Professional Documents
Culture Documents
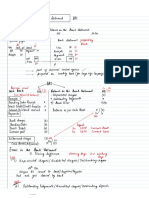
Corrective, Detective, Preventative Controls
Corrective, Detective, Preventative Controls
Uploaded by
Abdul Ahad YousafOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Corrective, Detective, Preventative Controls
Corrective, Detective, Preventative Controls
Uploaded by
Abdul Ahad YousafCopyright:
Available Formats
Corrective Controls:
Corrective controls are implemented in response to a security incident or a vulnerability that has been
identified. Their purpose is to minimize the damage caused by the incident, restore systems and services
to their normal state,
Examples of corrective controls include:
Incident response plans and procedures
Data backup and recovery systems
Management process to address vulnerabilities
System restoration processes
Detective Controls:
Detective controls are designed to identify and detect incidents, breaches, or unauthorized activities that
have already occurred. Their primary function is to monitor systems.
Preventive Controls: Preventive controls are proactive measures taken to minimize the likelihood of
security incidents, breaches, or unauthorized activities from occurring. These controls aim to prevent
threats and vulnerabilities from being exploited and reduce the overall risk exposure.
Example
firewalls, security awareness training, vulnerability management, and security policies and procedures.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Cost Classification Teachers-2Document16 pagesCost Classification Teachers-2Abdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- Ordinary DividendDocument1 pageOrdinary DividendAbdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument27 pagesInformation TechnologyAbdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Financial Technology (Fintech)Document31 pagesThe Impact of Financial Technology (Fintech)Abdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Statement-1Document5 pagesBank Reconciliation Statement-1Abdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation StatementDocument4 pagesBank Reconciliation StatementAbdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Statement-2 MCQSFFDDocument11 pagesBank Reconciliation Statement-2 MCQSFFDAbdul Ahad YousafNo ratings yet