Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elex
Uploaded by
Rico Allam (Qwertyba)Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elex
Uploaded by
Rico Allam (Qwertyba)Copyright:
Available Formats
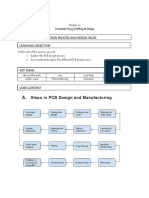
A printed circuit board, or PC board, or PCB, is a non-conductive material with conductive lines printed
or etched. Electronic components are mounted on the board and the traces connect the components
together to form a working circuit or assembly. There’s a by steps procedure in making pcs, first we
design, after all the checks are complete, I printed the PCB design. Like architectural drawings, PCB plans
don’t print out on a regular 8.5x11 sheet of paper. Instead, a special kind of printer, known as a plotter
printer, is used. The inside layers of the PCB are represented in two ink colors which is blank ink, used
for the copper traces and circuits of the PCB and clear ink, which denotes the non-conductive areas of
the PCB, like the fiberglass base. After the PCB design is printed onto a piece of laminate material, a
copper foil or copper coating is applied. The copper is then pre-bonded to that same piece of laminate,
which serves as the structure for the PCB. The copper is then etched away to reveal the blueprint from
earlier. Once the board has been prepared, it is washed with an alkaline solution to remove any of the
leftover photoresists. The board is then pressure washed to remove anything left on the surface and left
to dry. After drying, the only resist that should be left on the PCB is on the top of the copper that
remains as part of the PCB when its finally popped free. The core layers of the Printed circuit board need
to have extra copper removed before the PCB process can continue. When I etch, it involves covering
the necessary copper on the board and exposing the rest of the board to a chemical. The chemical
etching process removes all the unprotected copper from the PCB, leaving only the board’s necessary
amount. We’ve have done resist stripping so that any remaining resist covering the copper of the PCB
inner layer. Cleaning any resist remaining ensures the copper will not have anything hamper its
conductivity. Then we laminate, which uses heat and pressure to melt the bonding epoxy between the
layers. Once the PCB is done on laminating layers, the next thing to do is drilling. For a multilayer printed
circuit board to send signals from one layer to another, we drilled holes in to vias which connect them.
Then after the panel has been drilled, its ready to be plated. Before moving the PCB assembly stage, the
printed circuit board will be protected with a solder mask using a similar UV exposure found photoresist
stage. This gives printed circuit board its distinctive green color. Once the solder mask has been applied,
component reference designators and additional board markings are silkscreened onto the printed
circuit board. Finally, a surface finish is applied to exposed metal surfaces not covered by the solder
mask. This protects the metal and helps with soldering during the PCB assembly process. The plating
process uses a chemical to fuse all the different layers of the PCB together. After being cleaned
thoroughly, the PCB is bathed in a series od chemicals. After that, it is time to apply another layer of
photoresist. However, this time the photoresist is only applied to the outside layer, since it still needs to
be imaged. Once the layer has coated in photoresist and imaged, they’re plated in the exact same way
the interior layers of the PCB were plated. When it comes time to etch the outside layer for the last
time, the tin guard is used to help protect the copper during the etching process. Any unwanted copper
is removed Using the same copper solvent from earlier with the tin protecting the valued copper of the
etching area. As with the inner layer, the outer layer must also undergo double checking. This ensures,
the layer meets the exact requirements of the design. It also verifies that it’s removed all extra copper
from the layer to create a properly functioning printed circuit board that won’t create improper
electrical connections. After the PCB has been coated and cured, we perform a battery of electrical test
on the different areas of the PCB to ensure functionality. the main tests that performed are circuit
continuity and isolation tests. The circuit continuity test checks for any disconnections in the PCB, known
as ‘’open’. On the other hand, the circuit isolation test checks the isolation values of the PCB’s various
parts to check if there are any shorts.
You might also like
- PCB DesignDocument40 pagesPCB DesignInder Pal Singh100% (7)
- Training Notes (4.2 Printed Circuit Boards)Document12 pagesTraining Notes (4.2 Printed Circuit Boards)Anurag Yadav100% (1)
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) : Printed Circuit Boards (PCBS) Form The Backbone of AllDocument37 pagesPrinted Circuit Board (PCB) : Printed Circuit Boards (PCBS) Form The Backbone of AllPhil GainNo ratings yet
- 4.1 PCB Fabrication ProcessDocument10 pages4.1 PCB Fabrication ProcessArushiNo ratings yet
- PCB Manufacturing ProcessDocument19 pagesPCB Manufacturing ProcessNanny Pao Lmj100% (1)
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument3 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardBB HONEYNo ratings yet
- PCB Designing and Fabrication P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board)Document2 pagesPCB Designing and Fabrication P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board)Ashwani DhimanNo ratings yet
- Report 3 Ele DesignDocument8 pagesReport 3 Ele DesignMohd Azfar HakimNo ratings yet
- P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) : What Are Pcbs ?Document1 pageP.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) : What Are Pcbs ?tyffNo ratings yet
- Pcbnote 1Document2 pagesPcbnote 1sunilbabukp8637No ratings yet
- Industrial Training PCBDocument29 pagesIndustrial Training PCBjwndasukhraj100% (2)
- PCB Fabrication: 1. PCB's Are Necessary For Connecting A Large Number of Electronic Components in A VeryDocument4 pagesPCB Fabrication: 1. PCB's Are Necessary For Connecting A Large Number of Electronic Components in A VeryJyothsna ChennareddyNo ratings yet
- PCBDocument42 pagesPCBDivyanshu Agarwal100% (3)
- Double LayerDocument5 pagesDouble Layersanayila khalidNo ratings yet
- PCB MotorDocument8 pagesPCB MotorSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- PCB ProcessDocument10 pagesPCB ProcessChetan AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Steps in PCB Design and ManufacturingDocument9 pagesSteps in PCB Design and Manufacturingtinderlord akoNo ratings yet
- Trade 1 PDFDocument8 pagesTrade 1 PDFRajveer Singh SachdevNo ratings yet
- 10 Printed Circuit BoardDocument12 pages10 Printed Circuit BoardrameshNo ratings yet
- PCB ManufacturingDocument7 pagesPCB ManufacturingAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardsDocument31 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardsSUNNY_20_00100% (1)
- Circuit BoadDocument3 pagesCircuit Boadramon miko avomo eyangaNo ratings yet
- Q4 LAS Week 1-2Document15 pagesQ4 LAS Week 1-2Kram Kram100% (1)
- PCB DevDocument6 pagesPCB DevPoonam bhavsarNo ratings yet
- PCB Design WorkshopDocument18 pagesPCB Design WorkshopPrasun SinhaNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument25 pagesPrinted Circuit Boardchristineparpan100% (7)
- PCB InfoDocument19 pagesPCB InfoDarshan Iyer NNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PCBDocument19 pagesIntroduction To PCBAakash VisvanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document46 pagesChapter - 1Vineet KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Thing You Should Know About PCB Assembly ProcessDocument29 pagesBasic Thing You Should Know About PCB Assembly ProcessjackNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing: MaterialsDocument7 pagesManufacturing: MaterialsMaddyNo ratings yet
- Plated Through Hole Vs Via in A Circuit BoardDocument13 pagesPlated Through Hole Vs Via in A Circuit BoardjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Board: Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Document75 pagesPrinted Circuit Board: Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Ruby Pathak100% (2)
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument23 pagesPrinted Circuit Boardahmed100% (2)
- Shweta JadhavDocument18 pagesShweta JadhavInder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Internship PPT 7th SemDocument22 pagesInternship PPT 7th SemJAY JOSHINo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument6 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- PCB Design WorkshopDocument18 pagesPCB Design WorkshopPrasun SinhaNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Document75 pagesPresented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)AhmedMohabNo ratings yet
- 28 Layer PCB An Integrated Multi-Layer PCBsDocument4 pages28 Layer PCB An Integrated Multi-Layer PCBsjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Board: CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesPrinted Circuit Board: CharacteristicsSai Gautam100% (1)
- PCB Training PresentationDocument31 pagesPCB Training Presentationkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own PCBDocument5 pagesMake Your Own PCBveerakumarsNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument16 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- Making ProcessDocument3 pagesMaking ProcessfredyNo ratings yet
- What Are Through Holes On A PCBDocument15 pagesWhat Are Through Holes On A PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument6 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardSayan Das KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 5 Printed Circuit BoardDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 5 Printed Circuit BoardPeru IllaNo ratings yet
- High Quality Single Sided PCB ManufacturerDocument24 pagesHigh Quality Single Sided PCB ManufacturerjackNo ratings yet
