Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantum Information Science
Quantum Information Science
Uploaded by
john saher0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageQuantum information science combines quantum mechanics principles with information science to study information processing, transmission and analysis. It includes both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics. Scientific and engineering studies in quantum teleportation, entanglement and quantum computers depend on understanding quantum physics and engineering. Google and IBM have significantly advanced quantum computer hardware since 2010, though error rates remain high. Programming languages for quantum computers are still being developed along with resources to train more quantum programmers. Related fields in mathematics include quantum algorithms and complexity theory, with Peter Shor's 1994 quantum prime factorization algorithm posing a potential security threat if scaled to thousands of qubits.
Original Description:
Original Title
Quantum information science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentQuantum information science combines quantum mechanics principles with information science to study information processing, transmission and analysis. It includes both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics. Scientific and engineering studies in quantum teleportation, entanglement and quantum computers depend on understanding quantum physics and engineering. Google and IBM have significantly advanced quantum computer hardware since 2010, though error rates remain high. Programming languages for quantum computers are still being developed along with resources to train more quantum programmers. Related fields in mathematics include quantum algorithms and complexity theory, with Peter Shor's 1994 quantum prime factorization algorithm posing a potential security threat if scaled to thousands of qubits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageQuantum Information Science
Quantum Information Science
Uploaded by
john saherQuantum information science combines quantum mechanics principles with information science to study information processing, transmission and analysis. It includes both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics. Scientific and engineering studies in quantum teleportation, entanglement and quantum computers depend on understanding quantum physics and engineering. Google and IBM have significantly advanced quantum computer hardware since 2010, though error rates remain high. Programming languages for quantum computers are still being developed along with resources to train more quantum programmers. Related fields in mathematics include quantum algorithms and complexity theory, with Peter Shor's 1994 quantum prime factorization algorithm posing a potential security threat if scaled to thousands of qubits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Quantum information science
Quantum information science is a field that combines the principles of quantum
mechanics with information science to study the processing, analysis, and transmission
of information. It covers both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics,
including the limits of what can be achieved with quantum information. The
term quantum information theory is sometimes used, but it does not include
experimental research and can be confused with a subfield of quantum information
science that deals with the processing of quantum information.
Scientific and engineering studies
Quantum teleportation, entanglement and the manufacturing of quantum
computers depend on a comprehensive understanding of quantum physics and
engineering. Google and IBM have invested significantly in quantum computer
hardware research, leading to significant progress in manufacturing quantum computers
since the 2010s. Currently, it is possible to create a quantum computer with over
100 qubits, but the error rate is high due to the lack of suitable materials for quantum
computer manufacturing. Majorana fermions may be a crucial missing material.
Quantum cryptography devices are now available for commercial use. The one time
pad, a cipher used by spies during the Cold War, uses a sequence of random keys for
encryption. These keys can be securely exchanged using quantum entangled particle
pairs, as the principles of the no-cloning theorem and wave function collapse ensure the
secure exchange of the random keys. The development of devices that can transmit
quantum entangled particles is a significant scientific and engineering goal
Qiskit, Cirq and Q Sharp are popular quantum programming languages.
Additional programming languages for quantum computers are needed, as well as a
larger community of competent quantum programmers. To this end, additional learning
resources are needed, since there are many fundamental differences in quantum
programming which limits the amount of skills that can be carried over from traditional
programming.
Related mathematical subjects
Quantum algorithm and quantum complexity theory are two of the subjects
in algorithms and computational complexity theory. In 1994, mathematician Peter
Shor introduced a quantum algorithm for prime factorization that, with a quantum
computer containing 4,000 logical qubits, could potentially break widely used ciphers
like RSA and ECC, posing a major security threat. This led to increased investment
in quantum computing research and the development of post-quantum cryptography to
prepare for the quantum computing era.
