Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab3 Completed
Lab3 Completed
Uploaded by
Khalid MalikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab3 Completed
Lab3 Completed
Uploaded by
Khalid MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Experiment No. 03
OBJECTIVE:
To design and analyze the circuits of slew rate and CMRR using 741 Op-amp.
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:
• Function generator
• Op-amp 741
• Power Supply
• Oscilloscope
• Bread board
• Resistors
THEORY:
The Slew Rate of an op amp describes how fast the output voltage can change in response to an
immediate change in voltage at the input. One of the practical op-amp limitations is the rate at
which the output voltage can change. The limiting rate of change for a device is called its "slew
rate". The slew rate for the 741 is 0.5V/microsecond. By formula Slew rate is defined as:
Where: Vout (t) is the output produced by the amplifier as a function of time t.
The slew rate also affects sine wave (and audio) signals as well as square waves. The rate of change
of voltages in a sine wave is continually varying, it is changing at its fastest rate as the signal
voltage crosses zero, and the rate of change falls momentarily to zero (no change) at both the
positive and negative peaks of the wave. If the slew rate of the amplifier cannot keep up with the
fastest rate of change of the signal, some distortion will be produced. Therefore, to be sure of
amplifying large amplitude signals that are most likely to produce large (and fast) rates of voltage
change, an op amp needs to have a sufficiently high value of slew rate to cope with the greatest
possible rate of voltage change. If the largest possible voltage swing and the highest frequency of
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
the signal are known, the minimum required slew rate for the op amp can be calculated using the
formula:
SR ≥2 Π f x Vpk
Where: f is the operating frequency and Vpk is the peak amplitude of the waveform.
Figure: Slew rate effect on a square wave: red=
desired output, green= actual output.
Applying signals with transients that exceed this limit results in distorted output signals. The
slewrate can be measured by applying a large square waveform at the input. The frequency of the
input signal should be increased until the output becomes a triangular waveform. The slope of the
triangular waveform is the slew rate.
If a square wave is applied to the input of the op amp, the output should also be a square wave.
However, the fast rising and falling edges of the square wave can tend to cause the amplifier to
oscillate for a short time after the rise or fall. To prevent this effect, the op amp’s internal circuitry
contains a small amount of compensation capacitance that slows down the rate of change by acting
as a CR time constant so that very fast transient voltages do not trigger oscillation, but this
compensation also limits the slew rate of the op amp.
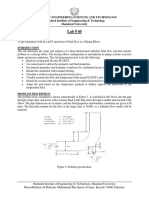
PROCEDURE
To measure slew rate, configure the op amp as a unity-gain buffer as shown below.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Figure: Unity Gain Voltage Follower
1. Apply the input voltage through Function Generator (Vp=10).
2. Select the Oscilloscope in Dual mode.
3. Select the Square waveform from Function Generator
4. Vary the frequency of Function Generator from 1 KHz to 20 KHz and observe the slew
rate effect on the oscilloscope (Difference between input & output waveform).
5. Repeat 3 for Sinusoidal and triangular waveform and notice the difference.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
S.No. Vin 1 Vin 2 Vout Theoretical Vout
1. 9.98 V 10 V 9.98 V 0.02 V
2. 4.99 V 5V 4.99 V 0.01 V
3. 1.99V 2V 1.99V 0.01 V
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
The CMRR in an operational amplifier is a common mode rejection ratio. Generally, the op amp
as two input terminals which are positive and negative terminals and the two inputs are applied at
the same point. This will give the opposite polarity signals at the output. Hence the positive and
the negative voltage of the terminals will cancel out and it will give the resultant output voltage.
The ideal op amp will have the infinite CMRR and with the finite differential gain and zero
common mode gain.
Or in other words, the common mode rejection ratio is the measure of a differential amplifier's
ability to reject signals that applied simultaneously to both inputs. Practical operational amplifiers
have a finite nonzero common-mode gain. If the two input terminals of the op-amp are tied together
and a signal Vcm is applied, the output voltage will be proportional to the input voltage by some
constant. This constant will be the common-mode gain Acm. Figure below illustrates this
definition.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Figure - Illustration and definition of the common mode gain
The ability of an op-amp to reject common mode signals is specified in terms of the common mode
rejection ratio (CMRR) that is defined as:
CMRR =
So the common mode voltage gain (Acm)
Acm = Vo/ Vin
And, differential mode gain (Ad)
Ad = Rf / Ri
Usually the CMRR is expressed in dB's.
