Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Series and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
Mark Reeve0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesThis document discusses series and parallel circuits and provides 11 questions about calculating current, resistance, and potential differences in various circuit configurations. It includes a circuit diagram with ammeters and voltmeters to measure different points. The questions involve calculating current through branches of a parallel circuit, potential differences across resistors, total resistance, and how changes to the circuit such as increasing a resistor or connecting components in series would affect the current.
Original Description:
Worksheet to accompany presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses series and parallel circuits and provides 11 questions about calculating current, resistance, and potential differences in various circuit configurations. It includes a circuit diagram with ammeters and voltmeters to measure different points. The questions involve calculating current through branches of a parallel circuit, potential differences across resistors, total resistance, and how changes to the circuit such as increasing a resistor or connecting components in series would affect the current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
Mark ReeveThis document discusses series and parallel circuits and provides 11 questions about calculating current, resistance, and potential differences in various circuit configurations. It includes a circuit diagram with ammeters and voltmeters to measure different points. The questions involve calculating current through branches of a parallel circuit, potential differences across resistors, total resistance, and how changes to the circuit such as increasing a resistor or connecting components in series would affect the current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
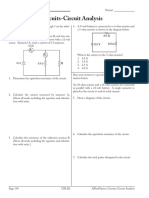
Series and Parallel Circuits
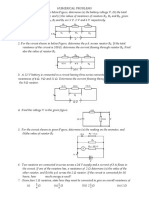
1. For the series circuit shown opposite each cell provides a potential
difference of 1.5V.
a. What is the total resistance of the circuit?
b. What is the potential difference across the 10 resistor?
2. For the parallel circuit opposites:
a. What is the total resistance of branch X of the circuit?
b. What is the total resistance of branch Y of the circuit?
c. What is the current through:
i. Branch X?
ii. Branch Y?
d. The potential difference of the supply is 10V.
iii. What is the value of V1?
iv. What is the value of V2?
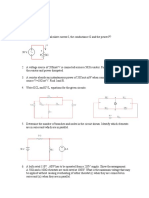
The following questions refer to the circuit diagram shown on the right. A number of ammeters and
voltmeters have been included to measure the current and potential difference at different points around
the circuit.
3. A1 reads 1A and A3 reads 0.8A. Calculate V
what current A2 reads. Explain your
reasoning.
4. Hence calculate what the potential difference
will be across the 20 resistor.
5. Calculate what the potential difference across A1 V
the 10 resistor will be.
10 20
6. Calculate what the total potential difference
will be across the cell. Explain your
A2
reasoning.
7. Explain what the potential difference across R
resistor R will be. A3
8. Remembering that A3 is reading 0.8 A,
calculate resistance R.
9. If resistance R was increased what would happen to the total current in the circuit A1?
10. If the circuit was changed and all three resistors were connected in series what would the total
resistance be?
11. What current would flow in the circuit described in question 10..
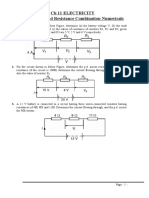
Series and Parallel Circuits
1. For the series circuit shown opposite each cell provides a potential
difference of 1.5V.
a. What is the total resistance of the circuit?
b. What is the potential difference across the 10 resistor?
2. For the parallel circuit opposites:
a. What is the total resistance of branch X of the circuit?
b. What is the total resistance of branch Y of the circuit?
c. What is the current through:
v. Branch X?
vi. Branch Y?
d. The potential difference of the supply is 10V.
vii. What is the value of V1?
viii. What is the value of V2?
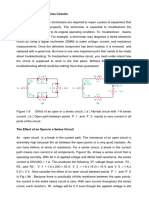
The following questions refer to the circuit diagram shown on the right. A number of ammeters and
voltmeters have been included to measure the current and potential difference at different points around
the circuit.
3. A1 reads 1A and A3 reads 0.8A. Calculate V
what current A2 reads. Explain your
reasoning.
4. Hence calculate what the potential difference
will be across the 20 resistor.
5. Calculate what the potential difference across A1 V
the 10 resistor will be.
10 20
6. Calculate what the total potential difference
will be across the cell. Explain your
A2
reasoning.
7. Explain what the potential difference across R
resistor R will be. A3
8. Remembering that A3 is reading 0.8 A,
calculate resistance R.
9. If resistance R was increased what would happen to the total current in the circuit A1?
10. If the circuit was changed and all three resistors were connected in series what would the total
resistance be?
11. What current would flow in the circuit described in question 10..
You might also like
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Circuits Worksheet ResistanceDocument3 pagesCircuits Worksheet ResistanceelchinNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument4 pagesCircuits WorksheetDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- 20-DC CircuitsDocument62 pages20-DC Circuitsrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits Worksheettuvvac67% (3)
- Worksheet 2022Document4 pagesWorksheet 2022Lael SomarNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits WorksheetTawan PetpaiboonNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 2Document8 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 2Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Potential Divider QuestionsDocument2 pagesPotential Divider Questionscrackerz83100% (1)
- Chapter 35 Circuits and Ohms LawDocument4 pagesChapter 35 Circuits and Ohms Lawbhumika mehtaNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Sample - 1Document3 pagesCH-3 Sample - 1jayNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuits: Learning ObjectiveDocument18 pagesSeries RLC Circuits: Learning Objectiveandrew smithNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersDocument4 pagesScience-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersMihika MathurNo ratings yet
- Circuits and Ohms Law2Document4 pagesCircuits and Ohms Law2Edu De LuqueNo ratings yet
- Circuits-Worksheet 101Document5 pagesCircuits-Worksheet 101wassimfakNo ratings yet
- 14 15 H2 DC Tutqns PDFDocument10 pages14 15 H2 DC Tutqns PDFeltytanNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice ExerciseDocument1 pagePhysics Practice ExercisemalabrigamarcjohnNo ratings yet
- (25366) 2. H Electrical Circuits QuestionsDocument10 pages(25366) 2. H Electrical Circuits QuestionsTriple M Guider NephaweNo ratings yet
- AC SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAC SubjectiveAgrima PrasadNo ratings yet
- M5 March 2021 End of Unit Electricity TestDocument5 pagesM5 March 2021 End of Unit Electricity TestEdu De LuqueNo ratings yet
- Tempat Belajar Infinite: Rukan Taman Meruya Blok M No. 75 Meruya Ilir Jakarta Barat 1Document5 pagesTempat Belajar Infinite: Rukan Taman Meruya Blok M No. 75 Meruya Ilir Jakarta Barat 1infinite onlineNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1Document20 pagesTopic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1felNo ratings yet
- 1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Document5 pages1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Faber O.MNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Exercise.4Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Exercise.4Chaitanya JoshiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument2 pagesElectricityyashasviupadhyay19No ratings yet
- Summative Test in Computer Hardware ServicingDocument32 pagesSummative Test in Computer Hardware ServicingWhipple AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Series and ParallelDocument7 pagesSeries and ParallelSuryaveer bhatiNo ratings yet
- EC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsDocument6 pagesEC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameDocument7 pagesChapter 19 Electric Circuits: NameTimothy KurbyNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet 2-Physics 2Document2 pagesCheat Sheet 2-Physics 2AnanyaBandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- EQ Resistance WKSHDocument3 pagesEQ Resistance WKSHeltytanNo ratings yet
- Sumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Document5 pagesSumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Manongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Assignment PDFThe Champ0% (1)
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Electricity Ohms Law and Combination of ResistorsDocument10 pagesCh12 Electricity Ohms Law and Combination of ResistorsHenisha ChodvadiyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy WorksheetsDocument14 pagesElectrical Energy WorksheetsKrista JacksonNo ratings yet
- GibiliscoDocument8 pagesGibiliscoChristian CuevasNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choices. Choose The Best Answer. Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceDocument3 pagesI. Multiple Choices. Choose The Best Answer. Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceJohn Rey ComplezaNo ratings yet
- 2022 16A DC AnsDocument15 pages2022 16A DC AnsPk PlooNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics L2Document17 pagesBasic Electronics L2msellereneNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Part 2Document13 pagesElectricity - Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- XII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFDocument2 pagesXII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- 26 Circuits-Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pages26 Circuits-Circuit AnalysiseltytanNo ratings yet
- CH 25 Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCH 25 Practice QuestionsaliNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 PDFDocument2 pagesSheet 2 PDFAya HassanNo ratings yet
- Mysuru Royal Institute of Technology, Mandya.: Question Bank-IDocument2 pagesMysuru Royal Institute of Technology, Mandya.: Question Bank-IJyothi M PNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Problems Worksheet 0910Document2 pagesSeries and Parallel Problems Worksheet 0910r sNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument2 pagesCircuitsEn En BelthereNo ratings yet
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)Document21 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- Exercise - IV: (Tough Subjective Problems)Document2 pagesExercise - IV: (Tough Subjective Problems)Tejas SalviNo ratings yet
- Ii. Conducting Wire'S ResistanceDocument10 pagesIi. Conducting Wire'S ResistanceZulaikah BlitarianNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document16 pagesTest 2edwardNo ratings yet
- CPP 5 Electrical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesCPP 5 Electrical Instrumentsullas agrawalNo ratings yet
- Apllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerDocument42 pagesApllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Electricity2 PDFDocument17 pagesElectricity2 PDFPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Circuits LabDocument5 pagesCircuits LabWyndellRioNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 - Ohms Law and Circuts BuildingDocument9 pagesPhysics 11 - Ohms Law and Circuts Buildingapi-538868691100% (2)
- CH 27-30Document69 pagesCH 27-30Richard Hammond50% (2)