You might also like
- Quantum Computing A Shift From Bits To Qubits 1nbsped 981199529x 9789811995293Document487 pagesQuantum Computing A Shift From Bits To Qubits 1nbsped 981199529x 9789811995293NabilMabroukNo ratings yet
- Switchboard & PanelboardDocument8 pagesSwitchboard & PanelboardWalidNo ratings yet
- Drill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderDocument14 pagesDrill Grinding With The PP-U3 Grinder Copy of The Deckel SO GrinderAndy L100% (1)
- Astrophotography For Westbridge PresentationDocument95 pagesAstrophotography For Westbridge PresentationVadim KunickiyNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Document21 pagesSeminar Report On ATM With An Eye 2011-12Vinod Kumar100% (1)
- QCbrochureDocument2 pagesQCbrochureMeditatia Transcendentala Romania100% (1)
- Shell MESC SPE 76-100-2013Document7 pagesShell MESC SPE 76-100-2013Sherif Abdel Hamid Fakhry0% (1)
- DSP Module 5 NotesDocument17 pagesDSP Module 5 NotesKesava Pedda100% (5)
- Amity School of Engineering: Report Heading: Quantum ComputingDocument38 pagesAmity School of Engineering: Report Heading: Quantum ComputinghimanshuNo ratings yet
- Quantum Information Processing and Quantum Error Correction: An Engineering ApproachFrom EverandQuantum Information Processing and Quantum Error Correction: An Engineering ApproachNo ratings yet
- Eintroduction To Quantum ComputingDocument11 pagesEintroduction To Quantum ComputingAbraizNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography - A Secure Path To Future CommunicationDocument7 pagesQuantum Cryptography - A Secure Path To Future Communicationharunkleoglu1No ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography Thesis 2013Document9 pagesQuantum Cryptography Thesis 2013aaqvuknbf100% (2)
- Quantum ComputingDocument5 pagesQuantum Computingkentjohnson158No ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography ThesisDocument7 pagesQuantum Cryptography ThesisDoMyCollegePaperJackson100% (2)
- Quantum Secure CommunicationDocument2 pagesQuantum Secure CommunicationJane LoNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Quantum CryptographyDocument6 pagesThesis On Quantum Cryptographyxcwjkvvff100% (2)
- Quantum Technology - QNu LabsDocument7 pagesQuantum Technology - QNu LabsAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- The Enigmatic World of Quantum Computing Revolutionizing TechnologyDocument4 pagesThe Enigmatic World of Quantum Computing Revolutionizing TechnologysybencoolNo ratings yet
- Title 5Document1 pageTitle 5bradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing Research Trends Report - ElsevierDocument13 pagesQuantum Computing Research Trends Report - Elseviersrishtityagi2020No ratings yet
- Understanding Quantum ComputingDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Quantum ComputingDivya KaushikNo ratings yet
- Here Is An Essay On Quantum CoDocument2 pagesHere Is An Essay On Quantum CoemmanuelkakayayaNo ratings yet
- Quantum ComputersDocument1 pageQuantum ComputersSPARKS F.SNo ratings yet
- AsdfvvDocument1 pageAsdfvvbradhakemanNo ratings yet
- AstDocument1 pageAstbradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Quantum Key Distribution Algorithm in Real Time IBM Quantum ComputersDocument7 pagesImplementation of Quantum Key Distribution Algorithm in Real Time IBM Quantum ComputersIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Title 2Document1 pageTitle 2bradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Creating A Functional Quantum CompuDocument1 pageCreating A Functional Quantum CompuSadeed SulemanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing: Quantum Key DistributionDocument4 pagesQuantum Computing: Quantum Key DistributionInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Artical QuntaumDocument3 pagesArtical Quntaumproject quantumNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Quantum Computing - Challenges, Opportunities, and Future ProspectsDocument2 pagesAdvancements in Quantum Computing - Challenges, Opportunities, and Future ProspectsfunukufuNo ratings yet
