Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DCT Exercise 1
Uploaded by
Paulina ShiimiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DCT Exercise 1
Uploaded by
Paulina ShiimiCopyright:
Available Formats
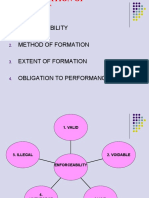
1.
Valid Contract:
A valid contract is an agreement between two or more parties that meets all the essential
legal requirements and is legally binding. For a contract to be void, certain elements must be
present:
There must be a clear offer by one party and an unconditional acceptance of that offer by
the other party.
The subject matter of the contract must be legal and not against public policy.
There must be an exchange of something of value between the parties.
Both parties must have the legal capacity to enter into the contract.
2. Void contracts
A void contract is a contract that is considered null and void form the outset, meaning it has
no legal effect, and the parties are not bound by its terms. A void contract lacks at least one
essential element required for a valid contract. Consequently it cannot be enforced by either
party, and the parties cannot seek legal remedies for any non-performance or breach.
For example, a contract to commit an illegal act or a contract with a person who lacks the
legal capacity to contract is a void.
3. Voidable Contracts:
A voidable contract is a contract that is initially valid and enforceable, but due to certain
circumstances or the presence of a legal defect, one of the parties has the option to either
enforce or void the contract. The party with the right to void the contract can choose to do
so, making the contract voidable.
Once the party with the right to void exercises their option, the contract becomes void, and
both parties are released from their obligations.
4. Essentialia, Neutualia, and Incidentalia of a contract:
Essentialia: The essential elements or requirements that must be present in a contract for it
to be considered valid, such as offer, acceptance, consideration and legal purpose.
Neutualia: Additional terms and conditions in a contract that are not essential but may be
included to provide further details about the agreement.
Incidentalia: Minor details in a contract that do not substantially impact the validity or
enforceability of the agreement.
5. Unenforceable Contracts:
Unenforceable contracts are contracts that may initially appear valid, but due to some legal
or technical issues, a court or authority will not enforce them. The primary difference
between the void and unenforceable contracts is that an unenforceable contracts may still
be valid and binding between the parties, but a court will not enforce it if a dispute arises.
6. Performance:
Performance is the context of contracts refers to the fulfilment or completion of the
obligation and promises made by the parties under the contract. When both parties perform
their respective duties as outlined in the contract, the contract is said to be executed or
perfumed.
You might also like
- Soccer (Football) Contracts: An Introduction to Player Contracts (Clubs & Agents) and Contract Law: Volume 2From EverandSoccer (Football) Contracts: An Introduction to Player Contracts (Clubs & Agents) and Contract Law: Volume 2No ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: Submitted FromDocument12 pagesAssignment # 1: Submitted FromAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- Business Law Chapter-3Document3 pagesBusiness Law Chapter-3Gita KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Contract LawDocument9 pagesContract LawMoses TemboNo ratings yet
- Law Assign 3Document5 pagesLaw Assign 3Qasim ImranNo ratings yet
- Akeem Abosede TimileyinDocument9 pagesAkeem Abosede TimileyinPaschal OdifeNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAM-Glyness Relox-CPE5-3Document4 pagesFINAL EXAM-Glyness Relox-CPE5-3Leizel ReloxNo ratings yet
- Law of ContractDocument4 pagesLaw of ContractTannu SinghNo ratings yet
- Contract PerfectionDocument16 pagesContract PerfectionDante Escudero100% (2)
- Elements Necessary For The Formation of A Valid ContractDocument18 pagesElements Necessary For The Formation of A Valid ContractwizirangaNo ratings yet
- Types of ContractDocument1 pageTypes of ContractSubodh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Voide - Voidable and Valid9commercial Law)Document4 pagesThe Difference Between Voide - Voidable and Valid9commercial Law)Elias Phiri100% (1)
- Legal Aspects of BSTDocument4 pagesLegal Aspects of BSTRX l Thunder100% (1)
- ContractDocument9 pagesContractNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- BLAW 280 Study Guide 2nd ExamDocument2 pagesBLAW 280 Study Guide 2nd Examjack stauberNo ratings yet
- Write A Short Note On Indian Contract Act 1872 and General Principles of ContractDocument14 pagesWrite A Short Note On Indian Contract Act 1872 and General Principles of Contractshyam1092004No ratings yet
- Name: Mazhar Iqbal: Reg No: MS120182076 Bba 6 Section B (S) Assignment: Business Law Submitted To Sir SaleemDocument12 pagesName: Mazhar Iqbal: Reg No: MS120182076 Bba 6 Section B (S) Assignment: Business Law Submitted To Sir SaleemMazhar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Classification of ContractDocument3 pagesClassification of ContractAmrita PatilNo ratings yet
- S3 Lecture 2 - Laws On ContractsDocument7 pagesS3 Lecture 2 - Laws On ContractsSamantha Joy AngelesNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice: Assignment No. 1Document9 pagesProfessional Practice: Assignment No. 1Wîżž ĶåľïfăNo ratings yet
- All Contracts Are Agreement But All Agreements Are Not ContractDocument3 pagesAll Contracts Are Agreement But All Agreements Are Not ContractRoshani Tamang75% (4)
- Espuelas Jessica P. Bsme 5a Melc Final Technical ReportDocument6 pagesEspuelas Jessica P. Bsme 5a Melc Final Technical ReportJan Michael RamosNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract 1Document31 pagesLaw of Contract 1a99984085No ratings yet
- CuestionarioDocument13 pagesCuestionarioJuli MisticNo ratings yet
- IMRANDocument10 pagesIMRANImran SohailNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective:O1: Understand The Essential Elements of A Valid Contract in A Business ContextDocument9 pagesLearning Objective:O1: Understand The Essential Elements of A Valid Contract in A Business ContextMeena JanNo ratings yet
- Legal & Tax Aspects of BusinessDocument238 pagesLegal & Tax Aspects of BusinessBhavin Mahesh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Privity of Contract and Breach of ContractDocument5 pagesPrivity of Contract and Breach of Contractpm86rxq4vhNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument3 pagesBusiness LawNabeeha AmerNo ratings yet
- HospitalityDocument6 pagesHospitalityPETER OWINONo ratings yet
- Contract NotesDocument16 pagesContract NotesAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Contract - GeneralDocument19 pagesContract - Generalarnoldochieng125No ratings yet
- Pakistani Version Contract Act 1872Document39 pagesPakistani Version Contract Act 1872Muhammad Zeshan Laang100% (1)
- The Law of ContractDocument19 pagesThe Law of ContractAbdiweli mohamedNo ratings yet
- Contract Act 1872 PDFDocument51 pagesContract Act 1872 PDFRana HumzaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT#3Document3 pagesASSIGNMENT#3DJ AXELNo ratings yet
- Contract Law in PakistanDocument7 pagesContract Law in PakistanSyeda Sana AliNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of A Valid ContractDocument2 pagesEssential Elements of A Valid ContractAaryan RautNo ratings yet
- Four Contractual ElementsDocument2 pagesFour Contractual ElementsShehroz AbbasiNo ratings yet
- The Law of ContractDocument4 pagesThe Law of Contractvictor100% (1)
- Unit-3, Session-1, Contracts ConceptsDocument13 pagesUnit-3, Session-1, Contracts ConceptsVikash RanjanNo ratings yet
- Law AssignmentDocument6 pagesLaw Assignmentdawitabebe1993No ratings yet
- BL NotesDocument140 pagesBL NotesBongale OmprakashNo ratings yet
- ContractDocument1 pageContractDiane GunnarsenNo ratings yet
- Business Contract. BDocument6 pagesBusiness Contract. BSIZA THE POETNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument1 pageBusiness LawMohamed Sameh KandilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document25 pagesChapter 9leoeoaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentAbdullah AzizNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument17 pagesContractsIsaac OnyanchaNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract ActDocument20 pagesIndian Contract ActkingsleyNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act 1872Document11 pagesThe Indian Contract Act 1872kitawsNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument43 pagesContractsAkirha SoNo ratings yet
