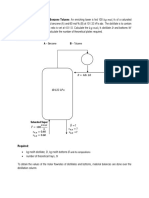
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EP Test For Methanol and 2-Propanol
Uploaded by
Hermansyah CitraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EP Test For Methanol and 2-Propanol
Uploaded by
Hermansyah CitraCopyright:
Available Formats
2.9.11. Test for methanol and 2-propanol EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.
A1 ´ I 2 ´ 100 Temperature :
A 2 ´ I1 ´ V1 Time Temperature
(min) (°C)
A1 = area of the peak due to ethanol in the chromatogram
Column 0 - 1.6 40
obtained with the test solution ;
A2 = area of the peak due to ethanol in the chromatogram 1.6 - 9.9 40 → 65
obtained with reference solution (c) ; 9.9 - 13.6 65 → 175
I1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the
13.6 - 20 175
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
I2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard Injection port 200
in the chromatogram obtained with reference Detector 200
solution (c) ;
V1 = volume of the preparation to be examined in the Detection : flame ionisation.
test solution, in millilitres. Injection : 1.0 mL of the gaseous phase of the test solution and
reference solution (c), at least 3 times.
Elution order : methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, 1-propanol.
Relative retention with reference to ethanol (retention
time = about 5.3 min) : methanol = about 0.8 ;
2-propanol = about 1.2 ; 1-propanol = about 1.6.
07/2019:20911 System suitability : reference solution (c) :
corrected 10.0 – resolution : minimum 5 between the peaks due to methanol
and ethanol.
Calculate the methanol content in per cent V/V using the
following expression :
A1 ´ I 2
2.9.11. TEST FOR METHANOL AND A 2 ´ I1 ´ 40
2-PROPANOL
A1 = area of the peak due to methanol in the
METHOD A chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
A2 = area of the peak due to methanol in the
Head-space gas chromatography (2.2.28).
chromatogram obtained with reference
Internal standard solution. Dilute 1.0 mL of propanol R1 solution (c) ;
to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to I1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the
20.0 mL with water R. chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
Test solution. Mix 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution I2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard
and 4.0 mL of the preparation to be examined and dilute to in the chromatogram obtained with reference
20.0 mL with water R. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution into solution (c).
an injection vial.
Reference solution (a). Mix 1.0 mL of methanol R2 and 1.0 mL Calculate the 2-propanol content in per cent V/V using the
of 2-propanol R2 and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute following expression :
1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with water R.
A3 ´ I 2
Reference solution (b). Dilute 5.0 mL of anhydrous ethanol R
to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 25.0 mL of the solution A 4 ´ I1 ´ 40
to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to
20.0 mL with water R. A3 = area of the peak due to 2-propanol in the
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
Reference solution (c). Mix 1.0 mL of the internal standard A4 = area of the peak due to 2-propanol in the
solution, 2.0 mL of reference solution (a) and 2.0 mL of
chromatogram obtained with reference
reference solution (b) and dilute to 20.0 mL with water R.
solution (c) ;
Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution into an injection vial.
I1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the
Close the vials immediately with a tight rubber membrane chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
stopper coated with polytetrafluoroethylene and secure with an
aluminium crimp cap. I 2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard
in the chromatogram obtained with reference
Column : solution (c).
– material : fused silica ;
METHOD B
– size : l = 30 m, Ø = 0.53 mm ; Gas chromatography (2.2.28).
– stationary phase : cyanopropyl(3)phenyl(3)methyl(94)polysi- Internal standard solution. Dilute 1.0 mL of propanol R1 to
loxane R (film thickness 3 μm). 100.0 mL with water R.
Carrier gas : helium for chromatography R. Test solution. Mix 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution
and 4.0 mL of the preparation to be examined and dilute to
Flow rate : 3 mL/min. 20.0 mL with water R.
Split ratio : 1:50. Reference solution (a). Mix 1.0 mL of methanol R2 and 1.0 mL
Static head-space conditions that may be used : of 2-propanol R2 and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute
1.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with water R.
– equilibration temperature : 85 °C ; Reference solution (b). Dilute 1.0 mL of anhydrous ethanol R
– equilibration time : 20 min. to 50.0 mL with water R.
342 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 10.0 2.9.14. Specific surface area by air permeability
Reference solution (c). Mix 1.0 mL of the internal standard A3 = area of the peak due to 2-propanol in the
solution, 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) and 2.0 mL of chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
reference solution (a) and dilute to 20.0 mL with water R. A4 = area of the peak due to 2-propanol in the
Column : chromatogram obtained with reference
solution (c) ;
– material : fused silica ; I1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
– size : l = 30 m, Ø = 0.53 mm ;
I2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard
– stationary phase : cyanopropyl(3)phenyl(3)methyl(94)polysi- in the chromatogram obtained with reference
loxane R (film thickness 3 μm). solution (c).