- Advent of New Technologies and Weapon Systems and It'S Effects in Strategic StabilityDocument4 pagesAdvent of New Technologies and Weapon Systems and It'S Effects in Strategic StabilityShan RanaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing Unit-1Document36 pagesQuantum Computing Unit-1sgovinduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Science 1Document1 pageIntroduction To Computer Science 1Muntean Filip MihaiNo ratings yet
- Title - The Powe-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageTitle - The Powe-WPS OfficesafwanNo ratings yet
- 07-08-2020 Techdispatch Quantum Computing en 0Document3 pages07-08-2020 Techdispatch Quantum Computing en 0MAKE THE MEGA KNIGHT GREAT AGAIN SUPERCELL PLSNo ratings yet
- AsdfewrwqerDocument1 pageAsdfewrwqerbradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Post-Quantum and Code-Based Cryptography-Some Prospective Research DirectionsDocument31 pagesPost-Quantum and Code-Based Cryptography-Some Prospective Research Directionsmohammed.it.11rNo ratings yet
- ID135Document11 pagesID135Sulbha GathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Science 1Document1 pageIntroduction To Computer Science 1Muntean Filip MihaiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing: Vision and ChallengesDocument16 pagesQuantum Computing: Vision and Challengesmevlana3992No ratings yet
- Quantum ComputersDocument21 pagesQuantum Computersshweta_bharti_7No ratings yet
- Quantum Computing: A Cheat Sheet: Live Event: Datastax Accelerate: The World'S Premier Apache Cassandra ConferenceDocument8 pagesQuantum Computing: A Cheat Sheet: Live Event: Datastax Accelerate: The World'S Premier Apache Cassandra Conferencemrme44No ratings yet
- Quantum Internet: Networking Challenges in Distributed Quantum ComputingDocument9 pagesQuantum Internet: Networking Challenges in Distributed Quantum ComputinghdjskhdkjsNo ratings yet
- The Fascinating World of Quantum Computing ?Document1 pageThe Fascinating World of Quantum Computing ?aNo ratings yet
- Title 4Document1 pageTitle 4bradhakemanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computers: A Seminar Presentation OnDocument19 pagesQuantum Computers: A Seminar Presentation Onjaya100% (1)
- Thesis Quantum CryptographyDocument5 pagesThesis Quantum CryptographyYasmine Anino100% (1)
- Quantum Cryptography Thesis PDFDocument7 pagesQuantum Cryptography Thesis PDFlorischadedesmoines100% (2)
- Explainable Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesExplainable Artificial IntelligencejougobbiNo ratings yet
- QuantumDocument12 pagesQuantumSandeepNo ratings yet
- The Future of Quantum ComputerDocument6 pagesThe Future of Quantum ComputerVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography Research Paper PDFDocument4 pagesQuantum Cryptography Research Paper PDFhbkgbsund100% (1)
- Quantum Computing Applications in Cryptography: A Comprehensive AnalysisDocument2 pagesQuantum Computing Applications in Cryptography: A Comprehensive Analysiskapitanjuan27No ratings yet
- An Overview of Major Developments, Applications and Challenges in Quantum CryptographyDocument9 pagesAn Overview of Major Developments, Applications and Challenges in Quantum CryptographyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cloud Computing Integration: Unleashing The Power of Quantum Algorithms in The CloudDocument4 pagesQuantum Cloud Computing Integration: Unleashing The Power of Quantum Algorithms in The CloudInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The World of Quantum Computers PresentationDocument14 pagesThe World of Quantum Computers Presentationalihassankhan2277No ratings yet
- Quantum Communication: Department of Telecommunication Science University of IlorinDocument3 pagesQuantum Communication: Department of Telecommunication Science University of IlorinAjao GafarNo ratings yet
- Quantum ComputingDocument2 pagesQuantum Computingvoidmagic200No ratings yet