CMRR = 20 x log Type equation here.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
S.No. Vin Rf Ri Ad = Vout Acm CMRR
Rf/Ri
1. 2V 100k 100 1k 35.612mv 0.030 90.45dB
2. 10V 50k 100 500 89.488mv 0.015 90.45dB
3. 5V 150k 100 1.5k 0.046 90.26dB
132.876mv
RESULT:
Attach the graph of the following circuit.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
EXERCISE:
1. Does voltage gain affect slew rate?
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
Answer:
Slew rate changes with the change in voltage gain. Therefore, it is generally specified at unity (+1) gain
condition. . This means that when a large step input signal is applied to the input, the electronic device
can provide an output of 10 volts in 1 microsecond.
2. Give reason whether the triangle waves suffer from slew rate limiting or not?
3. Calculate the common-mode voltage gain for the circuit
Acm = Vout/ Vcm
Acm = 0.0024
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
4. Design the given circuit in Multisim and determine the common mode output voltage having
CMRR=65db.
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Shara e Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
You might also like
- Bently Nevada MmsDocument30 pagesBently Nevada MmsMohamed Hamed100% (1)
- Manufacturing Considerations in Liquids: - Water Condensate ...................... - Steam .................Document12 pagesManufacturing Considerations in Liquids: - Water Condensate ...................... - Steam .................lola&losa farhanNo ratings yet
- Lab5 CompletedDocument8 pagesLab5 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab4 CompletedDocument13 pagesLab4 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab2 CompletedDocument14 pagesLab2 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- T F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitDocument4 pagesT F W R: O Design AND Simulate A ULL AVE Ectifier CircuitJunaid NazirNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 2Document6 pagesEna Lab 2Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 4Document5 pagesEna Lab 4Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 10Document4 pagesEna Lab 10Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 Basic ElectronicsDocument7 pagesLab 12 Basic ElectronicsMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPDocument8 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Open-Ended InverterDocument2 pagesOpen-Ended InverterAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- AUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalDocument7 pagesAUPEC 2020 Shuvra FinalAK KhanNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPDocument7 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Design of High PSRR Folded Cascode Operational Amplifier For LDO ApplicationsDocument5 pagesDesign of High PSRR Folded Cascode Operational Amplifier For LDO Applicationsjeevamk423No ratings yet
- Simulation & Analysis of PWM Inverter Using Matlab: FromDocument28 pagesSimulation & Analysis of PWM Inverter Using Matlab: FromnagatejaNo ratings yet
- Ac Lab Mannual BeyondDocument105 pagesAc Lab Mannual BeyondPrahlad ReddyNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter Iqbal100% (1)
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Expt 7, Comparator (Updated)Document3 pagesExpt 7, Comparator (Updated)Danish MujibNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signal Design Lab 3 (EC2061) Experiment No.: 03: Santosh Kumar Kishore RamisettyDocument10 pagesMixed Signal Design Lab 3 (EC2061) Experiment No.: 03: Santosh Kumar Kishore RamisettysanthoshNo ratings yet
- Ie CepDocument11 pagesIe Cepabdul shaggyNo ratings yet
- Lab1 CompletedDocument13 pagesLab1 CompletedKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- An Investigation On The Performance of Random PWM Controlled ConvertersDocument10 pagesAn Investigation On The Performance of Random PWM Controlled ConvertersALiftsNo ratings yet
- ANALOG AND DIGITAL IC Short Question With AnswerDocument46 pagesANALOG AND DIGITAL IC Short Question With AnswerMATHANKUMAR.S100% (2)
- RF Energy Harvesting in Relay NetworksDocument44 pagesRF Energy Harvesting in Relay NetworksYeshwanthSuraNo ratings yet
- MTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument5 pagesMTPA and Field Weakening Control of Synchronous Reluctance MotorIVAN FELIPE BERNAL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- RCN Elcu RG EgDocument2 pagesRCN Elcu RG EgXavi HernandezNo ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Techniques in Wireless Communication: Qasim Hadi KareemDocument29 pagesSpread Spectrum Techniques in Wireless Communication: Qasim Hadi KareemGafeer FableNo ratings yet
- Class-C Power Amplifier Design For GSM ApplicationDocument5 pagesClass-C Power Amplifier Design For GSM ApplicationJose David CastroNo ratings yet
- 1Document30 pages1Amarnath YadavNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation On Detection by RADAR byDocument4 pagesPaper Presentation On Detection by RADAR byJanmayjay SwetankNo ratings yet
- Analaysis Short Circuit SummaryDocument10 pagesAnalaysis Short Circuit Summarymohamad arifinNo ratings yet
- Test Equipment For AC/DC Drive and Power Electronic MeasurementsDocument6 pagesTest Equipment For AC/DC Drive and Power Electronic MeasurementsLin ChongNo ratings yet
- A High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignDocument6 pagesA High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignKhaja Mujeebuddin QuadryNo ratings yet
- Step Recovery DiodesDocument3 pagesStep Recovery DiodesfahkingmoronNo ratings yet
- CEP Impulse VoltageDocument10 pagesCEP Impulse VoltageKASHIF zamanNo ratings yet
- EE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusDocument66 pagesEE6311 LIC Lab - VidyarthiplusArun KumarNo ratings yet
- TytDocument9 pagesTytPrabhu MoorthyNo ratings yet
- CH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignDocument24 pagesCH3 - Diode Rectifiers DesignSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 2-15-1381147174-25 .Design of 1 V.FULL PDFDocument10 pages2-15-1381147174-25 .Design of 1 V.FULL PDFABHILASH RAINo ratings yet
- Parametric Tests For SemiconductorDocument25 pagesParametric Tests For SemiconductorAnonymous jByA78No ratings yet
- PWM To DC Voltage Conversion: Kyle Burgess 4/3/2015Document8 pagesPWM To DC Voltage Conversion: Kyle Burgess 4/3/2015NaranLoganNo ratings yet
- AS3935 AppNote HardwareDesignGuide EN v1Document3 pagesAS3935 AppNote HardwareDesignGuide EN v1trisectrixNo ratings yet
- Ena Lab 6Document10 pagesEna Lab 6Halar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices Circuit NoteDocument7 pagesAnalog Devices Circuit Notevighnesh shanbhagNo ratings yet
- Dc-choper المحاضرة السادسةDocument36 pagesDc-choper المحاضرة السادسةIbrahim YousifNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothDocument16 pagesWave Shaping Square, Triangular and Saw ToothKiranpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- SNDT ManualDocument42 pagesSNDT ManualDhaval BhojaniNo ratings yet
- WcdmaDocument22 pagesWcdmaPradeepVermaNo ratings yet
- Slip Test On Salient Pole MachineDocument3 pagesSlip Test On Salient Pole Machinedeepak reddyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual PDFDocument46 pagesAdvanced Communication Lab Manual PDFMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Voice Transission Using LaserDocument31 pagesVoice Transission Using LaserRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- Expt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDocument3 pagesExpt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDanish MujibNo ratings yet
- Expt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDocument3 pagesExpt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDanish MujibNo ratings yet
- Expt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDocument3 pagesExpt 06 LP & HP UPDATEDDanish MujibNo ratings yet
- Current Signal Processing-Based Techniques For Transformer ProtectionDocument332 pagesCurrent Signal Processing-Based Techniques For Transformer ProtectionJohNo ratings yet
- Design of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyDocument9 pagesDesign of RF To DC Rectifier at GSM Band For EnergyAchmad ShodikinNo ratings yet
- Pilot Wire Relaying SchemeDocument17 pagesPilot Wire Relaying SchemeBishnu Prasad SahooNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- LAB TasksDocument2 pagesLAB TasksKhalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 9Document4 pagesLab - 9Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 7Document5 pagesLab - 7Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document5 pagesLab 8Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 5Document8 pagesLab - 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 2Document7 pagesLab - 2Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 4Document5 pagesLab - 4Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 6Document7 pagesLab - 6Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab - 3Document3 pagesLab - 3Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document19 pagesLab 5Khalid MalikNo ratings yet
- Counseling LectureDocument24 pagesCounseling LectureDennis RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Previous Studies.: The Heb Sed Festival Sequence and Pbrooklyn 47.218.50Document8 pagesPrevious Studies.: The Heb Sed Festival Sequence and Pbrooklyn 47.218.50Mohammed MohieNo ratings yet
- Resume Joseph Thomas Holden (Inventor, Scientist, Engineer, and Sunsnest Consulting)Document3 pagesResume Joseph Thomas Holden (Inventor, Scientist, Engineer, and Sunsnest Consulting)earth shift100% (2)
- الماجستير المهنى فى العلوم الاكتوارية PDFDocument2 pagesالماجستير المهنى فى العلوم الاكتوارية PDFOmran KingNo ratings yet
- Biokimia Resume Jurnal Kelompok 1Document9 pagesBiokimia Resume Jurnal Kelompok 1Indana ZulfaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan EDITEDDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan EDITEDJoylen AcopNo ratings yet
- Designing Organizational Structure (Adaptive Designs)Document27 pagesDesigning Organizational Structure (Adaptive Designs)haseeb0% (1)
- S.No Particular Sokkia Total Station IM-105 IM-101 FX-101Document4 pagesS.No Particular Sokkia Total Station IM-105 IM-101 FX-101AshokNo ratings yet
- Essay Test: Discussant: Topic: Subject: ProfessorDocument2 pagesEssay Test: Discussant: Topic: Subject: ProfessorJenelyn ApinadoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 8e by Andrew B Abel 0133407926Document3 pagesTest Bank For Macroeconomics 8e by Andrew B Abel 0133407926Marvin Patterson100% (37)
- LG DV450 DV452 Reproductor DVD Manual de Servicio PDFDocument73 pagesLG DV450 DV452 Reproductor DVD Manual de Servicio PDFalberto castañoNo ratings yet
- English Final Exam-Music and FilmssDocument10 pagesEnglish Final Exam-Music and FilmssKhalis PrimaNo ratings yet
- The National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument194 pagesThe National Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines For Selected Non-Communicable DiseasesRajithaHirangaNo ratings yet
- Trivia Bank - The Business QuizDocument19 pagesTrivia Bank - The Business QuizRajaram SethuramanNo ratings yet
- Office Performance Commitment and Review (OPCRF) : Department of EducationDocument3 pagesOffice Performance Commitment and Review (OPCRF) : Department of EducationHero LaguitNo ratings yet
- LE CORBUSIER AND THE PROBLEM OF REPRESENTATION - Luis E. CarranzaDocument13 pagesLE CORBUSIER AND THE PROBLEM OF REPRESENTATION - Luis E. Carranzaanapaula1978No ratings yet
- Coastal Nursing Tourism To Improve Tourist Safety in Tourist AttractionDocument10 pagesCoastal Nursing Tourism To Improve Tourist Safety in Tourist AttractionihwanNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 LASQ1Document6 pagesCookery 10 LASQ1Erich Niña AyoNo ratings yet
- Controlling Profitability AnalysisDocument7 pagesControlling Profitability AnalysisNeelam SinghNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Sedimentation: Lecture # 4Document19 pagesReservoir Sedimentation: Lecture # 4amin alzuraikiNo ratings yet
- A4GpilotDaveRamsayPages MINDocument57 pagesA4GpilotDaveRamsayPages MINSpazSinbadNo ratings yet
- Cmmi 2.0Document13 pagesCmmi 2.0faridin bm2019No ratings yet
- Gas Burner PDFDocument26 pagesGas Burner PDFAriel NKNo ratings yet
- Guia Formacion SASDocument16 pagesGuia Formacion SASwespinoaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 CircuitDocument8 pagesLab 1 Circuitapi-610008741No ratings yet
- 2017 - YEAR5 - BI - Paper1 - 1st PRODocument13 pages2017 - YEAR5 - BI - Paper1 - 1st PRORani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 1 Question and Answer (Set E)Document3 pagesAIS Chapter 1 Question and Answer (Set E)John Carlos DoringoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406100% (1)
- Simplifying Expressions CSEC TOPICDocument2 pagesSimplifying Expressions CSEC TOPICLatoyaWatkinsNo ratings yet