Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FM 5
Uploaded by
gojo satoruCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FM 5
Uploaded by
gojo satoruCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5: ● Compound interest - interest earned on a given
deposit ad has become part of the principal at
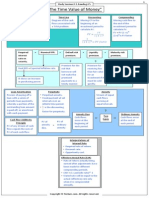
❖ Time Value of Money - observation that it is better the end of a specified period
to receive money sooner than later
➢ Invest money now = earn positive rate of return ● Principal - amount of money on which interest is paid
= more money tomorrow FVn = PV0 x (1+r)n
➢ Money now is worth more than money in the
future FVn = future value r = annual rate of interest
❖ Timeline - horizontal line on which time zero PV0 = initial principal n= number of periods
approaches at the leftmost end and future periods
are marked from left to right ● Simple Interest - earned only on an investment’s
➢ Used to depict investment cash flows original principal and not on interest that
accumulated over time
➢ Compounding - future value technique to find ● Present value - value of today’s dollars of some future
future value of each cash flow at the end of cash flow
investment’s life and sum these values to find PV0 = FVn / (1+r)n
the future value
■ Adding interest to an investment’s ❖ Annuity - stream of equal periodic cash flow over a
principal and paying interest on the specified time period
new higher balance ➢ Can be inflows or outflows
➢ Discounting - technique to find the present ➢ Ordinary annuity - cash flow occurs at the
value at time zero and sums these value to find end of each period
the value today ➢ Annuity due - cash flow occurs at the
■ Used by investors to make investing beginning of each period
decisions
■ Inverse of compounding Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity:
❖ Computational Tools
➢ Financial Calculators - numerous
preprogrammed financial routines
➢ Electronic Spreadsheet - built-in routines that
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity:
simplify time-value calculations
❖ Basic Pattern of Cash Flow
➢ Single amount - lump sum amount either
currently held or expected at some future date
➢ Annuity - level of periodic stream of cash flow
Future Value of an Annuity Due:
➢ Mixed-stream - not an annuity; stream of
unequal periodic cash flows that reflect no
particular pattern
SINGLE AMOUNTS: Present Value of an Annuity Due:
● Future value - value at some future date of
money you invest today
○ Terminal value, sum, the amount,
amount, accumulated amount
Always:
FV of Annuity Due > FV of Ordinary Annuity
PV of Annuity Due > Pv of Ordinary Annuity ● Effective (true) annual rate (EAR) - annual rate of
interest actually paid or earned
❖ Perpetuity - annuity with an infinite life, providing
continual annual cash flow
➢ PV0 = CF1 / r ● Annual percentage rate (APR) - nominal annual rate
➢ PV of a growing perpetuity: of interest, found by multiplying the periodic rate by
■ PV0 = CF1 / (r -g) the number of periods in one year, that must be
■ Applies only when discount rate is disclosed to consumers on credit cards and loans as
greater than the growth rate a result of “truth-in-lending laws”
■ If r ≤ g, cash flows grow so fast that PV ● Annual percentage yield (APY) - effective annual
= INFINITE rate of interest that must be disclosed to consumers
● r = interest rate; g = by banks on their savings products as a result of
growth rate “truth-in-savings laws”
❖ Mixed Stream - stream of unequal periodic cash SPECIAL APPLICATIONS OF TIME VALUE
flows that reflect no particular pattern
❖ FV of mixed stream - compute FV of each cash flow ● Determining deposits needed to accumulate a
at the specified FV and add all the individual FVs to future sum:
find the total FV
❖ PV of mixed stream - compute PV of each cash flow
and add all the individual PVs to find the total FV
COMPOUNDING INTEREST MORE FREQUENTLY THAN ● Loan amortization - determination of equal periodic
ANNUALLY loan payments necessary to provide a lender with a
specified interest return and to repay the loan
● Semiannual Compounding - compounding of interest principal over a specified period
over two periods within the year ● Loan amortization schedule - schedule of equal
● Quarterly Compounding - compounding of interest payments to repay a loan
over four periods within the year ○ Shows the allocation of each loan payment
to interest and principal
General Equation for Compounding:
To solve for payment:
● Continuous compounding - compounding of interest,
literally, all the time To solve for interest or growth rate:
○ Infinite number of times in a year
○ e=exponential function
To solve for the unknown number of periods:
● Nominal (stated) annual rate - contractual annual rate
of interest charged by a lender or promised by a
borrower
You might also like
- Time Value and MoneyDocument10 pagesTime Value and Moneymr haldarNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash Flows and ValuationDocument31 pagesDiscounted Cash Flows and ValuationkamranNo ratings yet
- FINMAN II - Time Value of MoneyDocument3 pagesFINMAN II - Time Value of MoneyAnne LunaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money PracticeDocument11 pagesTime Value of Money PracticeUmer ArshadNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument44 pagesTime Value of MoneyJoenna Marie Morales0% (1)
- Finman TheoriesDocument4 pagesFinman TheoriesMoguriNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesFinancial Management - Midterm NotesPrincess Ericka CastleNo ratings yet
- FIN202Document6 pagesFIN202Dang Ngoc Van (K17 DN)No ratings yet
- Time Value of Money (TVM)Document5 pagesTime Value of Money (TVM)Yesha Jade SaturiusNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math ReviewerFinalsDocument5 pagesGen. Math ReviewerFinalsCezter AbutinNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Lecture 2Document27 pagesFinancial Management Lecture 2Tesfaye ejetaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument24 pagesTime Value of MoneyShashank100% (1)
- BCH 503 SM02Document4 pagesBCH 503 SM02sugandh bajajNo ratings yet
- Async CFin-I Annuities and Perpetuities Friday 5august2022Document35 pagesAsync CFin-I Annuities and Perpetuities Friday 5august2022SSNo ratings yet
- CH - 02 Concept of Value and ReturnDocument25 pagesCH - 02 Concept of Value and Returnpriyanshu jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument23 pagesTime Value of Moneyhardika jadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Time Value of MoneyDocument24 pagesChapter Three Time Value of MoneytezanaNo ratings yet
- CH - 02 Concept of Value and ReturnDocument25 pagesCH - 02 Concept of Value and ReturnMrhunt394 YTNo ratings yet
- Time Value OF MoneyDocument16 pagesTime Value OF MoneyKomal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 NOTES and LOANS PAYABLEDocument4 pagesTOPIC 2 NOTES and LOANS PAYABLEDustinEarth Buyo MontebonNo ratings yet
- NH l1sshbb 2los5Document1 pageNH l1sshbb 2los5Oliver SheringhamNo ratings yet
- 05 Fixed Income SecuritiesDocument55 pages05 Fixed Income SecuritiessukeshNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of Money: Mike Shaffer April 15, 2005Document23 pagesThe Time Value of Money: Mike Shaffer April 15, 2005Ritika SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyPhạm Hoàng Diệu VyNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesTime Value of MoneyIIMnotesNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument42 pagesTime Value of MoneyCatalan MelodyNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument13 pagesTime Value of MoneyAulia EndiniNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Time Value of MoneyDocument26 pagesUnit-3 Time Value of MoneySushil KharelNo ratings yet
- FE1 Chapter 4Document41 pagesFE1 Chapter 4Hùng PhanNo ratings yet
- Law On Partnership ReviewerDocument2 pagesLaw On Partnership ReviewerEMZy ChannelNo ratings yet
- Finance Reviewer: Time-Value of MoneyDocument1 pageFinance Reviewer: Time-Value of MoneyAngela ChuaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - TVMDocument30 pagesTopic 4 - TVMDeepika SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Problem SetDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Problem SetNasir Ali RizviNo ratings yet
- CFA Prep Level 1: Session 1 - Ajinkya Bhat - Ankit BhargavaDocument15 pagesCFA Prep Level 1: Session 1 - Ajinkya Bhat - Ankit BhargavaPrakarsh Aren100% (1)
- AnnuitiesDocument6 pagesAnnuitiesFaith MagluyanNo ratings yet
- 2 Time Value of Money - StudDocument36 pages2 Time Value of Money - StudAshwamedhNo ratings yet
- The Time Value of MoneyDocument34 pagesThe Time Value of MoneykamranNo ratings yet
- TVMDocument38 pagesTVMbenjamin.labayenNo ratings yet
- Compounding and DiscountingDocument20 pagesCompounding and DiscountingShivansh Dwivedi100% (1)
- Time Value of Money: Topic 02Document5 pagesTime Value of Money: Topic 02ravindu 11111No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MeasurementDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - MeasurementCait PostNo ratings yet
- 1: Time Value of Money: Tuesday, 28 December 2021 10:18 PMDocument14 pages1: Time Value of Money: Tuesday, 28 December 2021 10:18 PMalexa ubaldoNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money PDF Notes - Download HereDocument7 pagesTime Value of Money PDF Notes - Download HereUnni KuttanNo ratings yet
- FN 202 Chapter 4Document38 pagesFN 202 Chapter 4BablooNo ratings yet
- ENECON ReviewerDocument5 pagesENECON ReviewerJomeljames Campaner PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Value and Return - Chapter 2Document26 pagesConcepts of Value and Return - Chapter 2RabinNo ratings yet
- FM 4Document3 pagesFM 4gojo satoruNo ratings yet
- FM I Note - Chapter Three (TVM)Document15 pagesFM I Note - Chapter Three (TVM)zewdieNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: by K Lubza NiharDocument21 pagesFinancial Management: by K Lubza NiharAashutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- TVM - Unit 4Document32 pagesTVM - Unit 4gajakesari738No ratings yet
- Reviewer PDFDocument4 pagesReviewer PDFMarian B TersonaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Concepts in ValuationDocument4 pagesTime Value of Money: Concepts in ValuationRia GayleNo ratings yet
- Bab 11 Manajemen Keuangan Dan Pembiayaan Usaha - ConceptDocument28 pagesBab 11 Manajemen Keuangan Dan Pembiayaan Usaha - ConceptMaria Dewinta AgustinNo ratings yet
- Resume Chapter 5 MKL - Fanny Noviana .J 201950352Document6 pagesResume Chapter 5 MKL - Fanny Noviana .J 201950352Fanny NovianaNo ratings yet
- Topic Two - A Review of Financial MathematicsDocument39 pagesTopic Two - A Review of Financial MathematicsPhương Anh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument14 pagesCapital BudgetingNelhey DllgNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument23 pagesTime Value of Moneyvinodkothari100% (1)
- Bafs s4 Personal Finance CHDocument3 pagesBafs s4 Personal Finance CHapi-516803253No ratings yet
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Financial Markets Chapter 1Document3 pagesFinancial Markets Chapter 1gojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Cash and ReceivablesDocument31 pagesCash and Receivablesgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Chapter 1 - NotesDocument3 pagesFinancial Markets Chapter 1 - Notesgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Chapter 2 - NotesDocument3 pagesFinancial Markets Chapter 2 - Notesgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- 1 NotesDocument1 page1 Notesgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Evolution and History of VolleyballDocument5 pagesEvolution and History of Volleyballgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Transfer Pricing: True / False QuestionsDocument284 pagesChapter 15 Transfer Pricing: True / False Questionsgojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Business Combination MergerDocument108 pagesBusiness Combination Mergergojo satoruNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document5 pagesQuestion 1Yono SéNo ratings yet
