Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demat Account
Uploaded by
shravanz252Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demat Account
Uploaded by
shravanz252Copyright:
Available Formats
Demat Account: De-materialized account to trade in listed stocks or debentures required for investors by SEBI.
In demat account, shares and debentures are held electronically. A demat account is opened by the investor while registering with an investment broker. The demat account number is quoted for all the transactions to enable electronic settlements of trades to takes place. Access to demat account requires an Internet password and transaction password as well as initiating and confirming transfers or purchases of securities. Advantages: Reduces brokerage charges Enable quick ownership of securities Avoids confusion in ownership titles Provides easy receipts of public issue allotments or Initial Public Offerings Avoids signature mismatches Loss of certificates in transit Eliminates risk associated with forgery, counterfeiting and loss due to damaged stock certificates Depository system is nothing but electronic bookkeeping. Dematerializing securities is nothing but converting physical records of investments into electronic records. Debenture: A debenture is a document, which is; either creates a debt or acknowledges it. A debenture is thus like a certificate of loan or a loan bond evidencing the fact that the company is liable to pay a specified amount with interest and although the money raised by the debentures becomes the part of the companys capital structures. Securities: A security is a negotiable financial instrument, which holds financial value. Securities are categorized into debt securities, equity securities and derivative contracts. Bank Note:
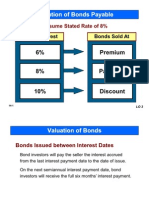
A bank note often known as a bill, paper money or simply a note, is a kind of negotiable instrument, a promissory note made by a bank payable to the bearer on demand, used as money, and in many jurisdictions as legal tender. Bonds: A bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holder a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use or to repay the principal at a later date termed as maturity. A bond is a formal contract to repay the borrowed money with interest at fixed intervals. Stocks: The capital stock of a business entity represents the original capital paid into or invested by its founders. It serves as a security for the creditors of the business since it cannot be withdrawn to the detriment of the creditors. Difference between Stocks and Bonds: Both bonds and stocks are debt securities, but the major difference is stockholders have an equity stake in the company i.e., they are the owners, whereas bondholders have creditor stake in the company i.e., they are the lenders. Another difference is that the bonds usually have a defined term, or maturity, after which the bond is redeemed, whereas stocks may be outstanding indefinitely. Equity Trading: Equity trading is the buying and selling of company stock shares. Shares in large publicly traded companies are bought and sold through one of the major stock exchanges such as NYSE, LSE, Tokyo Stock Exchange, which serve as managed auctions for stock trades. Stock shares in smaller public companies are bought and sold in over the counter market. Proprietary Trading is buying and selling for the traders own profit or loss. In this case, the principal is the owner of shares. Agency Trading is buying and selling by an agent, usually a stockbroker, on behalf of a client. Agents are paid a commission on performing the trade. Market Maker: A market maker is a company, or an individual, that quotes both a buy and a sell price in a financial instrument or commodity held in inventory, hoping to make a profit on the bid offer spread.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Level III of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Solutions (PM)Document46 pagesLevel III of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Solutions (PM)Lê Chấn PhongNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Test Bank Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition Saunders PDFDocument58 pagesTest Bank Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition Saunders PDFRa'fat Jallad100% (1)
- Control Break Statements SAP ABAPDocument3 pagesControl Break Statements SAP ABAPshravanz252No ratings yet
- SD Process FlowDocument54 pagesSD Process Flowshravanz252100% (1)
- Sales Order Creation Using Web Dynpro ABAPDocument12 pagesSales Order Creation Using Web Dynpro ABAPshravanz252No ratings yet
- ABAP WebDynproDocument19 pagesABAP WebDynproshravanz252No ratings yet
- Central Banking JntuDocument9 pagesCentral Banking Jntushravanz252No ratings yet
- Retail Banking SystemsDocument4 pagesRetail Banking Systemssheik abdullahNo ratings yet
- Dian Sari (A031171703) Tugas Akl IiDocument3 pagesDian Sari (A031171703) Tugas Akl Iidian sariNo ratings yet
- Bill of Supply: (Figures in:INR)Document1 pageBill of Supply: (Figures in:INR)Swati MishraNo ratings yet
- KYC PresentationDocument14 pagesKYC Presentationgoswami.karan13464No ratings yet
- Fabm 1-PTDocument10 pagesFabm 1-PTClay MaaliwNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Management and Investment Alternatives: Shruti ChavarkarDocument17 pagesPortfolio Management and Investment Alternatives: Shruti ChavarkarShrikant SabatNo ratings yet
- Adv Excel Practice 2 04nov2023Document120 pagesAdv Excel Practice 2 04nov2023Sakshi Marwah ChamolaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Marketable Securities Management SOLUTIONSDocument10 pagesCash and Marketable Securities Management SOLUTIONSJack Herer100% (2)
- Finance and Accounting Basics - Interview Quest & Answers-1Document48 pagesFinance and Accounting Basics - Interview Quest & Answers-1naghulk1No ratings yet
- Unit .2 The Accounting CycleDocument24 pagesUnit .2 The Accounting CycleTasfa Zarihun100% (2)
- Self Help GroupsDocument34 pagesSelf Help GroupsManashvi karthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Aditya Birla GroupDocument45 pagesAditya Birla GroupCalaghan EnthiadoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: ACCOUNTING 9706/32Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: ACCOUNTING 9706/32Shahmeer HasanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 6th Edition by TrotmanDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 6th Edition by TrotmanVivienne Lei BolosNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfr6540073No ratings yet
- Practice Questions Lecture 4-6Document5 pagesPractice Questions Lecture 4-6Reemshah Hassan0% (1)
- Kieso Ifrs Test Bank Ch17Document45 pagesKieso Ifrs Test Bank Ch17FaradibaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank AptitudeDocument94 pagesAxis Bank AptitudeladmohanNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document42 pagesCH 14maxhaakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Stement of Comprehensive Lesson 2Document12 pagesChapter 2 Stement of Comprehensive Lesson 2Ronald De La RamaNo ratings yet
- Lami Company Profile 2023Document14 pagesLami Company Profile 2023gerald waihuiniNo ratings yet
- Case Advertising AgencyDocument3 pagesCase Advertising AgencyNicolas ErnestoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Investment PropertiesDocument3 pagesTutorial Investment Propertiesnadya bujangNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Cryptocurrency Regulations in Kenya & Other JurisdictionsDocument23 pagesComparison of Cryptocurrency Regulations in Kenya & Other JurisdictionsSancho SanchezNo ratings yet
- HSBC - Personal Banking Agreement en PDFDocument52 pagesHSBC - Personal Banking Agreement en PDFRuslan ParisNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Uang Elektronik Dalam Sistem PembayaranDocument33 pagesKarakteristik Uang Elektronik Dalam Sistem PembayaranDicky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Corporation Resolution To Open A Bank AccountDocument2 pagesCorporation Resolution To Open A Bank AccountEdmond Aragon PareñasNo ratings yet
- Internals II - Managerial Accounting Question PaperDocument3 pagesInternals II - Managerial Accounting Question PaperasdeNo ratings yet