Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Balance Scorecard
Uploaded by
Sonal Chaturvedi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views3 pagesBalance Scorecard
Uploaded by
Sonal ChaturvediCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
BALANCE SCORECARD
A balanced scorecard is a performance metric
used to identify, improve, and control a business's
various functions and resulting outcomes.
The concept of BSCs was first introduced in 1992
by David Norton and Robert Kaplan.
It involves measuring four main aspects of a
business: Learning and growth,
business processes,
customers,
and finance.
It helps companies to gather information in a
single report, provide information into service and
quality in addition to financial performance, and
to help improve efficiencies.
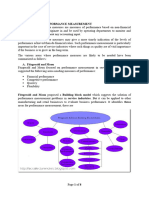
Characteristics of the Balanced Scorecard Model (BSC)
Information is collected and analyzed from four
aspects of a business:
1. Learning and growth are analyzed through the
investigation of training and knowledge resources.
This first leg handles how well information is
captured and how effectively employees use that
information to convert it to a competitive
advantage within the industry.
2. Business processes are evaluated by investigating
how well products are manufactured. Operational
management is analyzed to track any gaps, delays,
bottlenecks, shortages, or waste.
3. Customer perspectives are collected to gauge
customer satisfaction with the quality, price, and
availability of products or services. Customers
provide feedback about their satisfaction with
current products.
4. Financial data, such as sales, expenditures, and
income are used to understand financial
performance. These financial metrics may include
dollar amounts, financial ratios, budget variances,
or income targets.1
Benefits of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
There are many benefits to using a balanced scorecard.
1)the BSC allows businesses to pool together
information and data into a single report rather
than having to deal with multiple tools.
2)This allows management to save time, money, and
resources when they need to execute reviews to
improve procedures and operations.
3)Scorecards provide management with valuable
insight into their firm's service and quality in
addition to its financial track record. By measuring
all of these metrics, executives are able to train
employees and other stakeholders and provide
them with guidance and support. This allows them
to communicate their goals and priorities in order
to meet their future goals.
Examples of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Corporations can use their own, internal versions of
BSCs, For example, banks often contact customers and
conduct surveys to gauge how well they do in
their customer service. These surveys include rating
recent banking visits, with questions ranging from wait
times, interactions with bank staff, and overall
satisfaction. They may also ask customers to make
suggestions for improvement. Bank managers can use
this information to help retrain staff if there are
problems with service or to identify any issues
customers have with products, procedures, and
services.
You might also like
- The Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)From EverandThe Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- What Is The Balanced ScorecardDocument21 pagesWhat Is The Balanced ScorecardAndi Yanuar100% (1)
- Balanced Scorecard for Performance MeasurementFrom EverandBalanced Scorecard for Performance MeasurementRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Balanced Scorecard - Wells Fargo (BUSI0027D) PDFDocument12 pagesBalanced Scorecard - Wells Fargo (BUSI0027D) PDFRafaelKwong50% (4)
- R13 Oracle SCM Maintenance (EAM) Cloud Features SummaryDocument17 pagesR13 Oracle SCM Maintenance (EAM) Cloud Features SummarySrinivasa Rao AsuruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions Horngren Cost AccountingDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Solutions Horngren Cost AccountingAnik Kumar MallickNo ratings yet
- Q8 IM08 FinalDocument59 pagesQ8 IM08 FinalJb MacarocoNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Horngren IsmDocument19 pagesCh01 Horngren IsmKiều Thảo AnhNo ratings yet
- Commercial Invoice Po#6600210291-5057004301 PDFDocument1 pageCommercial Invoice Po#6600210291-5057004301 PDFSandra Lubana Garcia GomezNo ratings yet
- The 4 Perspectives of The Balanced ScorecardDocument6 pagesThe 4 Perspectives of The Balanced Scorecardnivedita patilNo ratings yet
- The Balanced ScorecardDocument13 pagesThe Balanced Scorecardssb_74100% (2)
- C.v... - Eman MahmoudDocument5 pagesC.v... - Eman Mahmoudeman mahmoudNo ratings yet
- The Electronic Commerce Act RA 8792Document18 pagesThe Electronic Commerce Act RA 8792GF Sotto100% (2)
- How to Improve Performance through the Balanced ScorecardFrom EverandHow to Improve Performance through the Balanced ScorecardRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Balanced ScorecardDocument27 pagesBalanced ScorecardharshbhatiaNo ratings yet
- AirAsia's Social Responsibility and CSR ProgramsDocument4 pagesAirAsia's Social Responsibility and CSR ProgramsPrivate TitaniumNo ratings yet
- Top Tables For The Sales and Distribution Module SD in SAP: Table - Name S/4HANA - Table and General NotesDocument7 pagesTop Tables For The Sales and Distribution Module SD in SAP: Table - Name S/4HANA - Table and General Notesramesh B100% (1)
- Balanced Score Card PDFDocument14 pagesBalanced Score Card PDFtyoafsNo ratings yet
- Assigment Individual2Document5 pagesAssigment Individual2haftamu GebreHiwotNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument4 pagesBalanced Scorecardhaftamu GebreHiwotNo ratings yet
- Challnenegeof What Is A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) ?: Key TakeawaysDocument18 pagesChallnenegeof What Is A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) ?: Key TakeawaysMalede WoledeNo ratings yet
- Non Financial Performance EvaluationDocument18 pagesNon Financial Performance EvaluationRachel GreeneNo ratings yet
- Project Report AnshulDocument25 pagesProject Report AnshulAnshul GoelNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Performance ManagementDocument19 pagesGroup 2 - Performance ManagementCARLYN JANE SALVADORNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument17 pagesPerformance ManagementSæra HashmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresDocument10 pagesTutorial PMS Non-Financial MeasuresAisyah ShahidanNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Horngrens Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis Canadian 8th Edition Datar Solutions Manual PDFDocument18 pagesDwnload Full Horngrens Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis Canadian 8th Edition Datar Solutions Manual PDFaffluencevillanzn0qkr100% (8)
- BSC and Other TechniquesDocument17 pagesBSC and Other TechniquesHARSHIT KUMAR GUPTA 1923334No ratings yet
- Assignment Term 2Document6 pagesAssignment Term 2andualem ayeleNo ratings yet
- Balanced Score Card SubhajitDocument4 pagesBalanced Score Card SubhajitSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard and Its Application As A Strategic Decision-Making ToolDocument10 pagesThe Balanced Scorecard and Its Application As A Strategic Decision-Making ToolHEGADESHOBHARAJNo ratings yet
- SIMA PresentattionDocument2 pagesSIMA PresentattionS2018401 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument14 pagesChapter 1 SolutionschloeNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument25 pagesPerformance ManagementIkmal IshamudinyyNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard by Rajat JhinganDocument15 pagesBalanced Scorecard by Rajat Jhinganrajat_marsNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Approach (BSC) - Definition, Limits and BenefitsDocument9 pagesBalanced Scorecard Approach (BSC) - Definition, Limits and Benefitsritika.jain197No ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Framework for Measuring Business PerformanceDocument17 pagesBalanced Scorecard Framework for Measuring Business PerformanceVirender Singh SahuNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting 6th Edition Atkinson Solutions ManualDocument43 pagesManagement Accounting 6th Edition Atkinson Solutions Manualeddiehickmanfwgdmnxbyz100% (14)
- Balanced Scorecard ExplainedDocument16 pagesBalanced Scorecard ExplainedChann ChannNo ratings yet
- BSC-Measuring Business PerformanceDocument18 pagesBSC-Measuring Business PerformanceKomalJindalNo ratings yet
- Assignment On BSCDocument18 pagesAssignment On BSCginnz66No ratings yet
- LECTURE-3 Non-Financial Performance MeasuresDocument8 pagesLECTURE-3 Non-Financial Performance MeasuresHarusiNo ratings yet
- AKMY 6e ch01 - SMDocument20 pagesAKMY 6e ch01 - SMMuhammad Ahad Habib Ellahi100% (2)
- FILAMER CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY Graduate School Defines Balanced ScorecardDocument4 pagesFILAMER CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY Graduate School Defines Balanced ScorecardHanna Vi B. PolidoNo ratings yet
- Balance Score Card: Roshith CP 2017MBARG151Document23 pagesBalance Score Card: Roshith CP 2017MBARG151roshith cpNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Information That Creates ValueDocument27 pagesManagement Accounting: Information That Creates ValueTraaidyNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Measuring Total Business Unit PerformanceDocument25 pagesThe Balanced Scorecard: Measuring Total Business Unit PerformanceSayma LinaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 7 Strategic Scorecards LECTUREDocument6 pagesGROUP 7 Strategic Scorecards LECTUREVassy EsperatNo ratings yet