- Contracts NotesDocument28 pagesContracts NotesMitaliNo ratings yet
- Types of ContractsDocument2 pagesTypes of ContractsRahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- CheggDocument5 pagesCheggAnasAhmedNo ratings yet
- Different Contracts in Legal Aspect of BankingDocument7 pagesDifferent Contracts in Legal Aspect of Bankingdrishya3No ratings yet
- Classification of Contract Lecture 2Document14 pagesClassification of Contract Lecture 2Abhra BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Business Law-1Document27 pagesBusiness Law-1rajshri0609No ratings yet
- Untitled Document-1Document3 pagesUntitled Document-1pubgpcbannedacc5No ratings yet
- 1.1. Principles of General InsuranceDocument22 pages1.1. Principles of General Insurancebeena antuNo ratings yet
- SIGNED Contract of Lease Parking Slot No. 1 MauiDocument5 pagesSIGNED Contract of Lease Parking Slot No. 1 Mauielvie epilNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document127 pagesSession 2AaronNo ratings yet
- Sounak - OPCDocument25 pagesSounak - OPCSounak VermaNo ratings yet
- US Internal Revenue Service: p938 - 1996Document90 pagesUS Internal Revenue Service: p938 - 1996IRS100% (1)
- ICICI Pru Saral Jeevan BimaDocument9 pagesICICI Pru Saral Jeevan BimaThampy ATNo ratings yet
- Question 1bDocument14 pagesQuestion 1bPankaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Section 68 in The Transfer of Property Act, 1882Document2 pagesSection 68 in The Transfer of Property Act, 1882Ragunathan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- 70002886268Document4 pages70002886268acme financialNo ratings yet
- Bank GuaranteeDocument14 pagesBank GuaranteeMason TangNo ratings yet
- Corporations in Financial Difficulty: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument26 pagesCorporations in Financial Difficulty: Multiple Choice QuestionsInsatiable LifeNo ratings yet
- Artist Contract TemplateDocument4 pagesArtist Contract TemplateIonut LenghenNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management 11 Edition: by Jeff MaduraDocument30 pagesInternational Financial Management 11 Edition: by Jeff MaduraDaefnate KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii Prospectus and Allotment of Securities: WWW - Edutap.co - inDocument14 pagesChapter Iii Prospectus and Allotment of Securities: WWW - Edutap.co - inVismit PariharNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument11 pagesCONTRACTSJoshua dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Indian Partnership Act, 1932Document13 pagesIndian Partnership Act, 1932Divya GuptaNo ratings yet
- ZARAH NOTES Letters of Credit ZarahDocument2 pagesZARAH NOTES Letters of Credit ZarahTinn ApNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Sales - 22 Jan 2020 (DGT) FinalDocument130 pagesBusiness Law - Sales - 22 Jan 2020 (DGT) FinalAndrea AtendidoNo ratings yet
- CRVI Question PaperDocument5 pagesCRVI Question PaperCma SankaraiahNo ratings yet
- NFRSDocument7 pagesNFRSDipesh GautamNo ratings yet
- Analisis Perbedaan Kualitas Akrual Dan Persistensi Laba Sebelum Dan Sesudah Konvergensi IfrsDocument15 pagesAnalisis Perbedaan Kualitas Akrual Dan Persistensi Laba Sebelum Dan Sesudah Konvergensi IfrsDillaNo ratings yet
- Agreement of CessionDocument3 pagesAgreement of CessionMilena Markovic40% (5)
- Chapter5 - Business Entities in MalaysiaDocument25 pagesChapter5 - Business Entities in Malaysiamalia warisNo ratings yet
- ABM 1 EVALUATION WEEK 4 and 5Document4 pagesABM 1 EVALUATION WEEK 4 and 5Christel Fermia RosimoNo ratings yet
- Purchase OrderDocument8 pagesPurchase Ordervg elumalaiNo ratings yet
- Grading & WarehousingDocument87 pagesGrading & WarehousingDoan Pham ManhNo ratings yet
- The Kosnar Group FDD QuestionnaireDocument51 pagesThe Kosnar Group FDD QuestionnaireCarl KosnarNo ratings yet
- SmartPlatinaPlus08042022 535458Document3 pagesSmartPlatinaPlus08042022 535458Srigandh's WealthNo ratings yet
- The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.: Presented By:-Dhiraj SadhwaniDocument21 pagesThe Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.: Presented By:-Dhiraj SadhwaniDhiraj SadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Legal Aspects of BusinessDocument20 pagesUnit - 2 Legal Aspects of BusinessmailtomanicksgmailcoNo ratings yet