- Lecture No-03 Course PCB Manufacturing IE-236 & Electronic Simulation and PCB Manufacturing (Repeaters Only)Document22 pagesLecture No-03 Course PCB Manufacturing IE-236 & Electronic Simulation and PCB Manufacturing (Repeaters Only)Ravi Shankar 31No ratings yet
- A Project Report of Industrial TrainingDocument22 pagesA Project Report of Industrial TrainingSubham PalNo ratings yet
- What Do You Need To Know About Trace PCBDocument8 pagesWhat Do You Need To Know About Trace PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Board: by B005, D057 Nyla Vaidya and Diya ShahDocument11 pagesPrinted Circuit Board: by B005, D057 Nyla Vaidya and Diya ShahNyla VaidyaNo ratings yet
- How Main PCB Impacts The Functionality of Electronic DevicesDocument4 pagesHow Main PCB Impacts The Functionality of Electronic DevicesjackNo ratings yet
- Bare PCB Manufacturing Process, Defects, and TestingDocument6 pagesBare PCB Manufacturing Process, Defects, and TestingjackNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document9 pagesExperiment 7Ashish patelNo ratings yet
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Designig: by ShubhamDocument15 pagesPCB (Printed Circuit Board) Designig: by Shubhamshubham SINGHNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Boards: Component Technology and Design Parameters'Document5 pagesPrinted Circuit Boards: Component Technology and Design Parameters'Ann MutisyaNo ratings yet
- Confirm Napolcom SlipDocument2 pagesConfirm Napolcom SlipMarkjason castilloNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 Dynamic Behaviour of Feedback Controller ProcessDocument12 pagesLect 8 Dynamic Behaviour of Feedback Controller ProcessZaidoon MohsinNo ratings yet
- EXP-LG-048822 Lighting Management - Wall mounting-DT-360°-for 93 M Areas - Flush MountingDocument1 pageEXP-LG-048822 Lighting Management - Wall mounting-DT-360°-for 93 M Areas - Flush MountingPercy GoitsemangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Perspective DrawingDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - Perspective DrawingChe Nora Che HassanNo ratings yet
- Evidence CasesDocument79 pagesEvidence Caseszyphora grace trillanesNo ratings yet
- Dell PowerEdge R620 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesDell PowerEdge R620 Spec SheetRosli YusoffNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4 2 Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity StudentDocument13 pagesCCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4 2 Mixed Layer 2 3 Connectivity StudentPeter Ndungu0% (2)
- Quadratic PDF UploadDocument11 pagesQuadratic PDF UploadNilansh RajputNo ratings yet
- Companion WebsiteDocument110 pagesCompanion WebsiteDren FazliuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3RosaNo ratings yet
- Personnel Protection Unit Test/Charge Systems: Technical Specification Collision Awareness SystemDocument3 pagesPersonnel Protection Unit Test/Charge Systems: Technical Specification Collision Awareness SystemAbhinandan PadhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 MiscellaneousSystemsDocument17 pagesChapter 24 MiscellaneousSystemsMark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - EthernetDocument76 pagesChapter 5 - EthernetfathaniaffNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Fusion Middleware Application Security GuideDocument898 pagesOracle® Fusion Middleware Application Security GuideamitvohraNo ratings yet
- GCE Advanced Level - ICT - தரவுத்தள முகாமைத்துவ முறைமைDocument57 pagesGCE Advanced Level - ICT - தரவுத்தள முகாமைத்துவ முறைமைThanuNo ratings yet
- K Mean ClusteringDocument27 pagesK Mean Clusteringashishamitav123No ratings yet
- BRO ASD535-532-531 en PDFDocument6 pagesBRO ASD535-532-531 en PDFArman Ul NasarNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-7-Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide-en-US PDFDocument551 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-7-Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide-en-US PDFRomain KoffiNo ratings yet
- Google DeveloperDocument121 pagesGoogle DeveloperGangadhar VijayNo ratings yet
- Ds 1621Document16 pagesDs 1621AnassFouadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Test InstrumentsDocument44 pagesElectrical Test Instrumentsשמעון פרידמןNo ratings yet
- Rsae ITP QA: Document Review and Cover Sheet Company: Construction ContractorDocument5 pagesRsae ITP QA: Document Review and Cover Sheet Company: Construction ContractorUtku Can KılıçNo ratings yet
- Four Dimensional ArtDocument14 pagesFour Dimensional ArtNoemi RenomeronNo ratings yet
- 990k HidraulicDocument15 pages990k Hidraulichitler morales gavidiaNo ratings yet
- cqm13392 7jDocument8 pagescqm13392 7jsunilbholNo ratings yet
- Epson FX 890 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson FX 890 DatasheetMarcos ZamorioNo ratings yet
- 18-Cellular Layout, Group Technology, Heuristic Approaches-08-11-2021 (08-Nov-2021) Material - II - 08-11-2021 - G.T - PDFDocument24 pages18-Cellular Layout, Group Technology, Heuristic Approaches-08-11-2021 (08-Nov-2021) Material - II - 08-11-2021 - G.T - PDFSahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat IncroperaDocument43 pagesHeat IncroperaAnonymous rEpAAK0iNo ratings yet
- Ranap Release CauseDocument397 pagesRanap Release CauseKamana Khare0% (1)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PM583 Di524 8 9 Ta521 Di524 PM583 Ta521 CM597 Ci522Document1 page1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PM583 Di524 8 9 Ta521 Di524 PM583 Ta521 CM597 Ci522mahmoud sheblNo ratings yet