Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Approach To Arrhythmias
Approach To Arrhythmias
Uploaded by
yosefsugiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Approach To Arrhythmias
Approach To Arrhythmias
Uploaded by
yosefsugiCopyright:
Available Formats
Yan Yu, 2012 (www.yanyu.
ca)
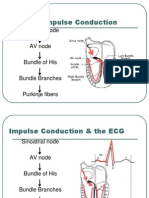
Diagnostic Approach to Arrhythmias
(abnormal cardiac rate and rhythm on ECG or Cardiac Monitor)
Is QRS normal or wide? Are P-waves present?
P-waves: present? Shape? Rate? Relationship btw P-waves
Relationship btw P-waves + QRS? and QRS?
Response to vagal maneuvers? Tachy-arrhythmias (>100bpm) Brady-arrhythmias (<60 bpm)
Regular Rhythm Irregular Rhythm
Wide QRS on ECG (>120ms) Narrow QRS on ECG (<120ms)
(slow ventricular depolarization) (fast ventricular depolarization) A/V
Normal Sinus
Rhythm dissociation
Sinus Bradycardia 3rd deg AV Missed QRS Sinus pauses,
Ventricular Tachy (VT) SVT with conduction (can be normal) block after P-waves chonotropic
Hx of MI (esp Anterior STEMIs): re- delay (“abherrancy”) Supra-ventricular 2nd deg AV incompetence
entrant circuit around ventricular scar (responds to/stops with Tachy (SVT) No P-waves PR interval > block Sick Sinus
Hx of other structural heart diseases: vagal maneuvers; Escape rhythms due 200ms Syndrome
Sudden-onset, constant
HF, ventricular hypertrophy, valve QRS morphology constant to SA block/arrest 1st deg AV Tachy-Brady
palpitations
disease, congenital abnormality regardless of heart rate) ECG: P-waves abnormal (Junctional, Idio- block syndrome (w/ A-
Hx of Long-QT syndromes (genetic, SVT w/ BBB Ventricular) fib/A-flutter)
potassium imbalance, etc) R/o A-fib if irregular Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
ECG: P-waves unrelated to QRS Antidromic AVRT No distinct P-waves, chaotic baseline (not isoelectric)
complexes, V1-V6 concordance of QRS (ventricular contractions via Caused by ectopic foci near pulmonary veins
complexes (all deflecting + or – ) accessory path only)
Sustained VT = dangerous! Could lead (Tx Wide-complex tachy Multifical Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
Regular Rhythm Irregular 3+ P-wave shapes; isoelectric baseline btw P-waves
to 0 cardiac output as VT until proven
otherwise) (constant P-P interval) Rhythm Caused by severe pulmonary disease/hypoxemia
Atrial Flutter w/ variable block
Monomorphic VT Polymorphic VT
Multiple ectopic foci
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Atrial rate P-wave morphology Carotid Sinus Massage
Lone re-entry circuit
or changing re-entry Triggered by V-tach in a pt w/ (bpm) response (↑ vagal tone)
around single scar
ECG: Capture + circuits Serious underlying heart dx
fusion beats, AV
Long QT predisposes 0 cardiac output, fatal! Sinus Tachy 100-180 Can be normal Atrial rate may ↓
R-on-T events (i.e.
dissociation Tx: immediate defibrillation!
torsades de pointes)
Anti-arrhythmics (prevent Re-entrant SVTs 140-250 Hidden in QRS, or May abruptly stop
(AVRT, AVNRT) (paroxysmal) retrograde
recurrence); ICD (Long-term; only
Treatment of VT: tx that ↓ mortality) Focal Atrial 130-250 Different shape, due to Doesn’t usually stop tachy
If unstable: electric cardioversion Tachycardia (paroxysmal) ectopic pacemaker AV block may ↑
If stable: anti-arrhythmic drugs
LT: implanted cardiac defibrillator Atrial Flutter 180-350 “saw-toothed” AV block may ↑
You might also like
- ECG Interpretations DR RPDocument109 pagesECG Interpretations DR RPArnis Putri RosyaniNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret An ECG in Seven StepsDocument5 pagesHow To Interpret An ECG in Seven StepsCM Najito100% (1)
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrhythmiassmurf096No ratings yet
- Rhythm Description Schematic Diagram Egc Characteristics Sample TraceDocument6 pagesRhythm Description Schematic Diagram Egc Characteristics Sample TraceJhenne Kyle Ko Dee100% (1)
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG GuidekaelenNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial NodeDocument80 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Nodesiusiuwidyanto100% (2)
- ArrhyDocument26 pagesArrhyMouriyan AmanNo ratings yet
- Rhythm Interpretation and Its ManagementDocument6 pagesRhythm Interpretation and Its Managementjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- ECG Rythum Study Guide PDFDocument9 pagesECG Rythum Study Guide PDFArtika MayandaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Rhythms: Normal Sinus RhythmDocument10 pagesEcg Rhythms: Normal Sinus RhythmJethJayme100% (1)
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Document47 pagesPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretations GoodDocument104 pagesECG Interpretations GoodaymenNo ratings yet
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Lab Values and Vital SignsDocument4 pagesLab Values and Vital SignsWole Olaluwoye100% (1)
- ECG ReviewDocument146 pagesECG ReviewThea DinoNo ratings yet
- Ekg Full BibleDocument6 pagesEkg Full BibleTJNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine #1Document167 pagesInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaNo ratings yet
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)Document3 pagesVentricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)goobyyplssNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineDocument88 pagesAdvanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineRoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Compatible ModeDocument93 pagesChapter 1 Compatible ModeJyha KhariNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds: Mitral Regurgitation Congestive Heart FailureDocument6 pagesHeart Sounds: Mitral Regurgitation Congestive Heart FailurecindyNo ratings yet
- Ekg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurDocument59 pagesEkg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurArum MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument89 pagesAcid BaseEdouinaNo ratings yet
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocument31 pagesECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani Kayed100% (1)
- EKG - Assignment Without AnswersDocument10 pagesEKG - Assignment Without AnswersJon Millhollon100% (1)
- Sympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyDocument10 pagesSympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyHaroon JavedNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Topic List 2015Document3 pagesInternal Medicine Topic List 2015Krystal Mae LopezNo ratings yet
- NOAC ChartDocument2 pagesNOAC Chartsgod34No ratings yet
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocument1 pagePoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFMiko RamosoNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Conduction DisturbancesDocument30 pagesVentricular Conduction DisturbancesNicholas PetrovskiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSEDocument112 pagesBasic Ecg: in The Eyes of NURSESam jr TababaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDocument23 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJNo ratings yet
- TelemetryDocument3 pagesTelemetryKelly PrattNo ratings yet
- ECG NotesDocument11 pagesECG NotesСео ЮнгааNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (Ecg) : Presented By: Fahad I. HussienDocument102 pagesElectrocardiography (Ecg) : Presented By: Fahad I. HussienMustafa A. DawoodNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1Document34 pagesArrhythmias: Sing Khien Tiong Gpst1preethi preethaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Test 4Document11 pagesMedsurg Test 4Tori RolandNo ratings yet
- Sample Acls For DummiesDocument3 pagesSample Acls For DummiesTodd Cole100% (1)
- ECG Made Easy - An Abnormal LookDocument46 pagesECG Made Easy - An Abnormal LookabdallahNo ratings yet
- P Waves: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocument31 pagesP Waves: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning Program.100% (1)
- Hypertensive CrisisDocument1 pageHypertensive Crisisapi-495201002No ratings yet
- 007 - Cardiovascular Physiology) MASTER ECGDocument8 pages007 - Cardiovascular Physiology) MASTER ECGSWATHIKA L100% (1)
- Guaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsDocument2 pagesGuaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsAmberNo ratings yet
- ACLS RhythmsDocument2 pagesACLS RhythmsValerie BatesNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation: Presented by:-ROHINI RAI M SC Nursing Part I, C.O.N, N.B.M.C.HDocument69 pagesEcg Interpretation: Presented by:-ROHINI RAI M SC Nursing Part I, C.O.N, N.B.M.C.HRohini RaiNo ratings yet
- Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDocument70 pagesJoseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPcarmsNo ratings yet
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomNo ratings yet
- ECG Workout Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDocument27 pagesECG Workout Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDima HabanjarNo ratings yet
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocument8 pagesNormal Sinus RhythmRosalyn YuNo ratings yet
- Soap TemplateDocument3 pagesSoap TemplaterohitNo ratings yet
- Cs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsDocument2 pagesCs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsColeen YraolaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument9 pagesCardiac Study GuideJane DiazNo ratings yet
- IV PDFDocument63 pagesIV PDFelbagouryNo ratings yet
- Cardiac II Study GuideDocument6 pagesCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs LectureDocument67 pagesVital Signs LectureJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Phlebolymphology: Vol 28 - No. 1 - 2021 - P1-36 No. 103Document39 pagesPhlebolymphology: Vol 28 - No. 1 - 2021 - P1-36 No. 103Jing CruzNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals BookletDocument32 pagesTransport in Animals Bookletsreetyy jNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesLesson 4 - The Circulatory SystemAimee GraceNo ratings yet
- R Series Product ManualDocument186 pagesR Series Product ManualppdeepakNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy SeminarDocument17 pagesCardiomyopathy SeminarJyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- PAVSDMAPCAsDocument3 pagesPAVSDMAPCAsRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sony Hilal Wicaksono, MD Universitas Indonesia HospitalDocument14 pagesSony Hilal Wicaksono, MD Universitas Indonesia HospitalSonyHilalWicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Penyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanDocument63 pagesPenyakit-Penyakit Jantung Kongenital.: M.S.GanesanSyukri SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Principle Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome: Nahar Taufiq Bagian Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskuler FK UGM YogyakartaDocument57 pagesPrinciple Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome: Nahar Taufiq Bagian Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskuler FK UGM YogyakartaIntan Farida YasminNo ratings yet
- PT EducationDocument4 pagesPT Educationapi-248017509No ratings yet
- Holter Contec TLC9803 User Manual - EnglishDocument53 pagesHolter Contec TLC9803 User Manual - EnglishEdward MoralesNo ratings yet
- Peds Shelf NotesDocument74 pagesPeds Shelf NotesRandy BornmannNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL PHARMA QuestionsDocument13 pagesCLINICAL PHARMA QuestionsAminatNo ratings yet
- 01 STR 29 1 251Document6 pages01 STR 29 1 251RAFAEL BRITONo ratings yet
- Effects of Vasopressors On Cerebral Circulation.6Document11 pagesEffects of Vasopressors On Cerebral Circulation.6diego morenoNo ratings yet
- Reading ExercisesDocument20 pagesReading Exercisesmuhammad dzikra azidanNo ratings yet
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument25 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasesAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of HEART - 1Document175 pagesPathology of HEART - 1Abdukadir AzamNo ratings yet
- AmyloidosisDocument15 pagesAmyloidosisNicoletta OrphanouNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - Pericardial Disease PDFDocument1 pageCardiology - Pericardial Disease PDFPshtiwan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument5 pagesHypertensionCia Yee YeohNo ratings yet
- CardiacDocument10 pagesCardiacMarcus Reynolds100% (1)
- Stroke AHA GuidelinesDocument104 pagesStroke AHA GuidelinesCristina ZeamaNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument9 pagesResearch ProposalAbiola IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDocument1 page9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Circulation Blood Components Worksheet 2021Document4 pagesCirculation Blood Components Worksheet 2021api-523306558No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument108 pagesHeart FailureDeasy Rizka Rahmawati100% (1)
- Fluid Management in Neurology & Neurocritical Care: DR Nagesh JadavDocument12 pagesFluid Management in Neurology & Neurocritical Care: DR Nagesh JadavNagesh JadavNo ratings yet
- 1 Acute Inferior Wall MI With First Degree BlockDocument53 pages1 Acute Inferior Wall MI With First Degree BlockKarthik KannappanNo ratings yet