Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Binomial and Doubly Ended Queue
Uploaded by
Ajit Pawar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views23 pagesPriority queues can be used for event-driven simulations, data compression algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's, and operating system process queues. A binary heap can be used to implement a priority queue with operations like insert, extract minimum, and decrease key taking O(logn) time. A doubly ended priority queue can implement minimum and maximum heaps simultaneously, and can be used for external quicksort by removing the minimum or maximum element from the queue and outputting it to the left or right groups. Fibonacci heaps have a less rigid structure than binomial heaps and lazily consolidate trees until the next delete minimum operation.
Original Description:
.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPriority queues can be used for event-driven simulations, data compression algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's, and operating system process queues. A binary heap can be used to implement a priority queue with operations like insert, extract minimum, and decrease key taking O(logn) time. A doubly ended priority queue can implement minimum and maximum heaps simultaneously, and can be used for external quicksort by removing the minimum or maximum element from the queue and outputting it to the left or right groups. Fibonacci heaps have a less rigid structure than binomial heaps and lazily consolidate trees until the next delete minimum operation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views23 pagesBinomial and Doubly Ended Queue
Uploaded by
Ajit PawarPriority queues can be used for event-driven simulations, data compression algorithms like Dijkstra's and Prim's, and operating system process queues. A binary heap can be used to implement a priority queue with operations like insert, extract minimum, and decrease key taking O(logn) time. A doubly ended priority queue can implement minimum and maximum heaps simultaneously, and can be used for external quicksort by removing the minimum or maximum element from the queue and outputting it to the left or right groups. Fibonacci heaps have a less rigid structure than binomial heaps and lazily consolidate trees until the next delete minimum operation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
Priority Queues
▪ Event-drivensimulations (particle collisions,
queuing customers,traffic)
▪Data compression
dijikstras and prims
Operating systems (process queue)
Graph searching
▪first() - get the smallest key-value(but leave it there)
▪insert() - add a new key-value
▪ extractMin() - remove the smallest key-value
▪decreaseKey() - reduce the key of a node
▪ merge() - merge two queues together
Binary heap implementation of
priority queue
Could use a min-heap (like the max-heap we
saw for heapsort
insert() : time taken is o(logn)
find min() : o(1) find top most element
extractMin() : find topmost element (o(1) )
and then delete that + adjust (o(logn)
Binomial heap
▪The largest bit possible is (lg n + 1)-th bit
▪So there can't be more than(lg n + 1) roots/trees
Doubly ended priority queue
A double-ended priority queue (DEPQ) is a
queue where we can implement min and max
heap at the same time.
Each element has a priority or value.
1. getMin() ... return element with minimum
priority
2. getMax() ... return element with maximum
priority
3. put(x) ... insert the element x into the DEPQ
4. removeMin() ... remove an elementwith
minimum priorityand return this element
5. removeMax() ... remove an elementwith
maximum priorityand return this element
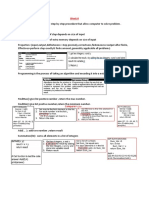
Doubly ended priority queue use in
external quick sort
The basic idea in quick sort is to partition the elements to
be sorted into three groups L, M , and R.
The middle group M contains a single element called the
pivot,
all elements in the left group L (smaller or equal to m)
and all elements in the right group with greater or equal to
m
The external quick sort strategy
Read in as many elements as will fit into an internal DEPQ.
Read in the remaining elements.
If the next element is the smallest element in the DEPQ, output
this next element as part of the left group.
If the next element is the largest element in the DEPQ, output
this next element as part of the right group. Otherwise, remove
either the max or min element from the DEPQ (the choice may
be made randomly or alternately); if the max element is
removed, output it as part of the right group; otherwise,
output the removed element as part of the left group; insert
the newly input element into the DEPQ.
fibonacci heap
Basic idea.
Similar to binomial heaps, but less rigid structure.
Binomial heap: eagerly consolidate trees after each
insert.
Fibonacci heap: lazily defer consolidation until next
delete-min.
You might also like
- M.C.a. (Sem - II) Paper - I - Data StructuresDocument132 pagesM.C.a. (Sem - II) Paper - I - Data Structuresbaluchandrashekar2008No ratings yet
- Stress Critical Line ListDocument1 pageStress Critical Line ListJitendraSurveNo ratings yet
- HeapsDocument29 pagesHeapsMemoona IshfaqNo ratings yet
- Parallel Ant Colonies For Combinatorial Optimization ProblemsDocument9 pagesParallel Ant Colonies For Combinatorial Optimization ProblemsAdrian George NăstaseNo ratings yet
- Adc 4Document61 pagesAdc 4ati atiNo ratings yet
- W5 PriorityQueueDocument54 pagesW5 PriorityQueuedastanktl26No ratings yet
- Min Max HeapsDocument22 pagesMin Max HeapsyashikabirdiNo ratings yet
- Adsa-2unit Heap ContinueDocument20 pagesAdsa-2unit Heap Continuesharmilahema33No ratings yet
- Quicksort: Merge SortDocument1 pageQuicksort: Merge SortMdv PrasadNo ratings yet
- QuickSort Is A Divide and Conquer AlgorithmDocument2 pagesQuickSort Is A Divide and Conquer AlgorithmAakash AggarwalNo ratings yet
- DAA Lab-ManualDocument38 pagesDAA Lab-Manualraviy3083No ratings yet
- DeapsDocument45 pagesDeapsVoila ShaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I DSDocument39 pagesUnit-I DShafzalmjrNo ratings yet
- AOAD Assignment: Topic: Quick Sort (Average Case)Document3 pagesAOAD Assignment: Topic: Quick Sort (Average Case)ohafcNo ratings yet
- Data Structure: Chapter 5 - Trees 5.6 5.10Document10 pagesData Structure: Chapter 5 - Trees 5.6 5.10Sang Hyeok KimNo ratings yet
- Sorting 1Document27 pagesSorting 1Fazrul RosliNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit 2Document105 pagesDAA Unit 2sunnyvemulavadatrynow6506No ratings yet
- Analysis & Design of Algorithms (3466) 2Document9 pagesAnalysis & Design of Algorithms (3466) 2Tooba Hassan 364-FSS/BSIAA/F19No ratings yet
- Heap SortDocument7 pagesHeap SortYogender SinghNo ratings yet
- Advanced Network Design Assignment HelpDocument8 pagesAdvanced Network Design Assignment HelpComputer Network Assignment Help100% (1)
- Abstract Data Types (Adts) : Applications of Data StructuresDocument16 pagesAbstract Data Types (Adts) : Applications of Data StructuresSuryaNo ratings yet
- Naïve Approach-: 2) O (K) Time. The Total Time Complexity Will Be O (K)Document3 pagesNaïve Approach-: 2) O (K) Time. The Total Time Complexity Will Be O (K)Sia SharmaNo ratings yet
- Selection SortDocument6 pagesSelection SortSherdilNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 7 Heap and Priority QueueDocument4 pagesExercise No. 7 Heap and Priority QueueLaado SabunNo ratings yet
- DSA SPL NotesDocument5 pagesDSA SPL NotesDebanik DebnathNo ratings yet
- Cs 97si: Introduction To Programming Contests: Jaehyun ParkDocument39 pagesCs 97si: Introduction To Programming Contests: Jaehyun ParkAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Detail Explanation of Heap, Reheap Up, Reheap Down.. With An ExampleDocument27 pagesDetail Explanation of Heap, Reheap Up, Reheap Down.. With An ExampleSandesh Manohar100% (1)
- XIIComp - SC - Data StructuresDocument19 pagesXIIComp - SC - Data StructuresAmbesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Session On Technical Skill - Competitive Coding: Topic: STACK 19/11/2021Document54 pagesSession On Technical Skill - Competitive Coding: Topic: STACK 19/11/2021Dheeraj ChalasaniNo ratings yet
- Heap / Priority QueueDocument17 pagesHeap / Priority QueueMihai NanNo ratings yet
- Eecs 281 HeapsDocument25 pagesEecs 281 HeapsCharlie YanNo ratings yet
- Clo2 Cis2203Document3 pagesClo2 Cis2203maryamNo ratings yet
- Ms 2019 BitDocument15 pagesMs 2019 BitSudharshanNo ratings yet
- 2Y DSA2 Tutorial3 2Document2 pages2Y DSA2 Tutorial3 2xboxmoulay2003No ratings yet
- Iare Ds Lecture Notes 2vishDocument85 pagesIare Ds Lecture Notes 2vishAmit BohraNo ratings yet
- DS Data Structures PPT-module-6Document13 pagesDS Data Structures PPT-module-6ravikumar03508No ratings yet
- Unit I: Introduction: AlgorithmDocument17 pagesUnit I: Introduction: AlgorithmajNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument28 pagesData StructuresMohammed JeelanNo ratings yet
- Ds 5-StacksDocument26 pagesDs 5-StacksayushiNo ratings yet
- Lab01 ArrayDocument6 pagesLab01 ArraySwaira RiazNo ratings yet
- AdisaDocument6 pagesAdisaKayla shakira anjaniNo ratings yet
- Priority QueuesDocument13 pagesPriority QueuesVivekGargNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 Priority QueueDocument19 pagesUnit - 5 Priority QueueKumara RagavendraNo ratings yet
- Heaps and Priority Queues 1Document25 pagesHeaps and Priority Queues 1ababbaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document16 pagesModule 5Aman DesaiNo ratings yet
- Heaps and QueuesDocument48 pagesHeaps and QueuesrajanNo ratings yet
- Viva Final DS - LabDocument30 pagesViva Final DS - LabAsquare FoundationNo ratings yet
- II Sem DS Unit IDocument55 pagesII Sem DS Unit InmxkorbetNo ratings yet
- Iare Iare Ads Lecture NotesDocument86 pagesIare Iare Ads Lecture NoteshuylimalaNo ratings yet
- Min Heap in JavaDocument7 pagesMin Heap in JavaNaufal AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Linear Data Structures Stacks and Queues ExercisesDocument4 pagesLinear Data Structures Stacks and Queues ExercisesTest LouNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II - StacksDocument26 pagesUNIT - II - StacksfitsumNo ratings yet
- Queues (N-Z)Document31 pagesQueues (N-Z)vijaita kashyapNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Data Structure: - Niraj AgarwalDocument176 pagesFundamentals of Data Structure: - Niraj Agarwaljeysam100% (1)
- DS UnitIDocument59 pagesDS UnitIRexline S JNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Dsa (2017)Document30 pagesChap4 Dsa (2017)YOHANIS YADETANo ratings yet
- AI Lab4Document6 pagesAI Lab4Extreme EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmDocument33 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmajNo ratings yet
- SemiFinals Lesson3Document4 pagesSemiFinals Lesson3THRISHA JOYCE GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Lab04 ArraysDocument6 pagesLab04 ArraysHồ NamNo ratings yet
- 03 Data StructuresDocument44 pages03 Data StructuresChintu MahadaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 JavascriptdocumentDocument122 pagesChapter 5 JavascriptdocumentKinNo ratings yet
- Calculus For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 13th Edition Barnett Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesCalculus For Business Economics Life Sciences and Social Sciences 13th Edition Barnett Solutions Manualdanieltrangm8i100% (27)
- Extended Revision Exercises: Data Handling: Worksheet 20: Histograms and Frequency Distribution DiagramsDocument3 pagesExtended Revision Exercises: Data Handling: Worksheet 20: Histograms and Frequency Distribution Diagramsmk hatNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech II Semester II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations August - 2014 Control Systems 2014Document8 pagesII B. Tech II Semester II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations August - 2014 Control Systems 2014Sandeep YandamuriNo ratings yet
- Mips IsaDocument79 pagesMips Isaphan_vinh_20No ratings yet
- COUNTIF in Excel - Count If Not Blank, Greater Than, Duplicate or UniqueDocument3 pagesCOUNTIF in Excel - Count If Not Blank, Greater Than, Duplicate or UniquePEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Modeling in Transport Phenomena: A Conceptual Approach by Ismail Tosun Errata For Second EditionDocument3 pagesModeling in Transport Phenomena: A Conceptual Approach by Ismail Tosun Errata For Second EditionCepa UgolNo ratings yet
- Data Mining AbhasDocument24 pagesData Mining AbhasMohit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- De Thi Ioe Tieng Anh Lop 5 Vong 1 Den 35 7191Document10 pagesDe Thi Ioe Tieng Anh Lop 5 Vong 1 Den 35 7191Nguyễn Thu HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Codigos de Funcion y Direccion MODBUSDocument19 pagesCodigos de Funcion y Direccion MODBUSRuben Mondejar MaciánNo ratings yet
- What Is The Relation Between Resolution III and Confounded ResponsesDocument50 pagesWhat Is The Relation Between Resolution III and Confounded ResponsesrohitrealisticNo ratings yet
- CS 101 Assignment # 01: SolutionDocument3 pagesCS 101 Assignment # 01: SolutionNoori NoorNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Relations PDFDocument12 pagesMaxwell's Relations PDFAsif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- A2 53b GasesDocument50 pagesA2 53b GasesHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 LexicalAnalisysDocument17 pagesLecture2 LexicalAnalisysDorra BoutitiNo ratings yet
- Marginal Cost1Document7 pagesMarginal Cost1Randy KempNo ratings yet
- Seawater Leaching of Caliche Mineral in Column ExperimentsDocument9 pagesSeawater Leaching of Caliche Mineral in Column ExperimentsCamila ContrerasNo ratings yet
- EBP Project Table of Evidence TOE 2022-1Document3 pagesEBP Project Table of Evidence TOE 2022-1simon jordan1005No ratings yet
- The Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsDocument20 pagesThe Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Aile LandscapeDocument28 pagesAile LandscapeSalisu BorodoNo ratings yet
- EC6404-Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument9 pagesEC6404-Linear Integrated CircuitsmohanNo ratings yet
- Fisher's Linear Discriminant: Jianxin WuDocument18 pagesFisher's Linear Discriminant: Jianxin WuXg WuNo ratings yet
- Composite Functions PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Functions PDFShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Wave Function and ProbabilitiesDocument13 pagesWave Function and ProbabilitiesAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Quiz SLTN 4Document7 pagesQuiz SLTN 4frabziNo ratings yet
- Cs507 Quiz Solved #2Document18 pagesCs507 Quiz Solved #2Power GirlsNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and Variance Analysis Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument26 pagesStandard Costs and Variance Analysis Standard Costs and Variance Analysischiji chzzzmeowNo ratings yet