- ENG - Ebook Kurangkan Hutang Kita!-1Document21 pagesENG - Ebook Kurangkan Hutang Kita!-1Mr DummyNo ratings yet
- Lalaine Espina - Business Finance-Interest RateDocument2 pagesLalaine Espina - Business Finance-Interest RateLalaine EspinaNo ratings yet
- AfarDocument53 pagesAfarrodell pabloNo ratings yet
- Notes On National Credit Act 34 of 2005Document9 pagesNotes On National Credit Act 34 of 2005Noxolo MotloungNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Lieu of 2nd Internal-FT-IV (E F G) - BFSDocument2 pagesAssignment in Lieu of 2nd Internal-FT-IV (E F G) - BFSSiddhesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Simple InterestDocument2 pagesSimple InterestNathan Dungog100% (2)
- Mock TestDocument26 pagesMock TestRadhika KushwahaNo ratings yet
- (Please Tick Whichever Is Applicable) : CSO/PNBHFL/Supplementary Agreement Format/ Version 9.0.0 Page 1 of 2Document2 pages(Please Tick Whichever Is Applicable) : CSO/PNBHFL/Supplementary Agreement Format/ Version 9.0.0 Page 1 of 2Rohan SakpalNo ratings yet
- Options Futures and Other Derivatives Global 9th Edition Hull Test BankDocument8 pagesOptions Futures and Other Derivatives Global 9th Edition Hull Test Bankconalkeishaywx100% (27)
- Interest and Annuity Tables For Discrete CompoundingDocument19 pagesInterest and Annuity Tables For Discrete CompoundingWan Muhd FaizNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Deposit of Title Deeds Krishna RajaDocument4 pagesMemorandum of Deposit of Title Deeds Krishna Rajavairam88No ratings yet
- Loan Cheat Sheet by Jocelyn PredovichDocument1 pageLoan Cheat Sheet by Jocelyn PredovichJocelyn Javernick PredovichNo ratings yet
- Generating Immediate Cash From Accounts ReceivableDocument4 pagesGenerating Immediate Cash From Accounts ReceivableNylan AnyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, 3 4 Financial Statements (Part 2)Document34 pagesChapter 2, 3 4 Financial Statements (Part 2)Aidil Osman17No ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit4: XYZ Bank Balance SheetDocument4 pagesWritten Assignment Unit4: XYZ Bank Balance SheetMarcusNo ratings yet
- Revathy Assg Ratio CalculationDocument2 pagesRevathy Assg Ratio CalculationAishvini ShanNo ratings yet
- AOFM Portfolio Overview Jun 2010 v2Document6 pagesAOFM Portfolio Overview Jun 2010 v2trader_10No ratings yet
- Working Paper Egrement Ika SalinanDocument1 pageWorking Paper Egrement Ika Salinanfc BundaNo ratings yet
- HiwalahDocument17 pagesHiwalahMahyuddin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Argentina - Letter of Support For Joint ProposalDocument14 pagesArgentina - Letter of Support For Joint ProposalBAE NegociosNo ratings yet
- Insolvency Law Study Guide 2014 - UNISADocument219 pagesInsolvency Law Study Guide 2014 - UNISADawn McGowan100% (1)
- ch13 Testbank Intermediate AccountingDocument43 pagesch13 Testbank Intermediate Accountingalaa96% (53)
- Practice - Fabm1 q3 Mod3 Accountingequation Final 1 PDFDocument23 pagesPractice - Fabm1 q3 Mod3 Accountingequation Final 1 PDFJdkrkejNo ratings yet
- 20 Current LiabilitiesDocument15 pages20 Current Liabilitieserica lamsenNo ratings yet
- Bonds Exercises With AnswersDocument10 pagesBonds Exercises With AnswersDenise Jane RoqueNo ratings yet
- Business Math Week 9Document10 pagesBusiness Math Week 9황혜진No ratings yet
- Civil - Law - BarQA - 2009 2017 Pages 161 182,1 7usDocument29 pagesCivil - Law - BarQA - 2009 2017 Pages 161 182,1 7usKAREENA AMEENAH ACRAMAN BASMANNo ratings yet
- W3 Module 5 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 3Document6 pagesW3 Module 5 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 3leare ruazaNo ratings yet
- 21 XXX XXX TP Cibil - ReportDocument6 pages21 XXX XXX TP Cibil - ReportVishnu GaikwadNo ratings yet