Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class XPhysicsElectricityP12022
Uploaded by
Oye DtOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class XPhysicsElectricityP12022
Uploaded by
Oye DtCopyright:
Available Formats
Class X Physics 2022-23
Electricity
1. Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. By how much does the
current change?
2. How does the resistance of a wire change when:
(a) Its length is tripled? (b) Its diameter is tripled?
(c) Its material is changed to one whose resistivity is three time?
3. If a wire is increased to 4 times its original length, by what factor does the resistivity change?
4. If the current passing through a conductor is doubled, what will be the change in the heat produced?
5. Why is an electric bulb filled with argon and nitrogen gas?
6. Explain why, the filaments of electric bulbs are made of tungsten.
7. How much work is done in moving a charge of magnitude 3 C across two points having a potential difference
of 12 V?
8. What does the slope of V – I graph at any point represent?
9. The electrical resistivity of silver is 1.60 × 10-6 Ω m. What will be the resistance of a silver wire of length 10
m and cross-sectional area 2 × 10-3 m2?
10. Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
11. Two coils of resistance R1 = 3Ω and R2 = 9Ω are connected in series across a battery of potential difference
14 V. Draw the circuit diagram. Find the electrical energy consumed in 1 min in each resistance.
12. What is the better way of connecting lights and other electrical appliances in domestic wiring? Why?
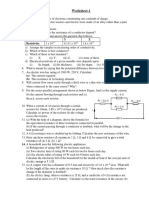
13. An electric lamp, whose resistance is 20 Ω, and a conductor of 4 Ω
resistance are connected to aft V battery (Fig.).
Calculate (a) the total resistance of the circuit, (b) the current through
the circuit, and (c) the potential difference across the electric
conductor.
14. A wire has a resistance of 10Ω. It is melted and drawn into a wire of half of its length. Calculate the
resistance of the new wire. What is the percentage change in its resistance?
15. If, in Figure R1 = 10 ohms, R2 = 40 ohms, R3, = 30 ohms, R4 = 20 ohms,
𝑅5 = 60 ohms and a 12 volt battery is connected to the arrangement,
calculate: (a) the total resistance and
(b) the total current flowing in the circuit.
16. A household uses the following electric appliances:
(i) Refrigerator of rating 400 W for ten hours each day.
(ii) Two electric fans of rating 80 W each for twelve hours each day.
(iii) Six electric tubes of rating 18 W each for 6 hours each day.
Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy is ₹
3.00.
17. A 4 kW heater is connected to a 220 V source of power. Calculate
(i) the electric current passing through the heater.
(ii) the resistance of the heater.
(iii) the electric energy consumed in 2 hour use of the heater.
18. Two resistance when connected in parallel give resultant value of 2 Ω. When connected in series, the value
becomes 9 Ω. Calculate the value of each resistance.
19. Two conducting wires of the same material and of the equal length and equal diameter are first connected in
series and then in parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference .Find the ratio of the heat produced
in series and parallel combination
20. How many bulbs of 100W each at 220V can be connected ion parallel across potential difference of 220V to
draw current of 5A?
You might also like
- 28th Physics 1 cls10Document2 pages28th Physics 1 cls10ARADHYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- ch12 Class 10th Science AssignmentDocument2 pagesch12 Class 10th Science AssignmentPriyanka Kasturia100% (1)
- CH 12 Electricity DPP - 01Document1 pageCH 12 Electricity DPP - 01HemantBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Electricity AssignmentDocument1 pageElectricity AssignmentSHANKARJEENo ratings yet
- Class - 10 - LN - 12 - Class TestDocument8 pagesClass - 10 - LN - 12 - Class TestSrivatsan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Electricity Sheet-14656887Document2 pagesElectricity Sheet-14656887Kartik MishraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet X PhysicsDocument31 pagesWorksheet X PhysicsGuru PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Rev XDocument2 pagesRev Xdaksh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Electricity Class X PhysicsDocument3 pagesWorksheet Electricity Class X Physicsvaibhav4gameNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Question BankDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity Question Bankdayanandan150% (2)
- 1699200545003.electricity Worksheet-2Document1 page1699200545003.electricity Worksheet-2NEEL PAREKHNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityTanmay SanchetiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityyashasviupadhyay19No ratings yet
- Assignment - Current ElectricityDocument11 pagesAssignment - Current ElectricityPresident ObamaNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10th Sure Questions - PhysicsDocument2 pagesCBSE 10th Sure Questions - Physicsrmgokul78No ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BankDocument6 pagesQdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BanknunjapiznesNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- Electricity Assignment HHWDocument5 pagesElectricity Assignment HHWAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- Ryan International School Class X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesRyan International School Class X Chapter: ElectricityAnnu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsSoham's Smart ShowNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Question BankDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity Question BankAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Physics For X - CbseDocument9 pagesPhysics For X - Cbsearshad_bahNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsCRUEL HUNTERNo ratings yet
- Sheets DCDocument19 pagesSheets DChatem aliNo ratings yet
- NUMERICALS On Electricity-10Document5 pagesNUMERICALS On Electricity-10Tanmay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Electricty Physics X..Document3 pagesElectricty Physics X..Mandeep Singh PlahaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- Electricity QuestionsDocument11 pagesElectricity QuestionsYuresh YNo ratings yet
- Electricity WorksheetDocument11 pagesElectricity Worksheetsrijankanduri14No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Class X ElectricityDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 Class X Electricityfarhaan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Ch.12Document2 pagesClass 10 Science Ch.12Komal PatilNo ratings yet
- Class - X Physics Worksheet - 1 Electricity: NumericalsDocument1 pageClass - X Physics Worksheet - 1 Electricity: NumericalsHima ShettyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits PracticeDocument4 pagesElectric Circuits PracticeaoaNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Part 2Document13 pagesElectricity - Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Electricity QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectricity QuestionsMicky2306No ratings yet
- Class 10 Electricity NumericalsDocument2 pagesClass 10 Electricity NumericalsMayank Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Electricity X Class Term Ii Imp QuesDocument8 pagesElectricity X Class Term Ii Imp Questech zone VIJI&CO (VIJI&CO MOBIL&WATCH)No ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectricity Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Physics - ElectricityDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics - Electricitybadnight4u100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set ADocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set AlalitNo ratings yet
- Physics.... ElectricityDocument7 pagesPhysics.... ElectricityJiveshNo ratings yet
- Question Bankof Physicsfor Class 10 THDocument16 pagesQuestion Bankof Physicsfor Class 10 THmeerneelofarh455No ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityMohit GargNo ratings yet
- Eec 115 Tutorial QuestionsDocument3 pagesEec 115 Tutorial QuestionsOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- X ScienceDocument7 pagesX ScienceSanghamitra ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10, Physics, CBSE - ElectricityDocument1 pageCBSE 10, Physics, CBSE - ElectricityAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class X CbseDocument3 pagesElectricity Class X CbseXxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Electricity Paper (Advance)Document2 pagesElectricity Paper (Advance)Vikram tomarNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Sample - 1Document3 pagesCH-3 Sample - 1jayNo ratings yet
