0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views24 pagesUnderstanding SAP ERP Software Basics
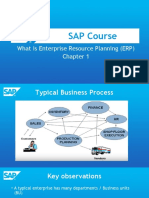
SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing. It is an ERP software developed by SAP SE, a European multinational. SAP consists of fully integrated modules that manage virtually all business operations and processes. It is the leading ERP software in the world with over 140,000 installations. SAP helps companies overcome issues with decentralized data management systems by providing a centralized system where all departments can access and update shared information in real-time, leading to improved coordination, reduced costs, and better customer service.
Uploaded by
Surya AnjuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views24 pagesUnderstanding SAP ERP Software Basics
SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing. It is an ERP software developed by SAP SE, a European multinational. SAP consists of fully integrated modules that manage virtually all business operations and processes. It is the leading ERP software in the world with over 140,000 installations. SAP helps companies overcome issues with decentralized data management systems by providing a centralized system where all departments can access and update shared information in real-time, leading to improved coordination, reduced costs, and better customer service.
Uploaded by
Surya AnjuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd