew PlacementDocument6 pagesInsertion Torque and Periotest Values Are Important Factors Predicting Outcome After Orthodontic Miniscrew PlacementGiovanni Eduardo Medina MartinezNo ratings yet
- Titanium Mesh Ridges RecontructionDocument11 pagesTitanium Mesh Ridges RecontructionМилутинМићићNo ratings yet
- Tasaka DKK 2022Document6 pagesTasaka DKK 2022Krysa AquilaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Article 546Document7 pages2018 Article 546giuseppelombard1984No ratings yet
- PIIS0022391304004056Document1 pagePIIS0022391304004056Najeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Malo ArticleDocument6 pagesMalo Articleishita parekhNo ratings yet
- Accuracy_of_Different_SurgicalDocument8 pagesAccuracy_of_Different_SurgicalVõHoàngThủyTiênNo ratings yet
- A Method For Mandibular Dental Arch Superimposition Using 3D Cone Beam CT and Orthodontic 3D Digital ModelDocument13 pagesA Method For Mandibular Dental Arch Superimposition Using 3D Cone Beam CT and Orthodontic 3D Digital Modelosama-alaliNo ratings yet
- 265-Article Text-1516-2-10-20200110 PDFDocument5 pages265-Article Text-1516-2-10-20200110 PDFmarwaNo ratings yet
- Factorial Analysis of Variables Affecting Bone Stress Adjacent To The Orthodontic Anchorage Mini-Implant With Finite Element AnalysisDocument8 pagesFactorial Analysis of Variables Affecting Bone Stress Adjacent To The Orthodontic Anchorage Mini-Implant With Finite Element AnalysisYeraldin EspañaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Interarch Space For ImplanDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Interarch Space For Implanwaf51No ratings yet
- Case Report Management of Adverse Tissue Response To Faulty Pontic Design-A Case ReportDocument5 pagesCase Report Management of Adverse Tissue Response To Faulty Pontic Design-A Case ReportNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0022391319300150Document2 pagesPi Is 0022391319300150Torito ZalgadoNo ratings yet
- Zhou - Virtual Shape ModelDocument10 pagesZhou - Virtual Shape ModelRicardo GrilloNo ratings yet
- Eview Rticle: Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences ResearchDocument3 pagesEview Rticle: Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences ResearchSwathiLingannagariNo ratings yet
- 3-Dimensional Accuracy of Dynamic Navigation Technology in Locating Calcified CanalsDocument9 pages3-Dimensional Accuracy of Dynamic Navigation Technology in Locating Calcified CanalsAlexandra Enache100% (1)
- Fabricating An Inexpensive Leaf Gauge Deprogrammer From Panoramic Radiographic FilmDocument3 pagesFabricating An Inexpensive Leaf Gauge Deprogrammer From Panoramic Radiographic FilmMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- A Tooth-Stabilized Surgical Template For AlveolectomyDocument3 pagesA Tooth-Stabilized Surgical Template For Alveolectomyheri asriyadiNo ratings yet
- An Easy Way of Chair-Side Stent Fabrication For Accurate Placement of Miniscrew ImplantDocument3 pagesAn Easy Way of Chair-Side Stent Fabrication For Accurate Placement of Miniscrew ImplantJORGE CARLOS MELGAR GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- T. Thygesen, C. Slots, M.B. Jensen, N. Ditzel, M. Kassem, L. Langhorn, M.Ø. AndersenDocument7 pagesT. Thygesen, C. Slots, M.B. Jensen, N. Ditzel, M. Kassem, L. Langhorn, M.Ø. AndersenAnca TomaNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Orthognathic SurgeryDocument3 pagesMinimally Invasive Orthognathic SurgeryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Esthetic Optimization of Surgical-Orthodontic TreatmentDocument22 pagesEsthetic Optimization of Surgical-Orthodontic TreatmentumadeviNo ratings yet
- Jeanine Meyer - Origami As A General Education Math CourDocument4 pagesJeanine Meyer - Origami As A General Education Math CourscheeleNo ratings yet
- Company & Project Information for Electrical, Instrumentation ServicesDocument28 pagesCompany & Project Information for Electrical, Instrumentation ServicesMrudul PatilNo ratings yet
- Tron Time Delay Fuse 500vDocument1 pageTron Time Delay Fuse 500valexjoelNo ratings yet
- 1,2,4-Triazoles: A Review of Synthetic Approaches and The Biological ActivityDocument22 pages1,2,4-Triazoles: A Review of Synthetic Approaches and The Biological Activitymf720383270No ratings yet
- DR Vatsal Patel AhmedabadDocument30 pagesDR Vatsal Patel AhmedabadSayali PhansekarNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Mining Skill TrainingDocument31 pagesProposal For Mining Skill Trainingdwarka prasad100% (1)
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- Life Without GravityDocument2 pagesLife Without GravityRomel Antonio Zorrilla RamirezNo ratings yet
- Saa6d170e-5 HPCR Egr Sen00190-04Document415 pagesSaa6d170e-5 HPCR Egr Sen00190-04Ahmad Mubarok100% (4)
- Production Choke BasicsDocument39 pagesProduction Choke Basicsbtmohamed7084100% (1)
- Kumiko Jigs Japanese Woodworking PDFDocument9 pagesKumiko Jigs Japanese Woodworking PDFJaime Montiel100% (1)
- Irrigation Project ManualDocument66 pagesIrrigation Project ManualHorace Prophetic DavisNo ratings yet
- Variac MFG Business Plan Annexure - 1Document6 pagesVariac MFG Business Plan Annexure - 1Manav MatetiNo ratings yet
- Amulets Talismans and CharmsDocument3 pagesAmulets Talismans and CharmsreikiladyNo ratings yet
- GX7000 New CatalogeDocument20 pagesGX7000 New CatalogeyohanesNo ratings yet
- Mintek Ar 2011Document76 pagesMintek Ar 2011Algradi MosheerNo ratings yet
- Graphing linear functions and writing equations in standard formDocument15 pagesGraphing linear functions and writing equations in standard formnmarjonoNo ratings yet
- 2) Inequality GraphsDocument14 pages2) Inequality Graphsmanobilli30No ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Food Labelling in Controlling Ones Calorie IntakeDocument33 pagesThe Effectiveness of Food Labelling in Controlling Ones Calorie IntakeKisha Ghay SudariaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995Document11 pagesThe Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995laith AtekNo ratings yet
- Hunter'S Bump: YsteryDocument3 pagesHunter'S Bump: YsteryMar De EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Mine Pool AtlasDocument172 pagesMine Pool AtlasRishiraj SahooNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument11 pages1 PB PDFaldo surya pratamaNo ratings yet
- KFS Ut U3Document5 pagesKFS Ut U3Ana DuarteNo ratings yet
- Users Manual: Documenting Process CalibratorDocument134 pagesUsers Manual: Documenting Process CalibratorSilvaa60No ratings yet
- For Student-General Chemistry I - Module 6 - Phan Tai HuanDocument41 pagesFor Student-General Chemistry I - Module 6 - Phan Tai HuanEsat Goceri100% (1)
- Amplifiers and OscillatorsDocument109 pagesAmplifiers and OscillatorsAdilNo ratings yet
- Series 9910 4-3/8" Sliding Glass Door (Cw30) : SectionDocument4 pagesSeries 9910 4-3/8" Sliding Glass Door (Cw30) : SectionAmro Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Surgical Methods of MTPDocument44 pagesSurgical Methods of MTPRajeev Sood100% (1)
- STAIRCASE DETAILSDocument76 pagesSTAIRCASE DETAILSpankaj DNo ratings yet