- Reference: University Physics by Sears, Zemansky and Young, Sixth Edition: Ch. 26Document4 pagesReference: University Physics by Sears, Zemansky and Young, Sixth Edition: Ch. 26Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- DPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Document12 pagesDPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Abhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Ce WS2Document4 pagesCe WS2Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Question 543500 3Document8 pagesQuestion 543500 3Nabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- EE1100 Spring 2020 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEE1100 Spring 2020 Tutorial 1Ram Lakhan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Electricity: Class-XDocument1 pageWorksheet-Electricity: Class-Xveeresh punjaniNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Trend Setter Test Paper Chap - Electricity - 03Document3 pagesClass 10 Trend Setter Test Paper Chap - Electricity - 03ARADHYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- EF45 Mounting and Installation Guide Mar 2017Document20 pagesEF45 Mounting and Installation Guide Mar 2017Bernardo PáramoNo ratings yet
- Pioneer DJM V10 User ManualDocument91 pagesPioneer DJM V10 User Manualdamien chagnaudNo ratings yet
- Resistor Value Tables - Guides - ES ComponentsDocument28 pagesResistor Value Tables - Guides - ES ComponentsSean CanoNo ratings yet
- TR IEC TS 62804-1-2019.previewDocument12 pagesTR IEC TS 62804-1-2019.previewFadhel GuesmiNo ratings yet
- 7SR224 - Argus Complete Technical Manual (201-300)Document100 pages7SR224 - Argus Complete Technical Manual (201-300)Rosa MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - Activity 1 - Physics ProblemsDocument6 pagesPhysics 2 - Activity 1 - Physics ProblemsChristian Paul A. AsicoNo ratings yet
- Manual EC20 (English) PDFDocument79 pagesManual EC20 (English) PDFDalat TigonNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Design ToolsDocument2 pagesSimulation and Design Toolsvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Straatman Solar SystemsDocument8 pagesStraatman Solar SystemsMNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric MAC-567IF-E Installation Manual EngDocument12 pagesMitsubishi Electric MAC-567IF-E Installation Manual EngxillanaNo ratings yet
- K85001-0668 - Genesis LED EG4 Series Wall Mount Notification DevicesDocument6 pagesK85001-0668 - Genesis LED EG4 Series Wall Mount Notification Devicesmauro garciaNo ratings yet
- Obe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalDocument22 pagesObe Curriculum For The Course: RGPV (Diploma Wing) BhopalHarshit Sahu CS-26No ratings yet
- CRST045N10N, CRSS042N10N: 100% Avalanche Tested 100% Avalanche Tested 100% Avalanche TestedDocument10 pagesCRST045N10N, CRSS042N10N: 100% Avalanche Tested 100% Avalanche Tested 100% Avalanche TestedLuis FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Lighting Lighting: HID-Basic Semi-Parallel Ballasts For SON/CDM/MH LampsDocument2 pagesLighting Lighting: HID-Basic Semi-Parallel Ballasts For SON/CDM/MH LampsNestor Fortunato Lopez VargasNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Blind Stick With GPS and GSM TrackingDocument11 pagesUltrasonic Blind Stick With GPS and GSM TrackingIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Hazards in E-Mobility v0.1bDocument9 pagesCapacitance Hazards in E-Mobility v0.1bStefNo ratings yet
- Military & Aerospace Electronics - February 2019Document40 pagesMilitary & Aerospace Electronics - February 2019Anthony Van HamondNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog: 8 2007 Agi GMBH Wiener Strasse 158 A-2352 Gumpoldskirchen Austria Europe Tel.: +43-2252-606Document34 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: 8 2007 Agi GMBH Wiener Strasse 158 A-2352 Gumpoldskirchen Austria Europe Tel.: +43-2252-606Mitica ScurtuNo ratings yet
- Detector de Llama - RFD-2000X ManualDocument35 pagesDetector de Llama - RFD-2000X ManualFernando BonillaNo ratings yet
- Pioneer HPM1100 OwnersDocument2 pagesPioneer HPM1100 OwnersStanko CaneNo ratings yet
- WEG - TransformerDocument20 pagesWEG - TransformerMarcus GregórioNo ratings yet
- Samsung Le32a65 Le37a65 Le40a65 Le46a65 Le52a65 Le37a616a 40a616a Chassis N46aDocument425 pagesSamsung Le32a65 Le37a65 Le40a65 Le46a65 Le52a65 Le37a616a 40a616a Chassis N46aenerjay80% (5)
- Harmonic Mitigating Transformers InformationDocument3 pagesHarmonic Mitigating Transformers InformationJoseph B Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller and InterfacingDocument3 pagesMicrocontroller and InterfacingAdil Ayub100% (1)
- Comparison of Simulation Tools ATP-EMTP and MATLAB PDFDocument15 pagesComparison of Simulation Tools ATP-EMTP and MATLAB PDFthanhntepsNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument35 pagesCapacitorsLourdes Marie MirasolNo ratings yet
- Fully Orchestrated Downhole Reservoir Testing Experience Case Study Real-Time Pressure Management Saves 1 15923085342021093Document1 pageFully Orchestrated Downhole Reservoir Testing Experience Case Study Real-Time Pressure Management Saves 1 15923085342021093Jorge Alberto AmbrizNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet 5mm Phototransistor T-1: FeaturesDocument7 pagesTechnical Data Sheet 5mm Phototransistor T-1: Features9cf634095aNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Digital 74hcDocument33 pagesDatasheet Digital 74hcСтанислав ИвановNo ratings yet
- CH3 TransformerDocument57 pagesCH3 TransformerDoktor CintaNo ratings yet