- PCM Term PaperDocument22 pagesPCM Term Paper8130089011No ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard GuideDocument19 pagesBalanced Scorecard GuidejhafjfNo ratings yet
- A Balanced Scorecard Is A Management Framework That Is Designed To Communicate MissionDocument1 pageA Balanced Scorecard Is A Management Framework That Is Designed To Communicate Missionkareen.arciaga1981No ratings yet
- The Balanced ScorecardDocument8 pagesThe Balanced ScorecardCaleb GetubigNo ratings yet
- Orientation On Balanced Scorecard (BSC)Document42 pagesOrientation On Balanced Scorecard (BSC)MikealayNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard: (1) The Financial PerspectiveDocument3 pagesBalanced Scorecard: (1) The Financial PerspectiveS. M. Zamirul IslamNo ratings yet
- The 4 Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard Management SystemDocument1 pageThe 4 Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard Management SystemHhrman HhuraaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management System - LAZODocument14 pagesPerformance Management System - LAZOMyles Ninon LazoNo ratings yet
- New Dimension in Management and Post Review of Budget.: National SeminarDocument13 pagesNew Dimension in Management and Post Review of Budget.: National Seminarminal bhojaniNo ratings yet
- BSCassignmentDocument4 pagesBSCassignmentBagas Wahyu LaksonoNo ratings yet
- RCM-5 TH UnitDocument13 pagesRCM-5 TH UnitPoovarasan KarnanNo ratings yet
- A Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessDocument22 pagesA Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessFeri100% (1)
- Balance Score CardDocument3 pagesBalance Score CardSwapna Wedding Castle EramaloorNo ratings yet
- Balance ScorecardDocument11 pagesBalance ScorecardkirandeepNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard PerspectivesDocument17 pagesBalanced Scorecard Perspectivesعثمان سلیمNo ratings yet
- Final Project - A STUDY OF GROWTH PROSPECTS OF ONLINE REATAILORS AND E-COMMERCE IN INDIADocument94 pagesFinal Project - A STUDY OF GROWTH PROSPECTS OF ONLINE REATAILORS AND E-COMMERCE IN INDIAhariiNo ratings yet
- Payal Pharma SolutionDocument1 pagePayal Pharma SolutionAkhil NarangNo ratings yet
- 01-BacarraIN2020 Audit ReportDocument91 pages01-BacarraIN2020 Audit ReportRichard MendezNo ratings yet
- Audit of Liabilities - Guidance Note PDFDocument22 pagesAudit of Liabilities - Guidance Note PDFRicalyn E. SumpayNo ratings yet
- Sana Mansoor Patel: Patelsana820Document3 pagesSana Mansoor Patel: Patelsana820Zoya KhanNo ratings yet
- GROW MORE FACULTY OF MANAGEMENT MCQsDocument51 pagesGROW MORE FACULTY OF MANAGEMENT MCQsChetan Patel (HOD, MBA)No ratings yet
- Alyssa Li ResumeDocument1 pageAlyssa Li ResumeMING JUNo ratings yet
- Dagnachew GetachewDocument91 pagesDagnachew GetachewAhsan HumayunNo ratings yet
- Nil 20210313Document32 pagesNil 20210313Ambrosia NeldonNo ratings yet
- K.C.S.E 2012 BUSINESS STUDIES PAPER 1 QUESTIONSDocument6 pagesK.C.S.E 2012 BUSINESS STUDIES PAPER 1 QUESTIONSUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Office of The Assistant Engineer, Lid & Ew Section Perumbalam GPDocument2 pagesOffice of The Assistant Engineer, Lid & Ew Section Perumbalam GPaneeshp_4No ratings yet
- Shree Samarth Tax InvoiceDocument3 pagesShree Samarth Tax InvoicePAVAN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Amit Mahajan MindBodyDocument3 pagesAmit Mahajan MindBodychampuyaNo ratings yet
- Walmart - Market Leader StrategiesDocument4 pagesWalmart - Market Leader Strategiesmurtaza mannanNo ratings yet
- RTM Cia 1Document9 pagesRTM Cia 1Shivani K Nair 2028149No ratings yet
- Cultural Difference Management, WalmartDocument6 pagesCultural Difference Management, WalmartMbugua Wa IrunguNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Working Capital Management: MeaningDocument30 pagesModule - 1 Working Capital Management: MeaningumeshrathoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit 1test 1 QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Unit 1test 1 QuestionsschoolramikaNo ratings yet
- San Miguel Drink Behavior Final Exam - Goedings - MarollanoDocument11 pagesSan Miguel Drink Behavior Final Exam - Goedings - MarollanoDrakon BgNo ratings yet
- MBA course summaries for second semesterDocument6 pagesMBA course summaries for second semesterSHASHANKNo ratings yet
- 5 Tips To Building Effective IBM Cognos Active ReportsDocument3 pages5 Tips To Building Effective IBM Cognos Active ReportsZameer SayedNo ratings yet
- National Teachers College ManilaDocument6 pagesNational Teachers College ManilaJeline LensicoNo ratings yet
- Solved A Monopolist Operates With The Following Data On Cost andDocument1 pageSolved A Monopolist Operates With The Following Data On Cost andM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- Jadwal OktoberDocument48 pagesJadwal OktoberFerbian FakhmiNo ratings yet