- Quantum ComputingDocument2 pagesQuantum ComputingArnold LngatNo ratings yet
- Quantum Random Number Generator ThesisDocument5 pagesQuantum Random Number Generator Thesistygocixff100% (2)
- Assignment - 1: Submitted By: AKASH (101703634)Document11 pagesAssignment - 1: Submitted By: AKASH (101703634)Akash DidhariaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computing and Cryptography Today PDFDocument22 pagesQuantum Computing and Cryptography Today PDFBill LasosNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument12 pagesSeminarpaswanaditya010No ratings yet
- Corporate PresentationDocument102 pagesCorporate Presentationgaurav pnrNo ratings yet
- Pile Installation Recorder (PIR) : Cost Effective. Real Time. AccurateDocument2 pagesPile Installation Recorder (PIR) : Cost Effective. Real Time. AccurateNhoek RenNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Emoji's: Emotional Insights of Facebook UsersDocument59 pages21 Century Emoji's: Emotional Insights of Facebook UsersLaurence OrtegaNo ratings yet
- OHRI Learning PathDocument2 pagesOHRI Learning PathbsrpropNo ratings yet
- Sample-Great-Depression-Worksheets-1 - Wall Street Crash of 1929 - Great Depression - Free 30-Day TRDocument18 pagesSample-Great-Depression-Worksheets-1 - Wall Street Crash of 1929 - Great Depression - Free 30-Day TRSuzanne MaffeiNo ratings yet
- Exam-5-5, MCQ, Forms11g, L-10 To 12Document2 pagesExam-5-5, MCQ, Forms11g, L-10 To 12ddd 49it1No ratings yet
- J7-c USB Tester English Manual (SZB)Document1 pageJ7-c USB Tester English Manual (SZB)GT S5360No ratings yet
- Am024nn1dch AzDocument1 pageAm024nn1dch AzHelen Cardenas HonoresNo ratings yet
- PGDM OM 3.1 Logistics ManagementDocument1 pagePGDM OM 3.1 Logistics ManagementAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- Abe21 14 2002 11 06Document2 pagesAbe21 14 2002 11 06haggNo ratings yet
- EEC201L Circuits 2 (Lab) : ExerciseDocument8 pagesEEC201L Circuits 2 (Lab) : ExerciseNicoNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Fatty OilDocument13 pagesCatalytic Hydrogenation of Fatty OilAina Afiqah RoslanNo ratings yet
- 73-Article Text-136-1-10-20200623Document10 pages73-Article Text-136-1-10-20200623Vero AndopaNo ratings yet
- Creating Flexible Mappings Between Building Information Models and Cost InformationDocument12 pagesCreating Flexible Mappings Between Building Information Models and Cost InformationCPittmanNo ratings yet
- DIff BW Abstraction and EncapsulationDocument1 pageDIff BW Abstraction and EncapsulationIndrasena ReddyNo ratings yet
- Trudy Elizabeth Taul Harris Honored As A Woman of The Month For July 2021 by P.O.W.E.R. - Professional Organization of Women of Excellence RecognizedDocument3 pagesTrudy Elizabeth Taul Harris Honored As A Woman of The Month For July 2021 by P.O.W.E.R. - Professional Organization of Women of Excellence RecognizedPR.comNo ratings yet
- Capturing VLAN TagsDocument82 pagesCapturing VLAN TagsIndrajit RoyNo ratings yet
- Dura Blok PDFDocument14 pagesDura Blok PDFclaudia karina monteverde zazuetaNo ratings yet
- 6.4.7 Factors Affecting Distillation Column Operation 1. Vapor Flow ConditionsDocument13 pages6.4.7 Factors Affecting Distillation Column Operation 1. Vapor Flow ConditionsAnita PanthiNo ratings yet
- Possible Failure Point Emerges in Miami-Area Building Collapse - The New York TimesDocument5 pagesPossible Failure Point Emerges in Miami-Area Building Collapse - The New York TimesMrMasterNo ratings yet
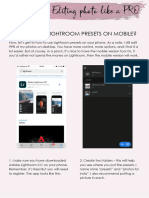
- Instruction To Install Lightroom Mobile PresetsDocument4 pagesInstruction To Install Lightroom Mobile PresetsInes HlupićNo ratings yet
- Make SRS For Visitors Management System?: Ques.1Document5 pagesMake SRS For Visitors Management System?: Ques.1Manish Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- 21st Cent3rd SUMMATIVEDocument6 pages21st Cent3rd SUMMATIVEMaricar Francisco-ValenciaNo ratings yet
- VAY Packaged Unit Operation Manual (06.09.18)Document21 pagesVAY Packaged Unit Operation Manual (06.09.18)Nebojsa MijovicNo ratings yet