Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 4 - Endo 2
Uploaded by
Dr. RemedyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1b, Amurao, Richmond A., SGD 4 - Endo 2
Uploaded by
Dr. RemedyCopyright:
Available Formats
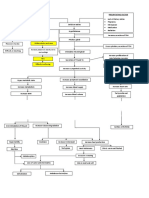
SGD - 4
ENDO II
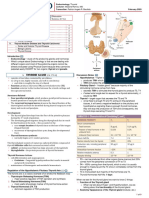
Case:
A 24 year old white female comes to her family doctor because of weight loss
despite having a good appetite; she also complains of increasing anxiety.
She admits to having frequent bouts of diarrhea, reduced sleep capacity, heat
intolerance, sweaty palms, palpitations, tremors and menstrual irregularity.
Physical examination:
Vital signs: tachycardia.
Tremors of outstretched hand; warm, moist skin; right lobe of thyroid palpably
enlarged; left lobe not palpable; no evidence of retrosternal goiter; no cervical
lymphadenopathy.
Laboratory tests:
Decreased plasma TSH; increased free T4 and T3; antihydroperoxidase antibody
absent
Imaging:
Nuc: hyperfunctioning hot thyroid nodule
Diagnosis: Plummer‟s nodule
Questions:
1. What is Plummer‟s nodule? "
Plummer 's nodule , also known as Toxic multinodular goitre
"
is a
type of
goiter where in the thyroid gland contains multiple autonomous
nodules w/o results to
functioning
hyperthyroidism due to overproduction of
thyroid hormones .
2. Differentiate the following conditions as to causes and hormonal picture:
A. Primary hyperthyroidism
Caused by overproduction of thyroid hormones Tg 'T Ty , due to an autoimmune
-
process that interferes w/ the negative feedback mechanism or
of
uncontrolled
growth hormone producing functional tissue In this disease .
Tz 'T Tt is increased while TSH and TRH are low .
B. Secondary hyperthyroidism
caused
by overstimulation of the thyroid due to either
-
increased production of TSH from the
Pituitary gland or
by an
TSH secreting tumor In this syndrome Tz Ty
.
and TSA
,
is increased while TRH is decreased ,
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
140
C. Tertiary hyperthyroidism
which
A
type of
hyperthyroidism when the
hypothalamus
-
occurs
secretes excess
thyroid releasing hormone This type
of
hyperthyroidism has Tz Ty Ts HI TRH all
.
increased in
secretion , , ,
.
3. Give the MOA of thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormones
namely Tz 'T Te stimulates diverse metabolic activities
, ,
host tissues leading to increase in basal metabolic rate A consequence
an .
of this activity is to
increase body heat production which seems to result at
least in part from increased oxygen consumption
, and rales of Atp
hydrolysis
4. Discuss the presence of the following:
A. Weight loss
-
thyroid nodules produce additional thyroxine hormones secreted by the ,
thyroid gland body to regulate functions like metabolism . Excess thyroxine causes
enhanced metabolism resulting to
weight loss .
B. Diarrhea
like in weight loss
-
thyroxine enhances the body 's metabolism therefore
,
speeding up digestion wk results to diarrhea
C. Tachycardia, palpitations
-
Tachycardia and palpitations is experienced by the patient for
thyroid hormones increase the heart rate of person And due to the patient a
having nodules that produce thyroxine thyroxine
.
, there will be an excess
D. Heat intolerance, warm and moist skin
Due to increase
body metabolism , the
body temperature rises to compensate
-
and also resulting to warm # moist skin .
5. What does a hyperfunctioning hot nodule mean? What is the effect on the
surrounding tissue and right lobe of the thyroid gland?
Hyper functioning hot nodule that the nodules
autonomously
means
produce thyroid hormone without regard for normal feedback control
mechanisms wlc
may lead to the development
, of
hyperthyroidism
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
141
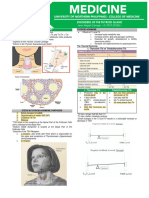
continuation of the case:
Surgery was done on the patient to remove the nodule. Immediately after
surgery, the patient developed spasm of the muscles of the face and extremities
followed by spasm of the muscles of the trunk.
Physical examination:
Positive Chvostek‟s sign
Positive Trousseau‟s sign
Laboratory exam:
Plasma calcium = 4 mg/dL
Question:
6. What happened to the patient?
-
The patient 's parathyroid gland was damaged during the.
surgery therefore PTH ,
or
parathyroid hormone levels decreases
the ,
resulting to low blood calcium level or hypercalcemia
7. How are the Chvostek‟s sign and Trousseau‟s sign elicited?
Chro stele 's
sign is the twitching of the facial muscles in
response to tapping over the area of the facial nerve .
Trousseau 's
sign is carpoped al spasm caused by inflating the blood
a
pressure cuff a level above
systolic pressure for 3 minutes .
8. Give the biologic actions of:
A. PTH Is the most endocrine
important regulator of calcium and
-
phosphorus concentration in extracellular fluid The
or PTH
increases the calcium levels in the blood
Parathyroid
. hormone
mobilization of calcium from bone
by stimulating 3 processes ,
intestine and
, enhancing absorption of calcium from the small
suppression of calcium loss in urine
B. Vitamin D
-
is a hormone involved in mineral metabolism and bone growth .
Its most
important effect is facilitate intestinal
to
it stimulates absorption of calcium although ,
absorption of phosphate f magnesium ions
C. Calcitonin -
is a
peptide hormone produced by the C cells of the thyroid
gland Its main biological effect is to inhibit bone
resorption
.
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
142
9. Differentiate the following conditions as to causes and hormonal picture:
A. True hypoparathyroidism
of
type hyperparathyroidism
where in it be caused by either
-
may
hypoplasia / congenital absence of
accidental removal of it This type
the
of
parathyroid gland and also an
parathyroid ish involves a decrease
.
in PTH bone resorption Vit D formation Intestinal absorption of Calcium
,
.
, ,
and Phosphate and kidney resorption of Catt It Phosphate
excretion
also involves . increase
B. Pseudohypoparathyroidism
of
type hyperparathyroidism where in there is resistance to PTH
-
due to diff
namely
inert PTH, PTA inhibitors in the
l PTH receptors
. reasons
body and abnormality
w
Normal hormone levels in the body but the
kidney does not
.
work properly therefore resulting to Calcium excretion decrease calcium or a
in the body and
increase in Phosphate because excretion of it is not
an
present .
C. Primary hyperparathyroidism
type of
hyperparathyroidism where in it be caused
by adenoma,
-
may
primary hyperplasia and parathyroid carcinoma . An increase in PTH can
be encountered here
leading to increased osteoclasts c and osteoblast c
'
'
activity .
D. Secondary hyperparathyroidism
of
type hyperparathyroidism where in it be caused
by any condition
-
may
that can result to chronic hypercalcemia which in turn , causes compensatory
Over
activity
intake of calcium Sfeatorrhea
of the parathyroid
gland
Here renal failure .
, inadequate
and , deficiency in Vitamin D are some of its
causes .
A decrease in calcium ¥ Vitamin D PTH and
increase in
increase
-
an an
decrease
, or
in
phosphate can be encountered w/ this
disease
This material is downloaded for Richmond A. Amurao (20200015401)
at FEU Dr. Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation.
For personal use only. No other uses without permission. All rights reserved.
143
You might also like
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicDocument2 pagesHashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicPetraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDocument73 pagesEndocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDaNy Chiriac50% (2)
- 610R0110A5 ForbiddenCuresUndrgrndMed WebDocument175 pages610R0110A5 ForbiddenCuresUndrgrndMed Webshakti-babalon100% (10)
- Review Correlation Between Diabetes Mellitus and Residual Ridge Resorption PDFDocument3 pagesReview Correlation Between Diabetes Mellitus and Residual Ridge Resorption PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- FINAL To The Highest HYPOTHYROIDISM TO HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument9 pagesFINAL To The Highest HYPOTHYROIDISM TO HYPERTHYROIDISMYssah Moira HamacNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersDocument11 pagesPharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersJuliann100% (1)
- 3.thyroid Hormones and DisordersDocument46 pages3.thyroid Hormones and DisorderssinayupeNo ratings yet
- Group A Case Study HyperthyroidismDocument14 pagesGroup A Case Study HyperthyroidismMari IllustriousNo ratings yet
- (MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersDocument5 pages(MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersEryl Franz HerreraNo ratings yet
- Transcript MidtermsDocument15 pagesTranscript MidtermsPrincess Krenzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Transcript Midterms PharmacologyDocument15 pagesTranscript Midterms PharmacologyPrincess Krenzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Talking Thyroid FactsDocument6 pagesTalking Thyroid FactsVegan Future100% (4)
- Thyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsDocument7 pagesThyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsPrincess Noreen SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroid DisordersDocument49 pagesHyperthyroid Disordersayu permata dewiNo ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument2 pagesHYPERTHYROIDISMHyacinth Joy Febria GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument6 pagesEndocrine DisordersCurib, Dayannah A.No ratings yet
- Endocrinology Part 2Document4 pagesEndocrinology Part 2Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37Document6 pagesChapter 37kdayeon018No ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders (Final Draft)Document17 pagesThyroid Disorders (Final Draft)mogesie1995No ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageThyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmkatNo ratings yet
- Trogens Propylthiouracil: HyperthyroidismDocument3 pagesTrogens Propylthiouracil: HyperthyroidismShannen Christelle AndradeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease (Chan)Document29 pagesThyroid Disease (Chan)Sidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- Approach To HyperthyroidismDocument58 pagesApproach To HyperthyroidismmedqehkkNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument4 pagesHyperthyroidismLamyaa Ali HasanNo ratings yet
- CC 3-Lab FKM 17Document4 pagesCC 3-Lab FKM 17mayabangkurtipotNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: NCM 116 Lec Mrs. Ma Jesseca P. MonsantoDocument6 pagesHyperthyroidism: NCM 116 Lec Mrs. Ma Jesseca P. MonsantoMarcel Quario OrinaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid: OutlineDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid: OutlineMelissa-Andreea Ardeleanu Carvajal OsorioNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageThyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmRezi HelperNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageThyroid Disorders Testing AlgorithmMuhamad SuriansyahNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid AxisDocument15 pagesHypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid AxisEdmari Joy Pojas MontilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmDocument73 pagesClinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmdiniNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument2 pagesHypothyroidismDanteAndreiNo ratings yet
- New Thyroid PDFDocument4 pagesNew Thyroid PDFCrystal Gayle Nario SabadoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesThyroid PathophysiologyS RiarNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 1Document29 pagesThyroid Disorders 1zxcvbzaki123No ratings yet
- Thyroid AgentsDocument10 pagesThyroid AgentsGab SanchezNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidDocument12 pagesHyperthyroidChristine Joy PepitoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: (Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism)Document28 pagesThyroid Disorders: (Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism)Mina RoxasNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism .... 2Document13 pagesHyperthyroidism .... 2guptaavni0000No ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument53 pagesThyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Tests: What Is The Thyroid?Document8 pagesThyroid Tests: What Is The Thyroid?JyotiNo ratings yet
- (Health) Thyroid Functions TestsDocument4 pages(Health) Thyroid Functions Testsmahendra3107No ratings yet
- Week 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPDocument57 pagesWeek 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPJoy KNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical Complications in Pregnancy: Ramon M. Gonzalez, MDDocument161 pagesMedical and Surgical Complications in Pregnancy: Ramon M. Gonzalez, MDaldeeray01No ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument86 pagesThyroid DisordersJEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- Nodular Non Toxic GoiterDocument36 pagesNodular Non Toxic Goiterjean_arellanoNo ratings yet
- Disorder of ThyroidDocument9 pagesDisorder of ThyroidJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- Hormones, Antagonists, and Other Agents Affecting Endocrine FunctionDocument36 pagesHormones, Antagonists, and Other Agents Affecting Endocrine Functionapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument9 pagesThyroid GlandZach ReyesNo ratings yet
- 6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)Document5 pages6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)KESEBELASAN RESOG 2023No ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseasesDocument44 pagesThyroid DiseasesPLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- CH 37 Thyroid and Parathyroid AgentsDocument6 pagesCH 37 Thyroid and Parathyroid Agentsericka abasNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism: Hormones & YouDocument1 pageHypothyroidism: Hormones & YoufelminaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument47 pagesThyroid Hormonesamalia100% (1)
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Production, Regulation, and Action of Thyroid HormonesDocument51 pagesProduction, Regulation, and Action of Thyroid HormonesNona AsolaNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument84 pagesThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormoneDocument46 pagesThyroid HormoneVictoria Cevallos BonillaNo ratings yet
- Persu Project FinalDocument15 pagesPersu Project FinalAshwinNo ratings yet
- Im-Thyroid DisordersDocument9 pagesIm-Thyroid DisordersRyan F. BernalNo ratings yet
- Zak Notes Hypothyroidism (Juma)Document34 pagesZak Notes Hypothyroidism (Juma)82cxp4n46wNo ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument1 pageHYPERTHYROIDISMAmber BlodduweddNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesDiabetes MellitusDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Respiratory-System, GITDocument2 pagesLipids, Respiratory-System, GITDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Sedative and HypnoticsDocument2 pagesSedative and HypnoticsDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Intro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDocument2 pagesIntro To CNS and Neurodegenerative SeatworkDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- 1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDocument2 pages1b, Amurao, Richmond A., HighercentersDr. RemedyNo ratings yet
- Choi A. Pharmacological Interventions For Osteoporosis 2023Document126 pagesChoi A. Pharmacological Interventions For Osteoporosis 2023jan puchalskiNo ratings yet
- NPI WP ZyCalBoneJoint 0419Document6 pagesNPI WP ZyCalBoneJoint 0419Sunil Murkikar (GM - PMI Quality Operations)No ratings yet
- Metabolic Bone DisordersDocument24 pagesMetabolic Bone Disordersbpt20% (1)
- Cissus Quadrangularis Plant Extract Enhances The Development of Cortical Bone and Trabeculae in The Fetal FemurDocument21 pagesCissus Quadrangularis Plant Extract Enhances The Development of Cortical Bone and Trabeculae in The Fetal FemurdellaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Homeostasis: Endocrine Regulation of (Ca)Document4 pagesCalcium Homeostasis: Endocrine Regulation of (Ca)PRANAB KUMAR MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- CCM TabletsDocument9 pagesCCM TabletssajantkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37 Berne and LevyDocument4 pagesChapter 37 Berne and LevyJoezelleNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis DR SawsawDocument19 pagesOsteoporosis DR SawsawNariman SternNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Pathophysiolog YDocument42 pagesOsteoporosis: Pathophysiolog YShared LifeNo ratings yet
- Intig-D Tablets-SuspensionDocument2 pagesIntig-D Tablets-Suspensionsweetsmarts85No ratings yet
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument13 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionsankarNo ratings yet
- Kidney MapDocument44 pagesKidney MapEfie KapaNo ratings yet
- Lippincott Pathology QuestionsDocument10 pagesLippincott Pathology Questionsابواحمد المجاهدNo ratings yet
- Host ModulationDocument7 pagesHost ModulationDr. Minkle GulatiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Bone GraftingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Bone GraftingJayanth Perumal100% (2)
- Secondary OsteoporosisDocument22 pagesSecondary OsteoporosisBenny Chris TantoNo ratings yet
- CatalogoDocument7 pagesCatalogoIsabela Campos SánchezNo ratings yet
- Melsen, B., 2001. Tissue Reaction To Orthodontic Tooth MovementDocument12 pagesMelsen, B., 2001. Tissue Reaction To Orthodontic Tooth MovementYerly Ramirez MuñozNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument16 pagesOsteoporosisDe Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- JAAOS - Volume 11 - Issue 01 January & February 2003Document77 pagesJAAOS - Volume 11 - Issue 01 January & February 2003kenthepaNo ratings yet
- Daruka Mahadevan - Handbook of Nutrition and Diet in Therapy of Bone DiseasesDocument505 pagesDaruka Mahadevan - Handbook of Nutrition and Diet in Therapy of Bone DiseasesAngelicaNo ratings yet
- OsteoblastDocument9 pagesOsteoblastPRATIK GANGULYNo ratings yet
- AIIMS PG 2005 Question Paper PDFDocument26 pagesAIIMS PG 2005 Question Paper PDFramNo ratings yet
- Anil S Et Al 2013 (Impact of Osteoporosis)Document7 pagesAnil S Et Al 2013 (Impact of Osteoporosis)Silviani FatmaNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue: OsteocytesDocument11 pagesBone Tissue: OsteocytesA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316Document36 pagesNCMB 316Venansius GanggusNo ratings yet
- Cissus Quadrangularis in The Treatment of OsteoporosisDocument10 pagesCissus Quadrangularis in The Treatment of OsteoporosisAl Vostru Beloved MthrfckrNo ratings yet