Carrier gas : helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate : 3 mL/min.
Split ratio : 1:50. 01/2008:20912
Temperature :
Time Temperature
(min) (°C)
Column 0 - 1.6 40 2.9.12. SIEVE TEST
1.6 - 9.9 40 → 65 The degree of fineness of a powder may be expressed by
9.9 - 13.6 65 → 175 reference to sieves that comply with the specifications for
non-analytical sieves (2.1.4).
13.6 - 20 175
Where the degree of fineness of powders is determined by
Injection port 200 sieving, it is defined in relation to the sieve number(s) used
Detector 200
either by means of the following terms or, where such terms
cannot be used, by expressing the fineness of the powder as a
percentage m/m passing the sieve(s) used.
Detection : flame ionisation. The following terms are used in the description of powders :
Injection : 1.0 μL of the test solution and reference solution (c), Coarse powder. Not less than 95 per cent by mass passes
at least 3 times. through a number 1400 sieve and not more than 40 per cent
by mass passes through a number 355 sieve.
Elution order : methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, 1-propanol.
Moderately fine powder. Not less than 95 per cent by mass
Relative retention with reference to ethanol (retention passes through a number 355 sieve and not more than 40 per
time = about 5.3 min): methanol = about 0.8 ; cent by mass passes through a number 180 sieve.
2-propanol = about 1.2 ; 1-propanol = about 1.6. Fine powder. Not less than 95 per cent by mass passes
through a number 180 sieve and not more than 40 per cent by
System suitability : reference solution (c) : mass passes through a number 125 sieve.
– resolution : minimum 5 between the peaks due to methanol Very fine powder. Not less than 95 per cent by mass passes
and ethanol. through a number 125 sieve and not more than 40 per cent by
mass passes through a number 90 sieve.
Calculate the methanol content in per cent V/V using the If a single sieve number is given, not less than 97 per cent of
following expression : the powder passes through the sieve of that number, unless
otherwise prescribed.
A1 ´ I 2 Assemble the sieves and operate in a suitable manner until
A 2 ´ I1 ´ 40 sifting is practically complete. Weigh the separated fractions
of the powder.
A1 = area of the peak due to methanol in the
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
A2 = area of the peak due to methanol in the
chromatogram obtained with reference 04/2017:20914
solution (c) ;
I1 = area of the peak due to the internal standard in the
chromatogram obtained with the test solution ;
I2 = area of the peak due to the internal standard
in the chromatogram obtained with reference 2.9.14. SPECIFIC SURFACE AREA BY
solution (c). AIR PERMEABILITY
The test is intended for the determination of the specific
Calculate the 2-propanol content in per cent V/V using the surface area of dry powders expressed in square metres per
following expression : gram in the sub-sieve region. The effect of molecular flow
(“slip flow”) which may be important when testing powders
consisting of particles less than a few micrometres is not taken
A3 ´ I 2 into account in the equation used to calculate the specific
A4 ´ I1 ´ 40 surface area.
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 343
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Etonaol Test Metodu EP Monogarfı 20424EDocument5 pagesEtonaol Test Metodu EP Monogarfı 20424EVeysel KocabeyNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2,4 Dichlorobenzyl AlcoholDocument2 pages2,4 Dichlorobenzyl AlcoholsamanehNo ratings yet
- 2.4.24. Identification and Control of Residual SolventsDocument5 pages2.4.24. Identification and Control of Residual SolventswilNo ratings yet
- Triamcinolone Acetonide EuropeaDocument2 pagesTriamcinolone Acetonide EuropeaMarcela Gomez100% (1)
- Prednisone: PrednisonumDocument3 pagesPrednisone: PrednisonumMarcosNo ratings yet
- Ambroxol Hydrochloride: Ambroxoli HydrochloridumDocument2 pagesAmbroxol Hydrochloride: Ambroxoli HydrochloridumANDERSON MNo ratings yet
- Nimodipine IV BPDocument2 pagesNimodipine IV BPsiroratssNo ratings yet
- DexpanthenolDocument2 pagesDexpanthenolArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Isoprenaline HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesIsoprenaline HydrochloridesofianesedkaouiNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument3 pagesMetoprololIli MarinaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol 96 Per Cent 1317eDocument3 pagesEthanol 96 Per Cent 1317edrs_mdu48No ratings yet
- PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesPROPOFOLArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Amisulpride EP 11.0Document2 pagesAmisulpride EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- CefaclorDocument3 pagesCefaclorLinh PhiNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl Citrate Impurities ChromatogramDocument2 pagesFentanyl Citrate Impurities ChromatogramMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Determining Percent Composition of NaCl and NaOH MixtureDocument50 pagesDetermining Percent Composition of NaCl and NaOH MixtureHarshit RajNo ratings yet
- PSMA-1007 (F) InjectionDocument3 pagesPSMA-1007 (F) InjectionCha Usacdin100% (1)
- Ethanol, AnhydrousDocument2 pagesEthanol, AnhydrousMiroslav IlicNo ratings yet
- Pyrantel Embonate: Pyranteli EmbonasDocument2 pagesPyrantel Embonate: Pyranteli EmbonasMiruna CarmenNo ratings yet
- Felodipine: FelodipinumDocument2 pagesFelodipine: FelodipinumIoana-Alexandra Lungu-NastaseNo ratings yet
- Zanamivir HydrateDocument2 pagesZanamivir HydrateTiago Luiz TortellaNo ratings yet
- European Pharm. IbuprofenDocument3 pagesEuropean Pharm. IbuprofenMeuthia Sharah AyuninNo ratings yet
- Ethanol (96 Per Cent) (1317)Document2 pagesEthanol (96 Per Cent) (1317)Mulayam Singh Yadav100% (1)
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride BPDocument4 pagesPhenylephrine Hydrochloride BPJai MurugeshNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen (Pharmacopoea)Document3 pagesIbuprofen (Pharmacopoea)Titis Adisti HapsariNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Oxide and Dioxan EP PDFDocument1 pageEthylene Oxide and Dioxan EP PDFWilsonNo ratings yet
- Ep7.0 02 1504Document2 pagesEp7.0 02 1504Sidahmed SiDo BouchenakNo ratings yet
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleateMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- NitrazepamDocument2 pagesNitrazepamĐoàn DươngNo ratings yet
- Belladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedDocument2 pagesBelladonna Leaf Tincture, StandardisedJjangyiNo ratings yet
- 0632EDocument2 pages0632EAat Prayoga MuhtarNo ratings yet
- Sulpiride European Pharmacopoeia 8.0Document3 pagesSulpiride European Pharmacopoeia 8.0Mohamed DahmaneNo ratings yet
- Enrofloxacin For Veterinary UseDocument3 pagesEnrofloxacin For Veterinary Usenguyentuanson167No ratings yet
- Dissolution Testing of Solid Oral Dosage FormsDocument33 pagesDissolution Testing of Solid Oral Dosage Formscarolalbert2100% (1)
- Limit TestDocument248 pagesLimit TestSyifa FauziahNo ratings yet
- CHLORTALIDONEDocument2 pagesCHLORTALIDONEartemNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Alcohol FEUMDocument2 pagesAlcohol FEUMSajimars SajimarNo ratings yet
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0, Vol. 2 - Европейская Фармакопея 8.0, Том 2 (PDFDrive)Document2,133 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia 8.0, Vol. 2 - Европейская Фармакопея 8.0, Том 2 (PDFDrive)YuNo ratings yet
- Clobazam EP 11.0Document2 pagesClobazam EP 11.0Alejandro RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Benzalkonii Chloridum: Benzalkonium ChlorideDocument2 pagesBenzalkonii Chloridum: Benzalkonium ChlorideMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Monografìa USP BenzocaínaDocument3 pagesMonografìa USP BenzocaínaLizettAndresNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPGuadalupe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Water For InjectionsDocument4 pagesWater For InjectionsAlvina Arum PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- 2465e-Irbesartan E.PDocument2 pages2465e-Irbesartan E.PRyk BelNo ratings yet
- Ep 8.0Document2 pagesEp 8.0Duyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- CH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALDocument11 pagesCH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALLora Bell100% (1)
- Nimodipine BP2Document2 pagesNimodipine BP2siroratssNo ratings yet
- Fluocinolone Acetonide: If IfDocument2 pagesFluocinolone Acetonide: If IfTrung TínNo ratings yet
- Fosfomycin trometamol analysisDocument2 pagesFosfomycin trometamol analysisrajtushasthaNo ratings yet
- PH - Eur. Acid UrsodeoxycolicDocument2 pagesPH - Eur. Acid UrsodeoxycolicGrigoras InaNo ratings yet
- IsomaltDocument3 pagesIsomaltsofianesedkaouiNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Sodium PhosphateDocument4 pagesDexamethasone Sodium PhosphateMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Fenofibrate EP 11.0Document2 pagesFenofibrate EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- DiacereinDocument3 pagesDiacereinMulayam Singh Yadav0% (2)
- Dexamethason ENGLDocument3 pagesDexamethason ENGLKim ThắmNo ratings yet
- Heparin Sodium: Heparinum NatricumDocument3 pagesHeparin Sodium: Heparinum NatricumartemNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument2 pagesNitric AcidAlexi Del Castillo MustaineNo ratings yet
- Artikel Ilmiah Priyanto 1Document7 pagesArtikel Ilmiah Priyanto 1yudhit bessieNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer Chromatography: Chemistry Lap ReportDocument15 pagesThin Layer Chromatography: Chemistry Lap ReportazoozalbelushNo ratings yet
- Diffractometric Debye-Scherrer Patterns of Powder SamplesDocument9 pagesDiffractometric Debye-Scherrer Patterns of Powder SamplesJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Proanthocyanidins From Grape SeedsDocument14 pagesCharacterization of Proanthocyanidins From Grape SeedsKimberly GutièrrezNo ratings yet
- Screening Concepts Characterization and Structural Analysis of Microbial-Derived Bioactive Lipopeptides A ReviewDocument19 pagesScreening Concepts Characterization and Structural Analysis of Microbial-Derived Bioactive Lipopeptides A ReviewJyothi RajeevNo ratings yet
- High Strength Abrasion Resistant Steel PlatesDocument5 pagesHigh Strength Abrasion Resistant Steel PlatesCao Mạnh CườngNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Sample Collection, Preservation and Storage: 3.1.1 Collecting Water SamplesDocument16 pages3.1 Sample Collection, Preservation and Storage: 3.1.1 Collecting Water Sampleshandoyo_eko20017573No ratings yet
- Syllabus Agri 2015Document248 pagesSyllabus Agri 2015parvathivignesh279No ratings yet
- Bulletin - 1760 - PROTEAN II Xi and XL CellsDocument2 pagesBulletin - 1760 - PROTEAN II Xi and XL CellsdnajenNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment-7,8Document4 pagesWater and Its Treatment-7,8Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titrations 2Document27 pagesAcid-Base Titrations 2John Henrick G. Uy100% (2)
- Question: The Following Primary Standards Can Be Used For The StandardiDocument5 pagesQuestion: The Following Primary Standards Can Be Used For The StandardiMustafa KhudhairNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ManualDocument69 pagesChemistry Lab ManualSushmaNo ratings yet
- !!!! Photoconjugation of An Fc-Specific PeptideDocument30 pages!!!! Photoconjugation of An Fc-Specific PeptideJan PolachNo ratings yet
- Heavy Metal Soil AnalysisDocument10 pagesHeavy Metal Soil AnalysisSolehah OmarNo ratings yet
- TLC, Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument23 pagesTLC, Thin Layer ChromatographyShaise Jacob80% (5)
- Partition Coefficient EditedDocument17 pagesPartition Coefficient EditedcoltalbNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of Reducing Sugars in Sugar Preparations Consisting of Sugar and DextrinDocument6 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Reducing Sugars in Sugar Preparations Consisting of Sugar and DextrinMuztika Andriana RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1.1Document5 pagesExperiment 1.1Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Membrane Technologies For Industrial Wastewaters TreatmentDocument40 pagesChapter 2. Membrane Technologies For Industrial Wastewaters TreatmentSophie LvNo ratings yet
- Figure M 39 Ethanol Water MixtureDocument10 pagesFigure M 39 Ethanol Water MixturediegoNo ratings yet
- Lec - 21 - Electron SpectrosDocument12 pagesLec - 21 - Electron SpectrosZahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- Natrium DiklofenakDocument3 pagesNatrium DiklofenakDestiKarmilasariNo ratings yet
- Enviromental Sampling For Trace AnalyticalDocument6 pagesEnviromental Sampling For Trace AnalyticalVanessa Millar0% (1)
- Experiment CHM 138 - 5Document3 pagesExperiment CHM 138 - 5Sara MaisaraNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Metal IonsDocument19 pagesQualitative Analysis of Metal IonsLaila ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- 11 4-7Document3 pages11 4-7Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vi Precipitation Titration: B.Kiruthiga Lecturer Dept of Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument17 pagesUnit-Vi Precipitation Titration: B.Kiruthiga Lecturer Dept of Pharmaceutical ChemistryAwais NaeemNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis - Oxalic AcidDocument3 pagesQuantitative Analysis - Oxalic AcidDev voraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument27 pagesChemical Equilibrium: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenKrish MundadaNo ratings yet