0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views2 pages2016 Motion Equations Review
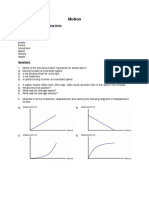
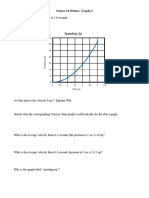
The document contains several examples of calculating acceleration, velocity, speed, distance, and time for objects moving with constant or changing motion. Examples include calculating the acceleration of a race car from its initial and final speeds over a time period, the acceleration of a rocket sled, and the maximum speeds reached by a two-stage rocket. Other examples show calculating average acceleration and average speed from changes in speed or distance over time. Graphs of distance vs time and velocity vs time are also used to determine acceleration, velocity, and distance at given times.
Uploaded by
Leslie RuoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views2 pages2016 Motion Equations Review
The document contains several examples of calculating acceleration, velocity, speed, distance, and time for objects moving with constant or changing motion. Examples include calculating the acceleration of a race car from its initial and final speeds over a time period, the acceleration of a rocket sled, and the maximum speeds reached by a two-stage rocket. Other examples show calculating average acceleration and average speed from changes in speed or distance over time. Graphs of distance vs time and velocity vs time are also used to determine acceleration, velocity, and distance at given times.
Uploaded by
Leslie RuoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd